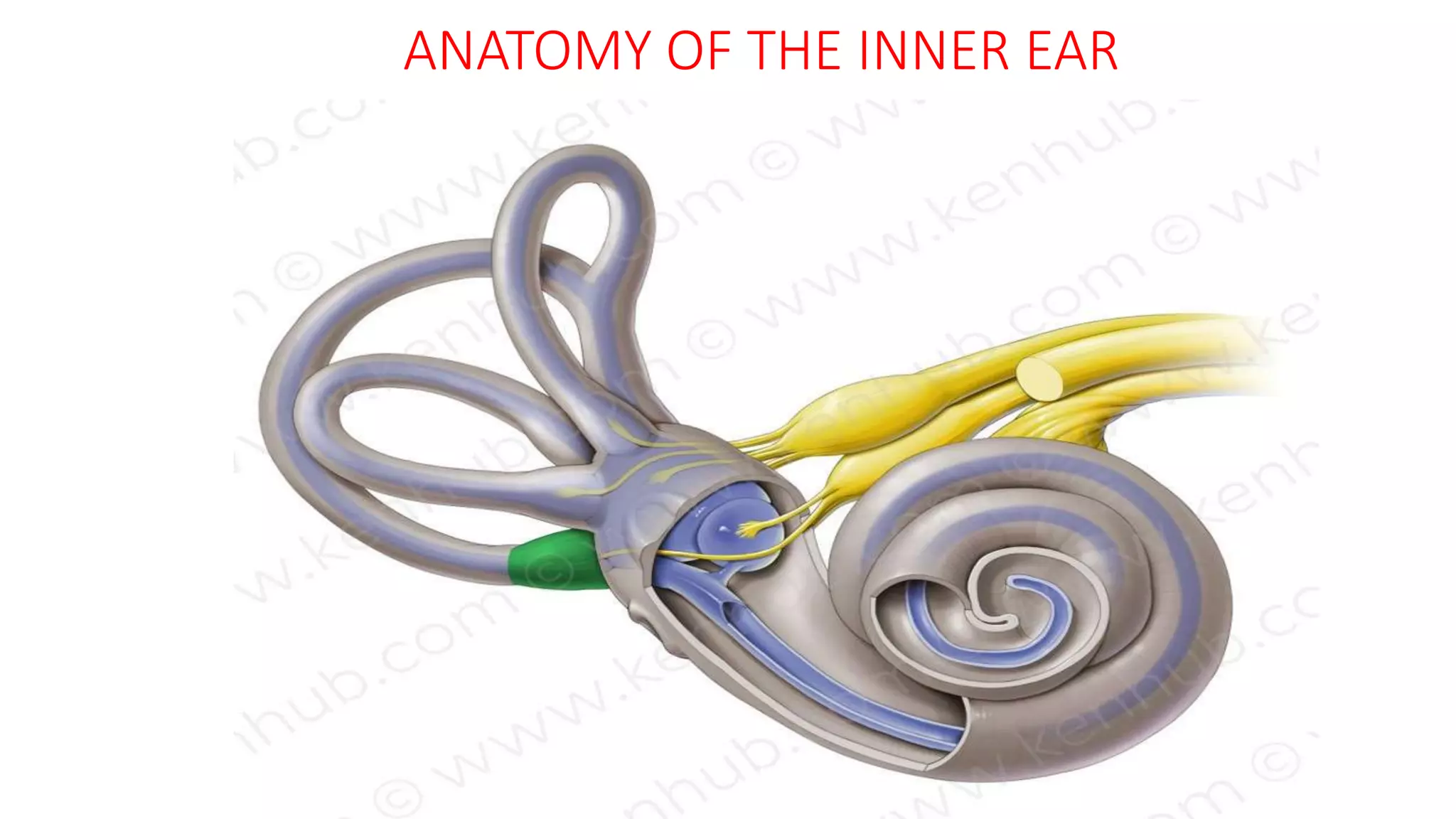
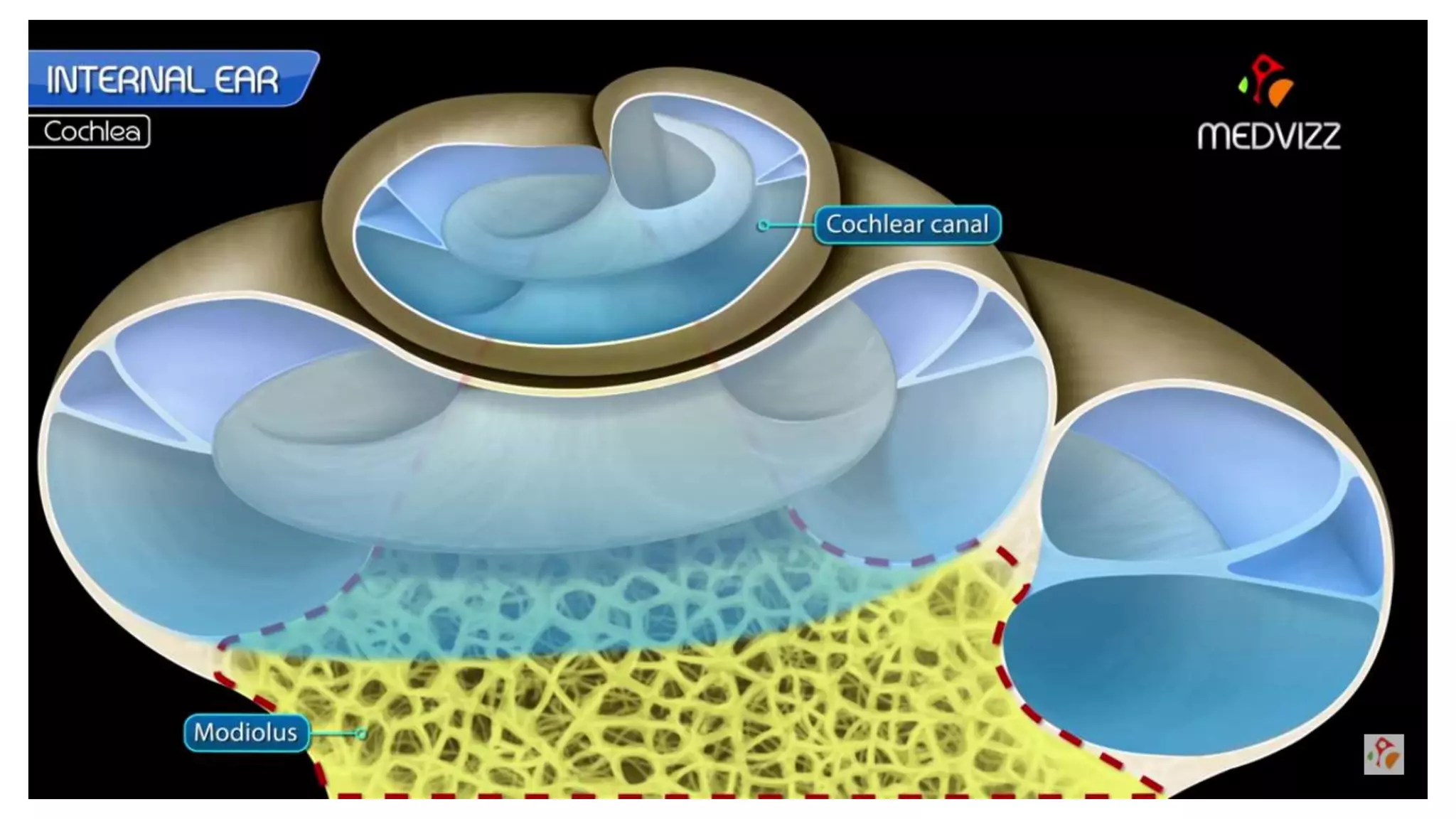
