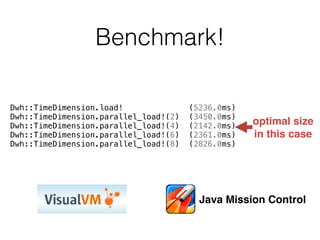
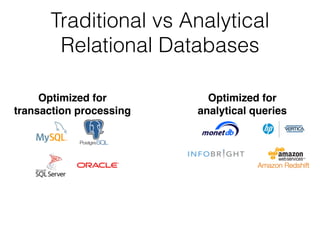
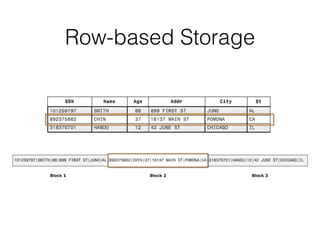
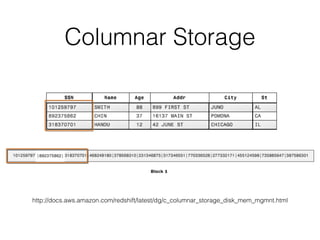
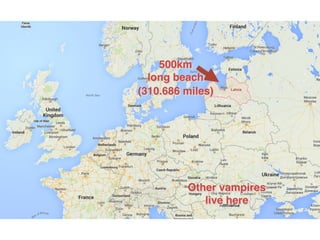
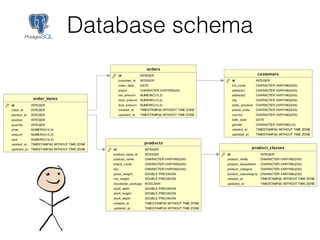
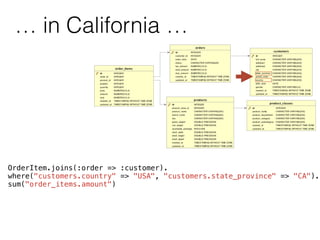
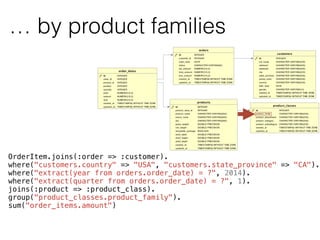
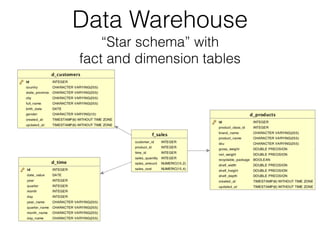
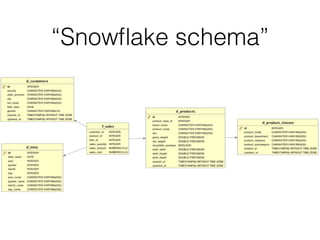
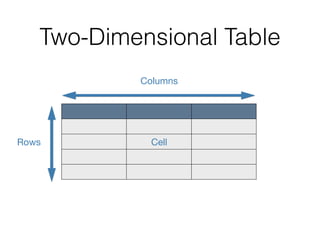
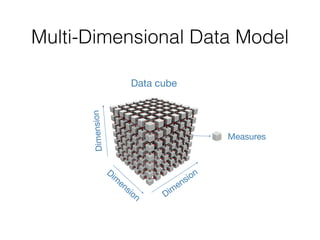
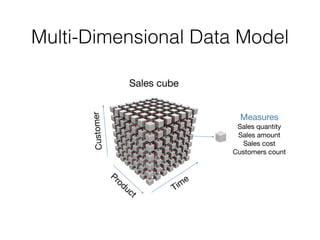
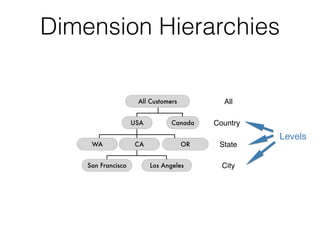
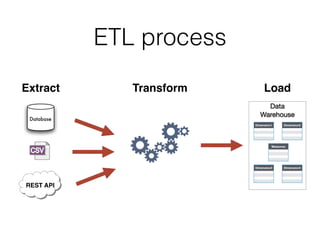
The document discusses data warehouses and multi-dimensional data analysis. It provides an example of modeling sales data across multiple tables in a relational database and shows how long queries take on large amounts of data. It then introduces dimensional modeling and how to structure data in a data warehouse using fact and dimension tables. Finally, it demonstrates how to model the sales data multidimensionally using a data cube and discusses OLAP technologies like Mondrian for multi-dimensional analysis.
















