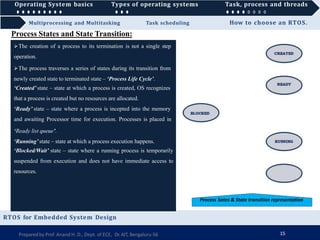
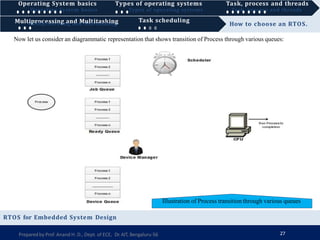
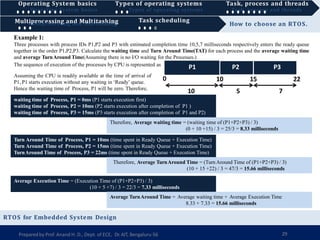
1) A real-time operating system (RTOS) guarantees that real-time applications receive a certain level of performance within a specified deadline, and are designed for critical systems and microcontrollers that have timing requirements measured in milliseconds.
2) The structure of an embedded real-time system includes various hardware and software components distributed to perform specific tasks within allowed time constraints.
3) An RTOS manages processes, memory, interrupts, I/O, security, and other functions to ensure real-time applications meet their deadlines.