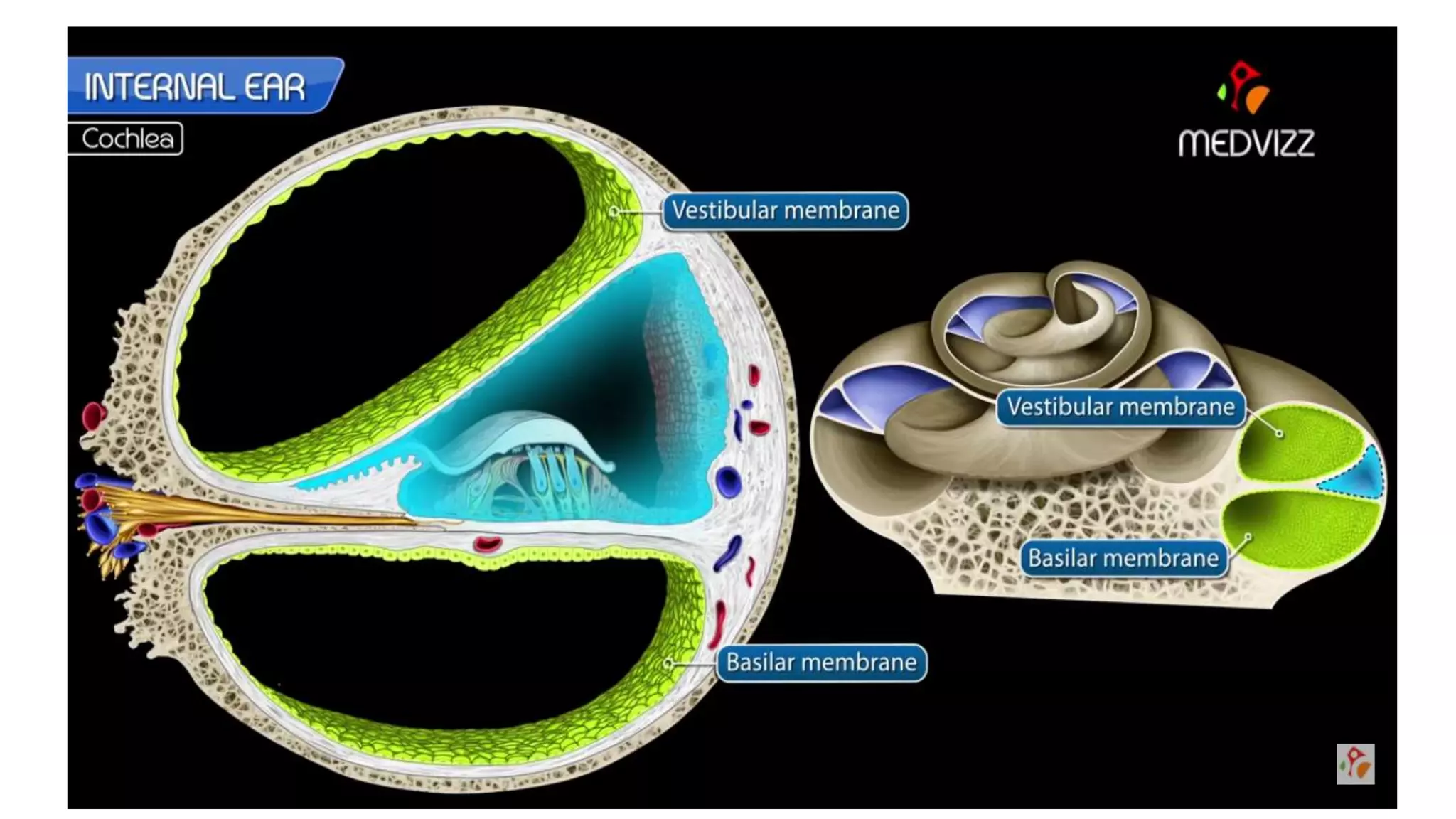
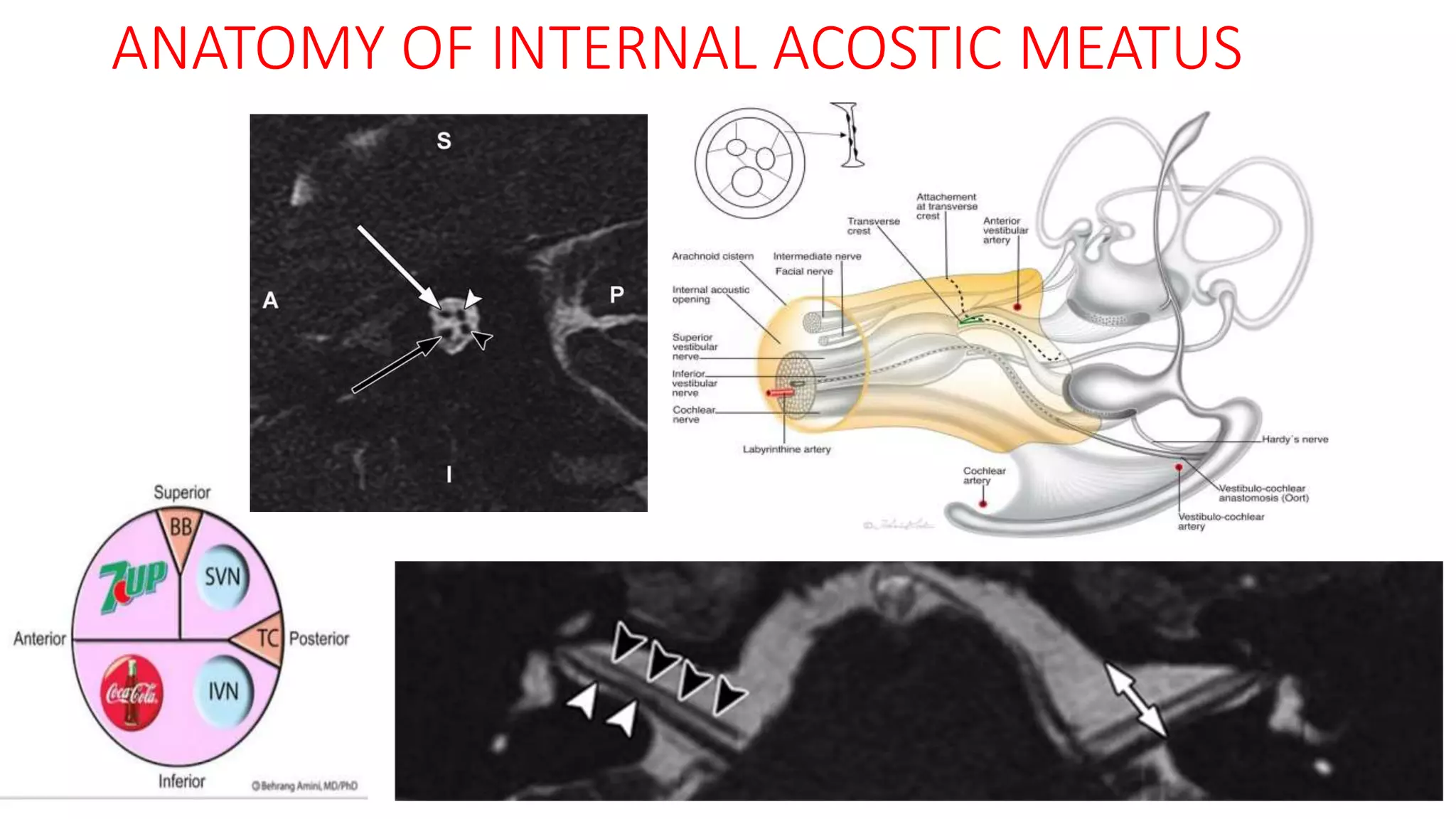