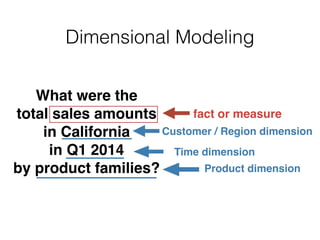
![Load Dimension
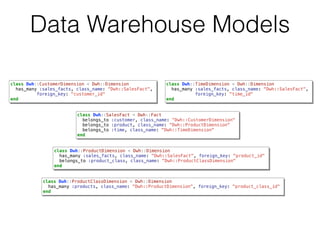
class Dwh::CustomerDimension < Dwh::Dimension
# ...
def self.truncate!
connection.execute "TRUNCATE TABLE #{table_name}"
end
def self.load!
truncate!
column_names = %w(id full_name city state_province country
birth_date gender created_at updated_at)
connection.insert %[
INSERT INTO #{table_name} (#{column_names.join(',')})
SELECT #{column_names.join(',')}
FROM #{::Customer.table_name}
]
end
end](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datawarehousesandmulti-dimensionaldataanalysis-150423131924-conversion-gate01/85/Data-Warehouses-and-Multi-Dimensional-Data-Analysis-28-320.jpg)
![Generate
Time
Dimension
class Dwh::TimeDimension < Dwh::Dimension
def self.load!
connection.select_values(%[
SELECT DISTINCT order_date FROM #{Order.table_name}
WHERE order_date NOT IN
(SELECT date_value FROM #{table_name})
]).each do |date|
year, month, day = date.year, date.month, date.day
quarter = ((month-1)/3)+1
quarter_name = "Q#{quarter} #{year}"
month_name = date.strftime("%b %Y")
day_name = date.strftime("%b %d %Y")
sql = send :sanitize_sql_array, [
%[
INSERT INTO #{table_name}
(id, date_value, year, quarter, month, day,
year_name, quarter_name, month_name, day_name)
VALUES
(?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?,
?, ?, ?, ?)
],
date_to_id(date), date, year, quarter, month, day,
year.to_s, quarter_name, month_name, day_name
]
connection.insert sql
end
end
end](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datawarehousesandmulti-dimensionaldataanalysis-150423131924-conversion-gate01/85/Data-Warehouses-and-Multi-Dimensional-Data-Analysis-29-320.jpg)
![Load Facts
class Dwh::SalesFact < Dwh::Fact
def self.load!
truncate!
connection.insert %[
INSERT INTO #{table_name}
(customer_id, product_id, time_id,
sales_quantity, sales_amount, sales_cost)
SELECT
o.customer_id, oi.product_id,
CAST(to_char(o.order_date, 'YYYYMMDD') AS INTEGER),
oi.quantity, oi.amount, oi.cost
FROM
#{OrderItem.table_name} oi
INNER JOIN #{Order.table_name} o ON o.id = oi.order_id
]
end
end](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datawarehousesandmulti-dimensionaldataanalysis-150423131924-conversion-gate01/85/Data-Warehouses-and-Multi-Dimensional-Data-Analysis-30-320.jpg)



![What were the
total sales amounts
in California
in Q1 2014
by product families?
olap.from("Sales").
columns("[Measures].[Sales Amount]").
rows("[Product].[Product Family].Members").
where("[Customer].[USA].[CA]", "[Time].[Quarter].[Q1 2014]")](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datawarehousesandmulti-dimensionaldataanalysis-150423131924-conversion-gate01/85/Data-Warehouses-and-Multi-Dimensional-Data-Analysis-39-320.jpg)
![MDX Query Language
olap.from("Sales").
columns("[Measures].[Sales Amount]").
rows("[Product].[Product Family].Members").
where("[Customer].[USA].[CA]", "[Time].[Quarter].[Q1 2014]")
SELECT {[Measures].[Sales Amount]} ON COLUMNS,
[Product].[Product Family].Members ON ROWS
FROM [Sales]
WHERE ([Customer].[USA].[CA], [Time].[Quarter].[Q1 2014])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datawarehousesandmulti-dimensionaldataanalysis-150423131924-conversion-gate01/85/Data-Warehouses-and-Multi-Dimensional-Data-Analysis-40-320.jpg)
![Results Caching
SELECT {[Measures].[Sales Amount], [Measures].[Sales Cost],
[Measures].[Customers Count]} ON COLUMNS,
[Product].[Product Family].Members ON ROWS
FROM [Sales] (21713.0ms)
SELECT {[Measures].[Sales Amount], [Measures].[Sales Cost],
[Measures].[Customers Count]} ON COLUMNS,
[Product].[Product Family].Members ON ROWS
FROM [Sales] (10.0ms)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datawarehousesandmulti-dimensionaldataanalysis-150423131924-conversion-gate01/85/Data-Warehouses-and-Multi-Dimensional-Data-Analysis-41-320.jpg)
![Additional Attribute Dimension
dimension 'Gender', foreign_key: 'customer_id' do
hierarchy all_member_name: 'All Genders', primary_key: 'id' do
table 'd_customers', schema: 'dwh'
level 'Gender', column: 'gender' do
name_expression do
sql "CASE d_customers.gender
WHEN 'F' THEN ‘Female'
WHEN 'M' THEN ‘Male'
END"
end
end
end
end
olap.from("Sales").
columns("[Measures].[Sales Amount]").