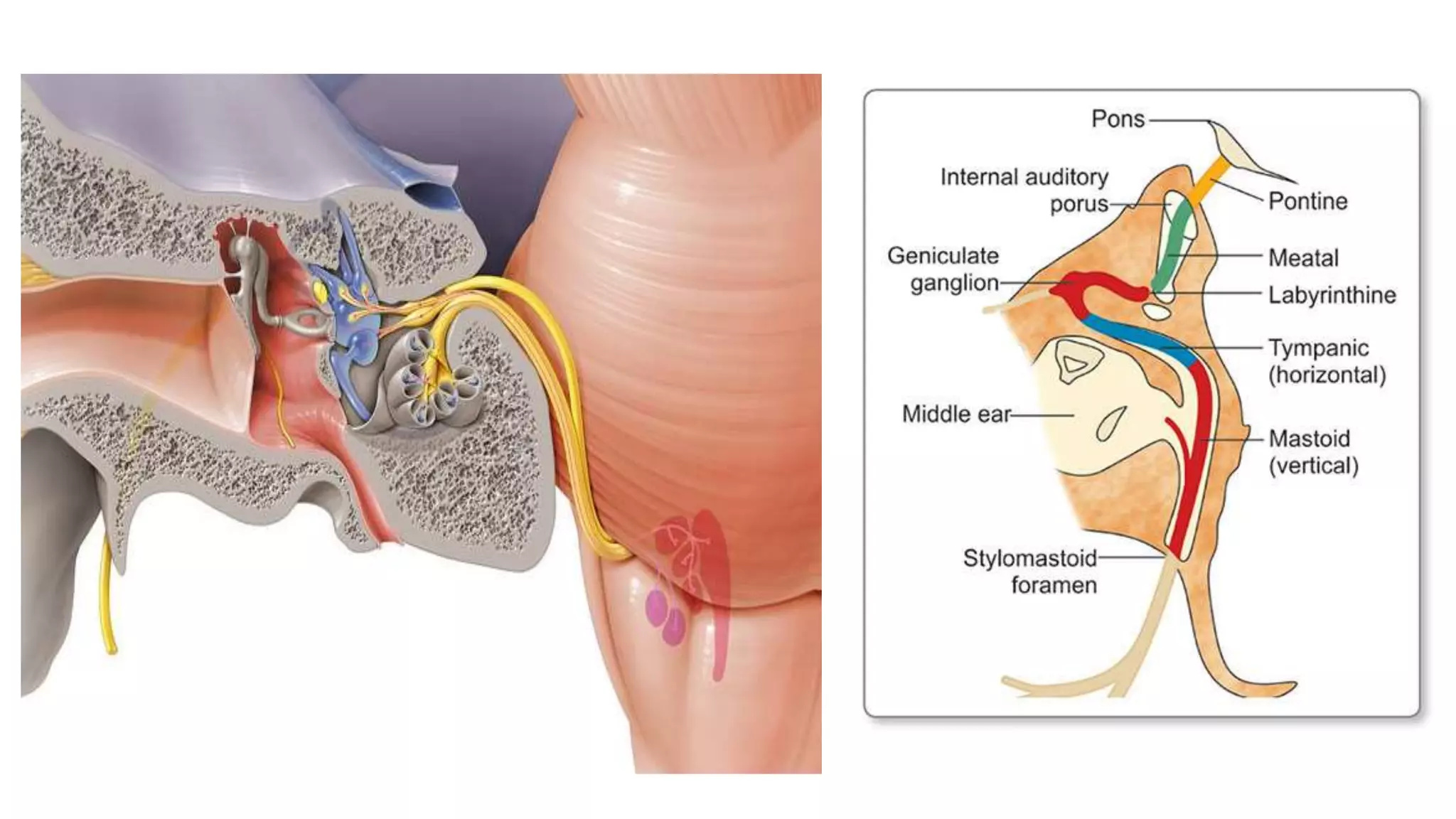
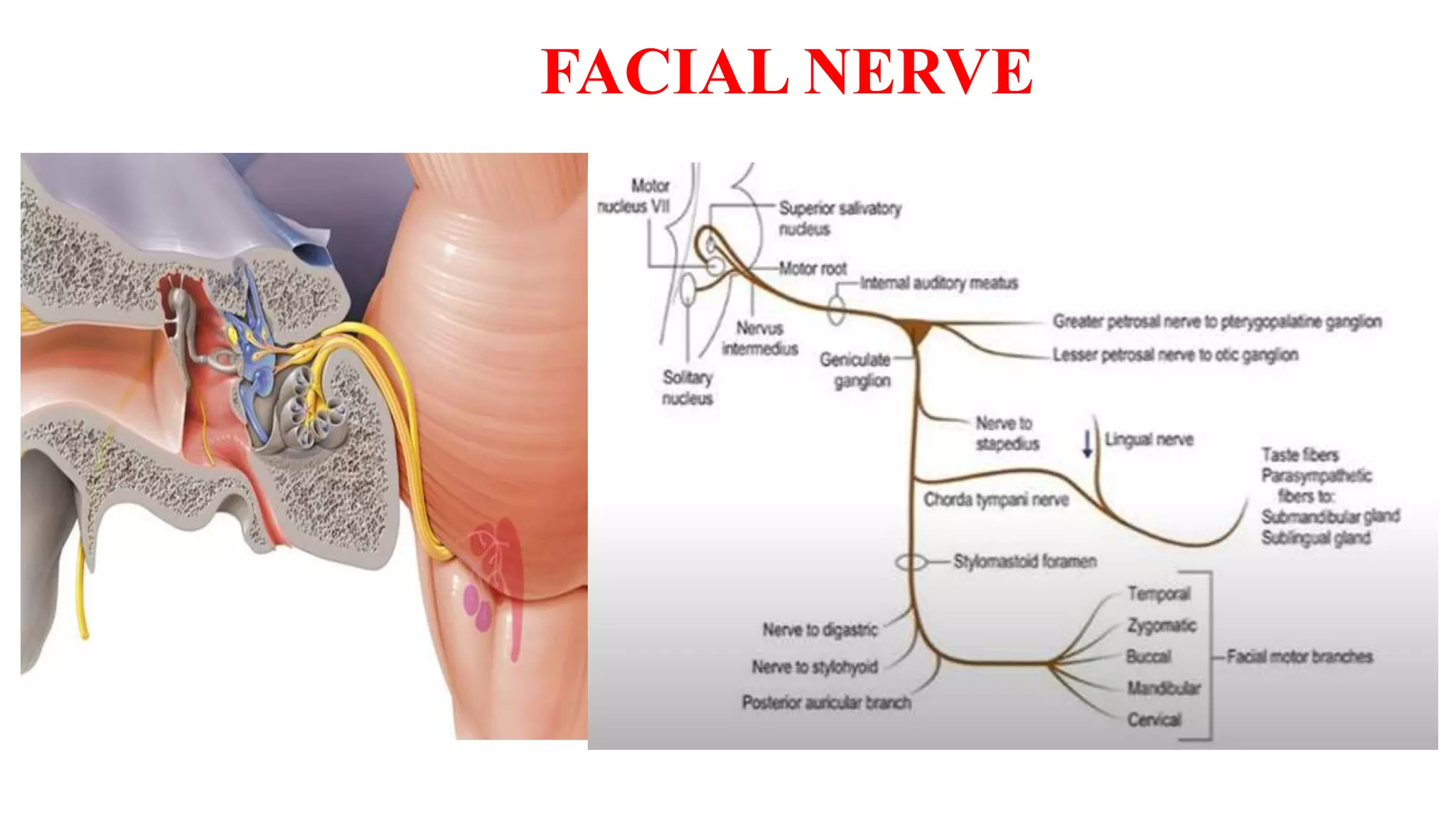
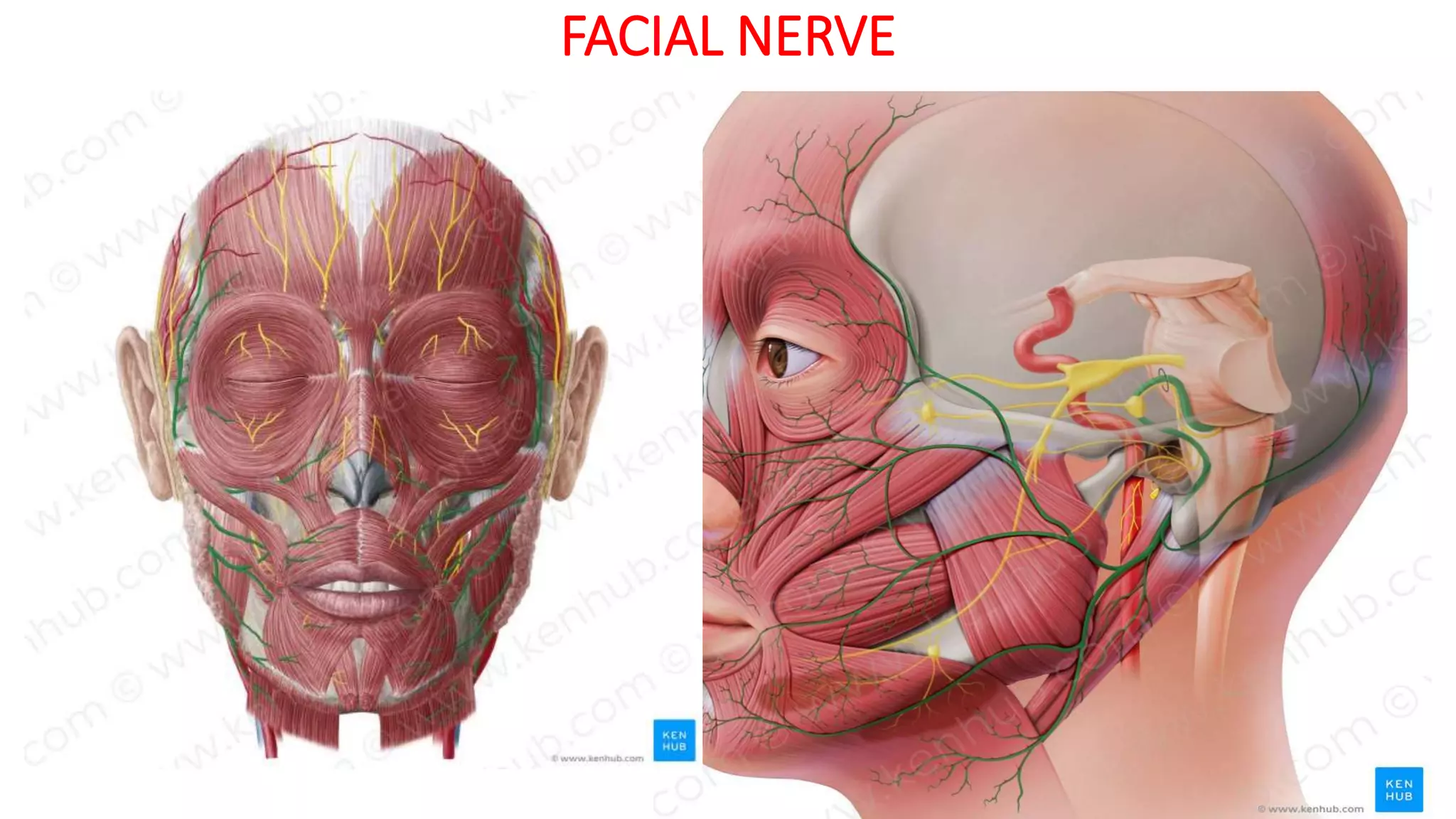
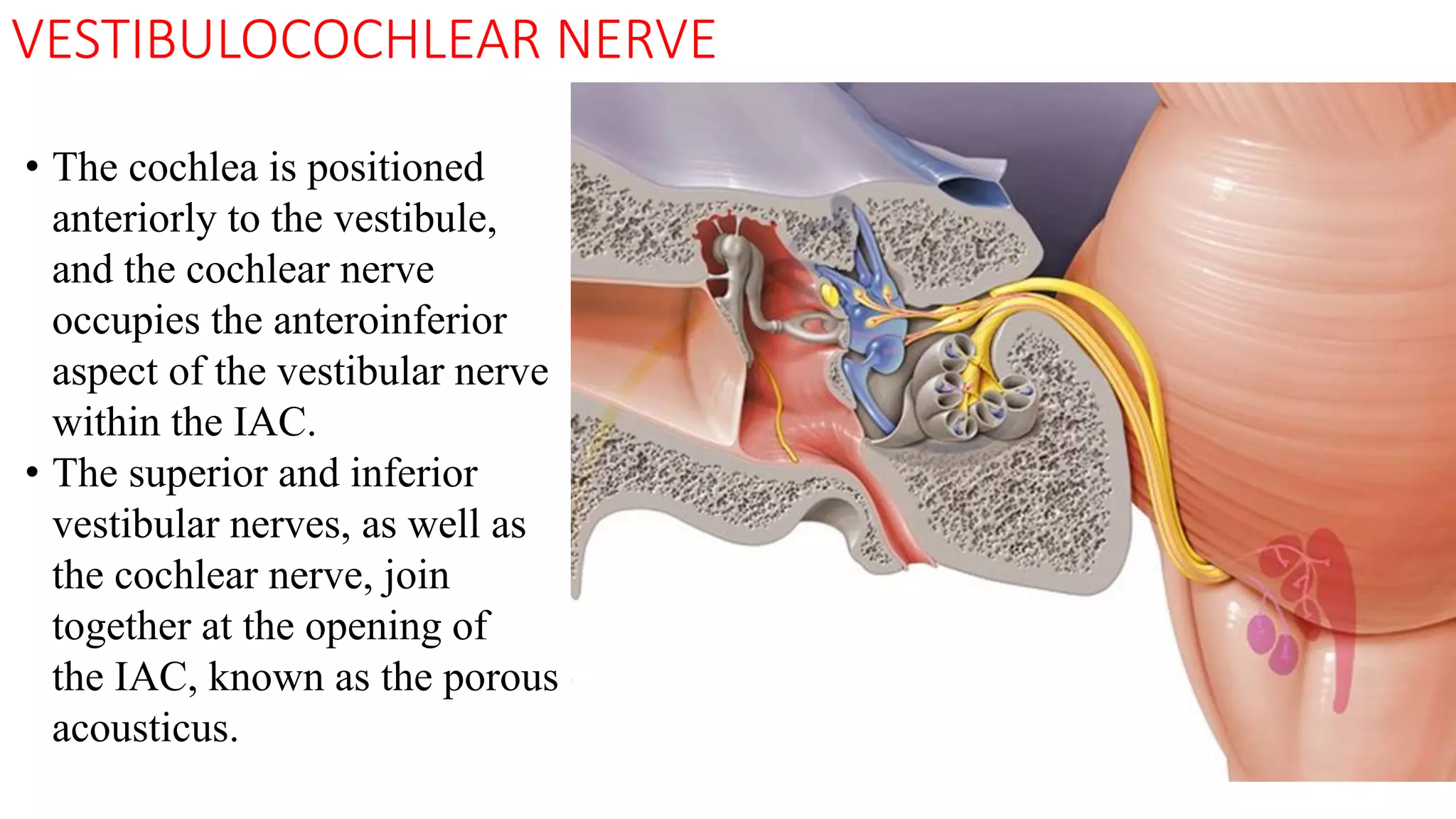