rows("[Gender].[Gender].Members")](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datawarehousesandmulti-dimensionaldataanalysis-150423131924-conversion-gate01/85/Data-Warehouses-and-Multi-Dimensional-Data-Analysis-42-320.jpg)
![Dynamic Attribute Dimension
dimension 'Age interval', foreign_key: 'customer_id' do
hierarchy all_member_name: 'All Age', primary_key: 'id' do
table 'd_customers', schema: 'dwh'
level 'Age interval' do
key_expression do
sql %[
CASE
WHEN age(d_customers.birth_date) < interval '20 years'
THEN '< 20 years'
WHEN age(d_customers.birth_date) < interval '30 years'
THEN '20-30 years'
WHEN age(d_customers.birth_date) < interval '40 years'
THEN '30-40 years'
WHEN age(d_customers.birth_date) < interval '50 years'
THEN '40-50 years'
ELSE '50+ years'
END
]
end
end
end
end
[Age interval].[<20 years]
[Age interval].[20-30 years]
[Age interval].[30-40 years]
[Age interval].[40-50 years]
[Age interval].[50+ years]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datawarehousesandmulti-dimensionaldataanalysis-150423131924-conversion-gate01/85/Data-Warehouses-and-Multi-Dimensional-Data-Analysis-43-320.jpg)
![Calculation Formulas
calculated_member 'Profit', dimension: 'Measures', format_string: '#,##0.00',
formula: '[Measures].[Sales Amount] - [Measures].[Sales Cost]'
calculated_member 'Margin %', dimension: 'Measures', format_string: '#,##0.00%',
formula: '[Measures].[Profit] / [Measures].[Sales Amount]'
olap.from("Sales").
columns("[Measures].[Profit]", "[Measures].[Margin %]").
rows("[Product].[Product Family].Members").
where("[Customer].[USA].[CA]", "[Time].[Quarter].[Q1 2014]")](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datawarehousesandmulti-dimensionaldataanalysis-150423131924-conversion-gate01/85/Data-Warehouses-and-Multi-Dimensional-Data-Analysis-44-320.jpg)

![Kiba example
# declare a ruby method here, for quick reusable logic
def parse_french_date(date)
Date.strptime(date, '%d/%m/%Y')
end
# or better, include a ruby file which loads reusable assets
# eg: commonly used sources / destinations / transforms, under unit-test
require_relative 'common'
# declare a source where to take data from (you implement it - see notes below)
source MyCsvSource, 'input.csv'
# declare a row transform to process a given field
transform do |row|
row[:birth_date] = parse_french_date(row[:birth_date])
# return to keep in the pipeline
row
end
# declare another row transform, dismissing rows conditionally by returning nil
transform do |row|
row[:birth_date].year < 2000 ? row : nil
end
# declare a row transform as a class, which can be tested properly
transform ComplianceCheckTransform, eula: 2015](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datawarehousesandmulti-dimensionaldataanalysis-150423131924-conversion-gate01/85/Data-Warehouses-and-Multi-Dimensional-Data-Analysis-48-320.jpg)
![Single
threaded
ETL
class Dwh::TimeDimension < Dwh::Dimension
def self.load!
logger.silence do
connection.select_values(%[
SELECT DISTINCT order_date FROM #{Order.table_name}
WHERE order_date NOT IN (SELECT date_value FROM #{table_name})
]).each do |date|
insert_date(date)
end
end
end
def self.insert_date(date)
year, month, day = date.year, date.month, date.day
quarter = ((month-1)/3)+1
quarter_name = "Q#{quarter} #{year}"
month_name = date.strftime("%b %Y")
day_name = date.strftime("%b %d %Y")
sql = send :sanitize_sql_array, [
%[
INSERT INTO #{table_name}
(id, date_value, year, quarter, month, day,
year_name, quarter_name, month_name, day_name)
VALUES
(?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?,
?, ?, ?, ?)
],
date_to_id(date), date, year, quarter, month, day,
year.to_s, quarter_name, month_name, day_name
]
connection.insert sql
end
end](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datawarehousesandmulti-dimensionaldataanalysis-150423131924-conversion-gate01/85/Data-Warehouses-and-Multi-Dimensional-Data-Analysis-50-320.jpg)
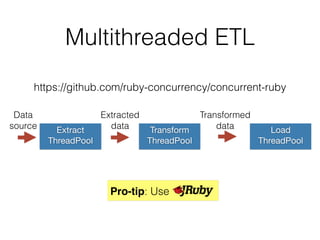
![require 'concurrent/executors'
class Dwh::TimeDimension < Dwh::Dimension
def self.parallel_load!(pool_size = 4)
logger.silence do
insert_date_pool = Concurrent::FixedThreadPool.new(pool_size)
connection.select_values(%[
SELECT DISTINCT order_date FROM #{Order.table_name}
WHERE order_date NOT IN (SELECT date_value FROM #{table_name})
]).each do |date|
insert_date_pool.post(date) do |date|
connection_pool.with_connection do
insert_date(date)
end
end
end
insert_date_pool.shutdown
insert_date_pool.wait_for_termination
end
end
end
ETL with
Thread Pool](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datawarehousesandmulti-dimensionaldataanalysis-150423131924-conversion-gate01/85/Data-Warehouses-and-Multi-Dimensional-Data-Analysis-51-320.jpg)