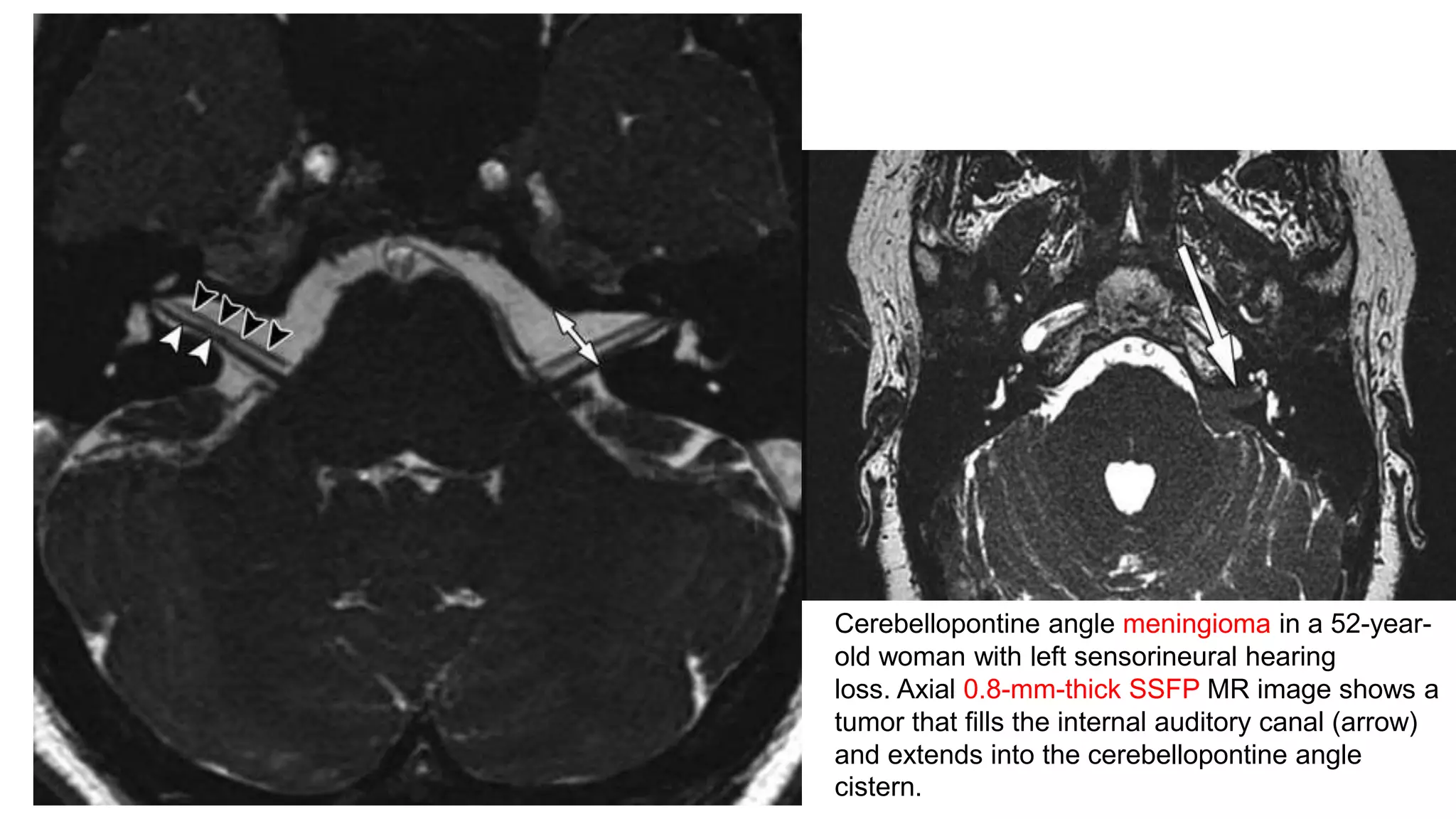
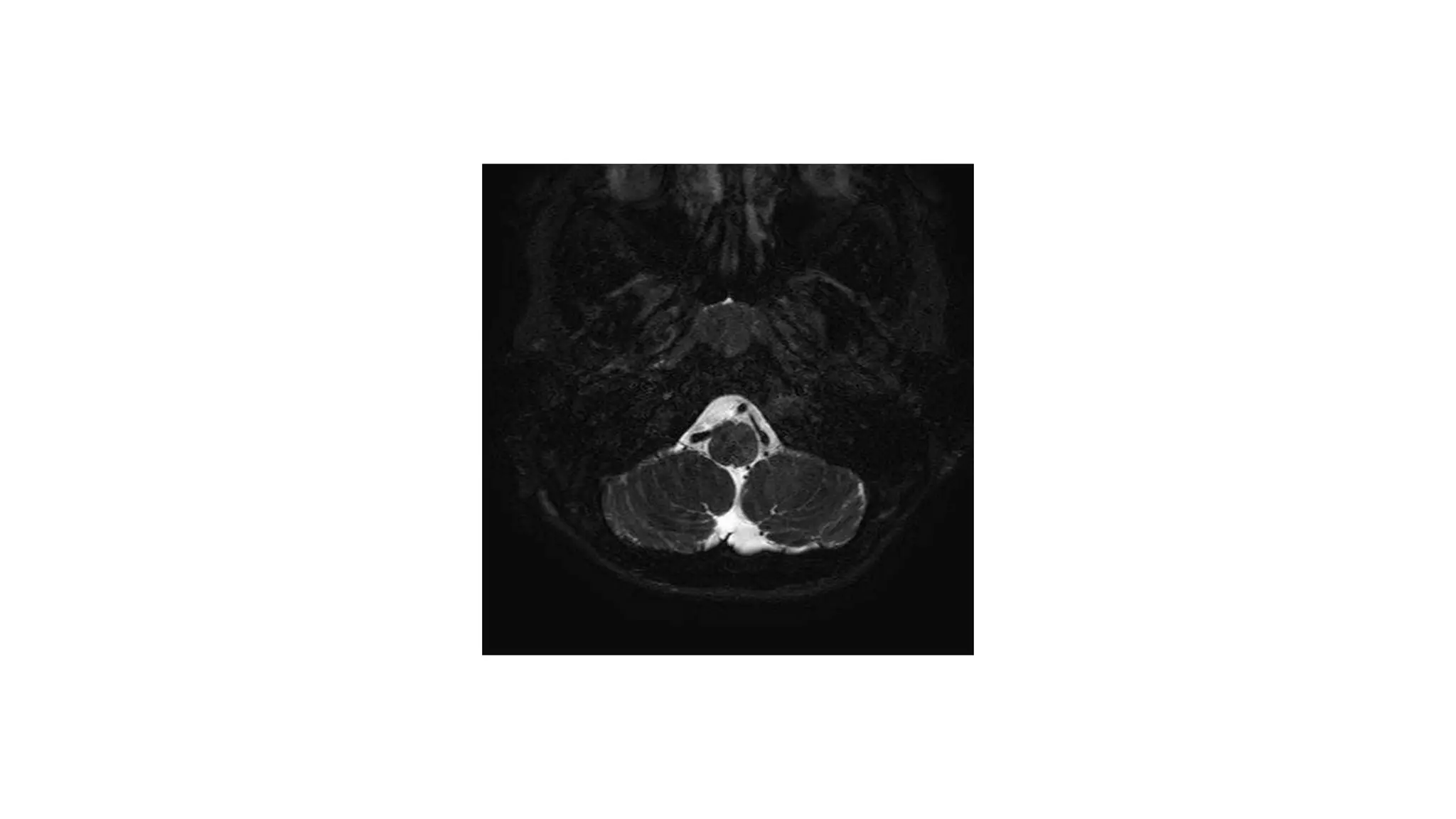
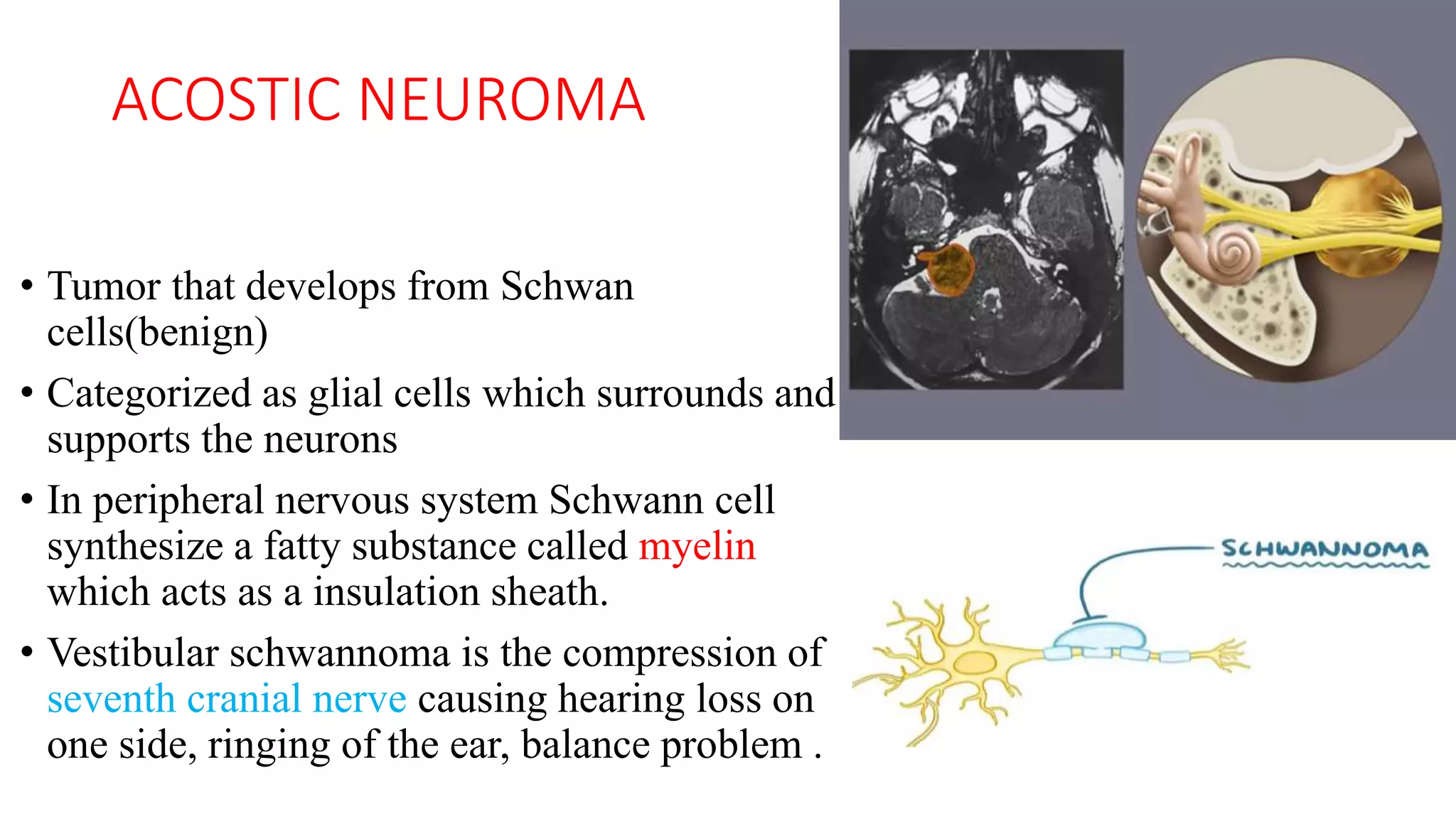
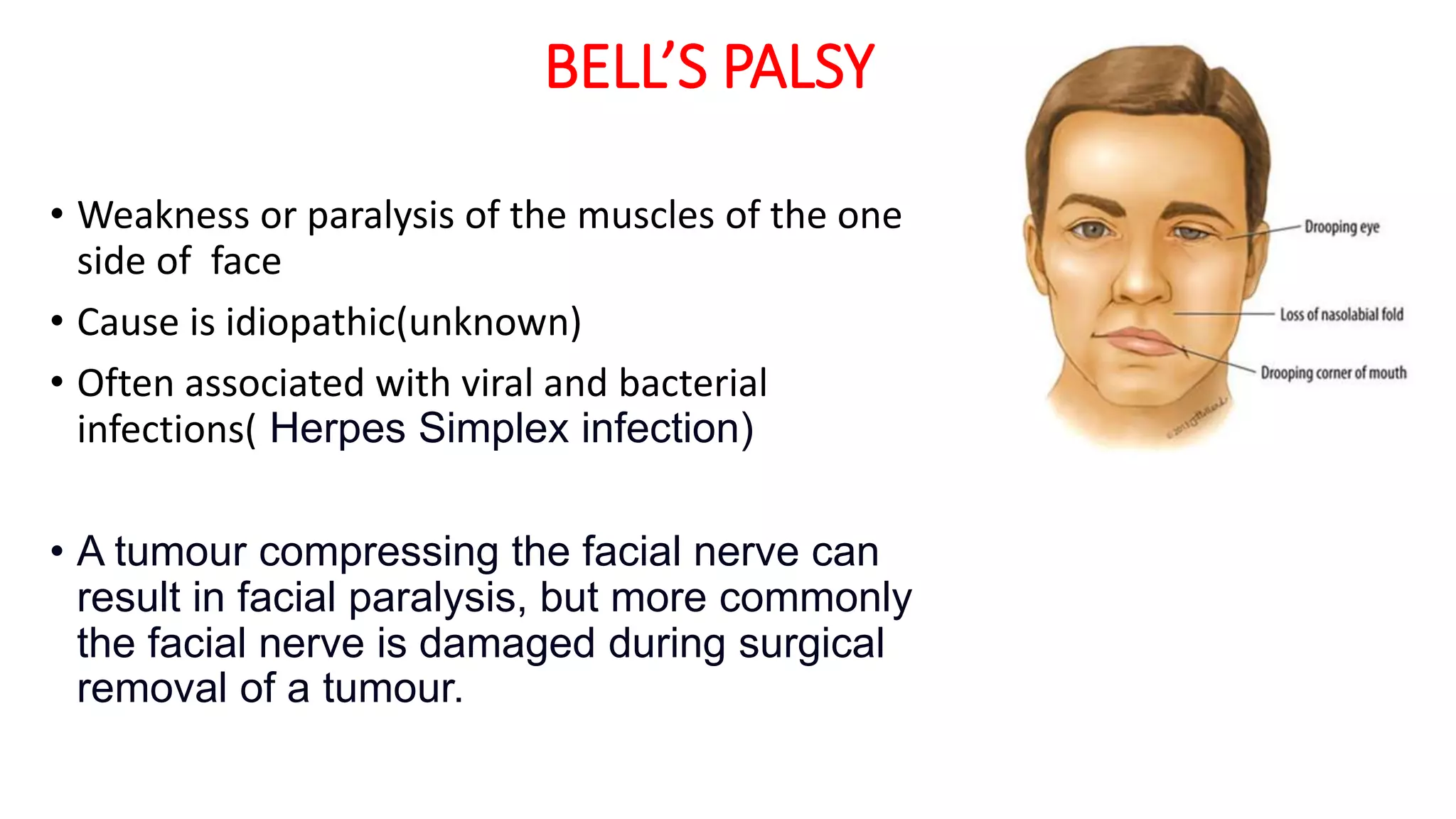
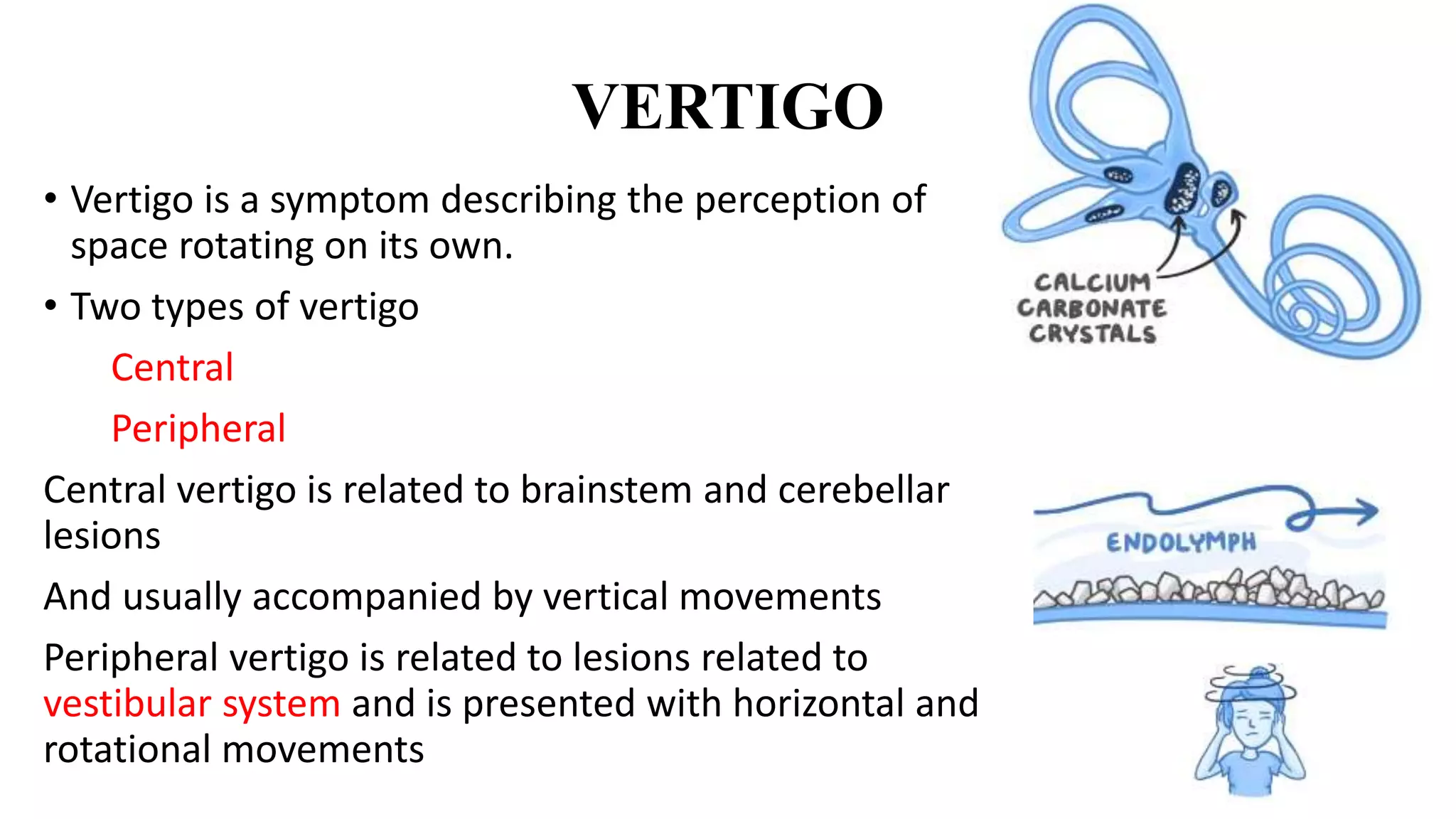
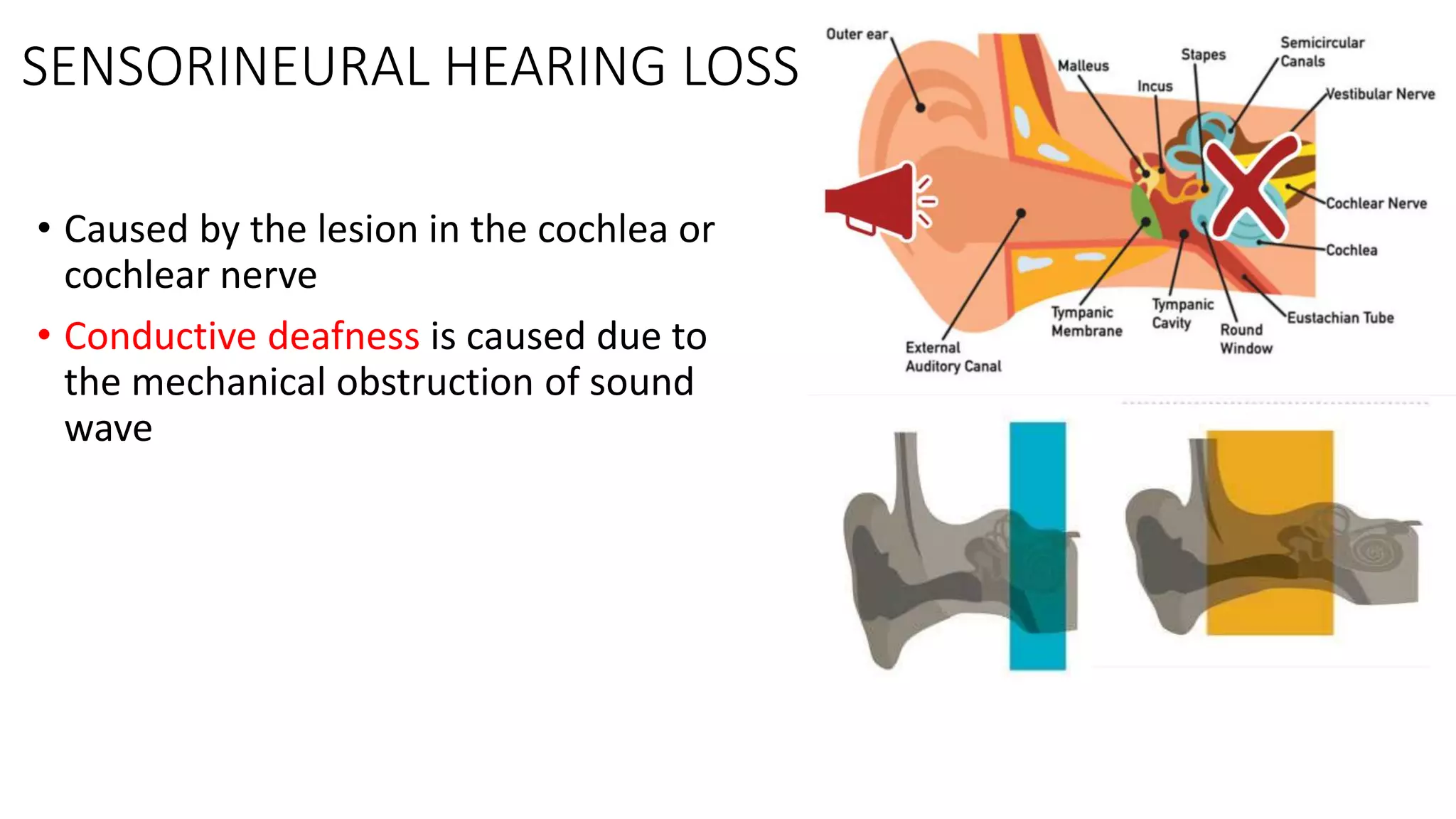
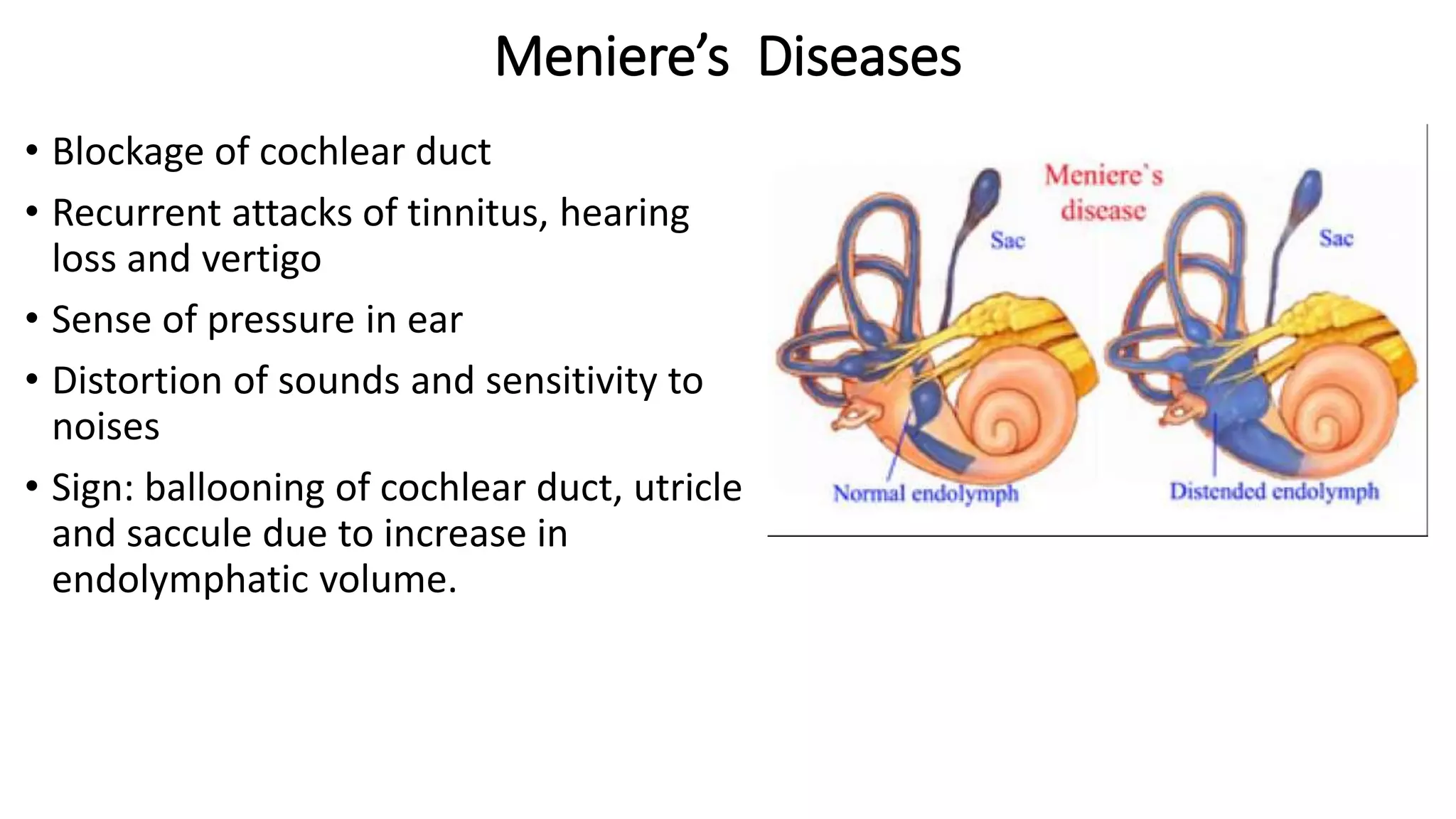
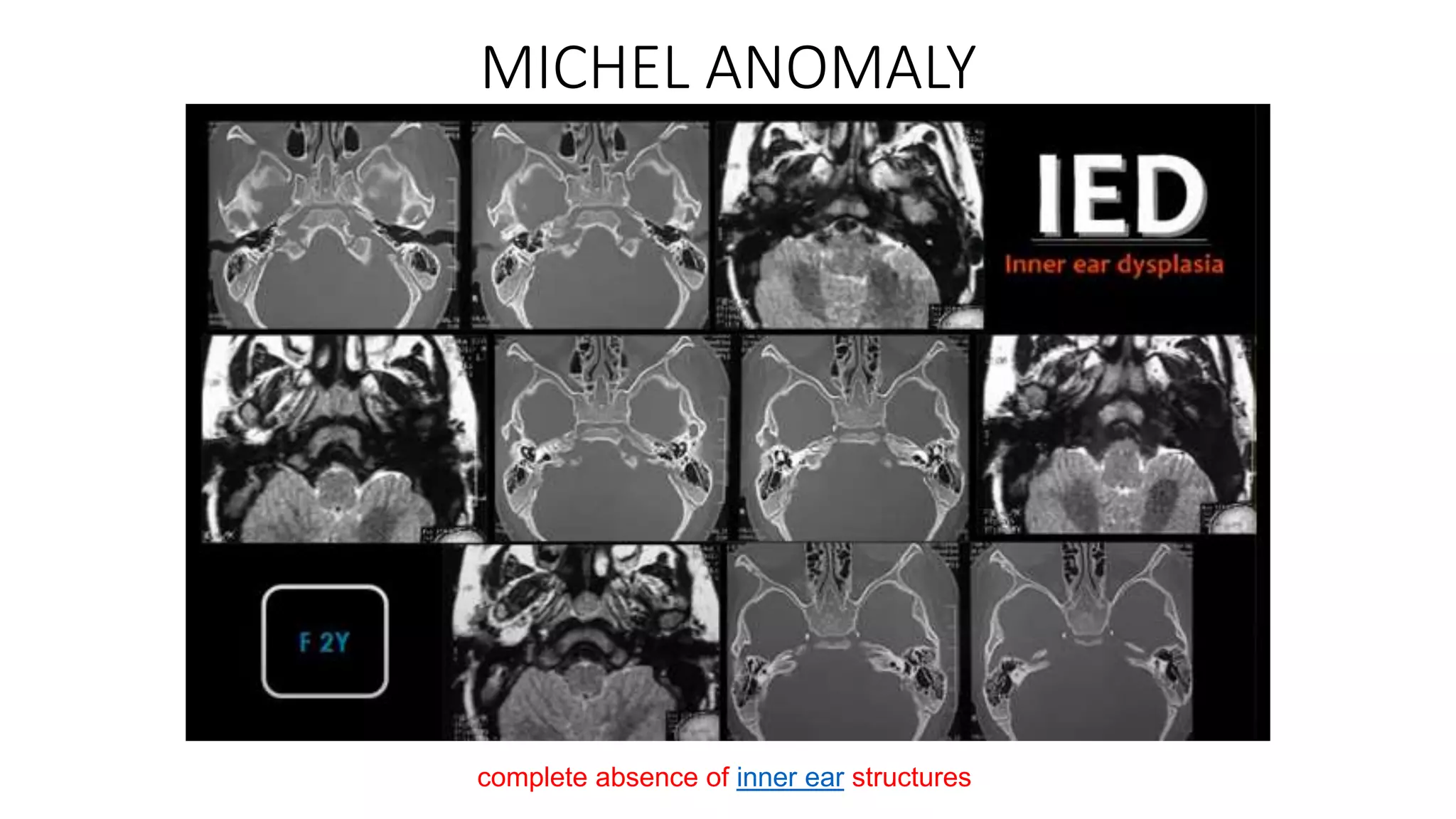
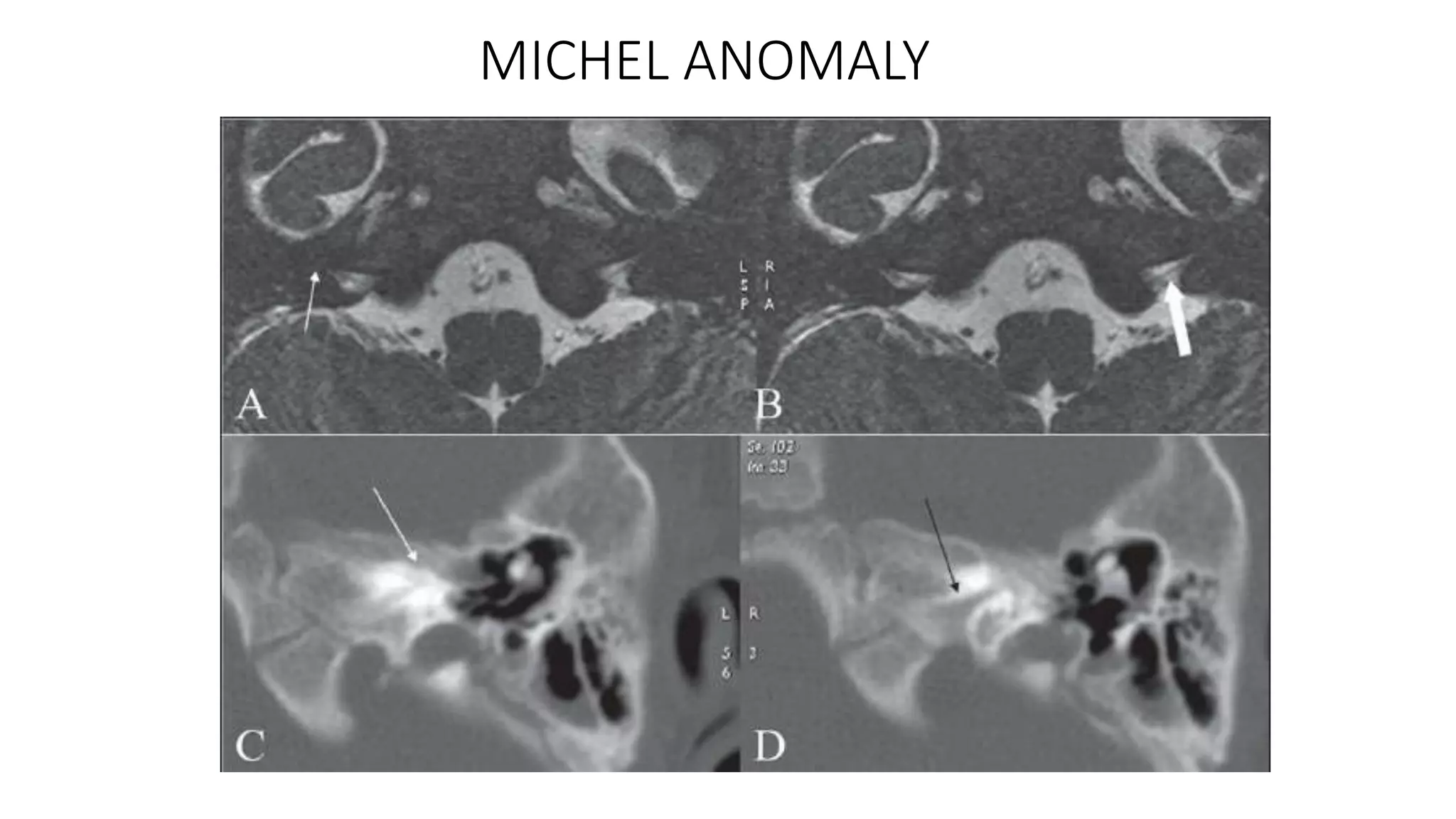
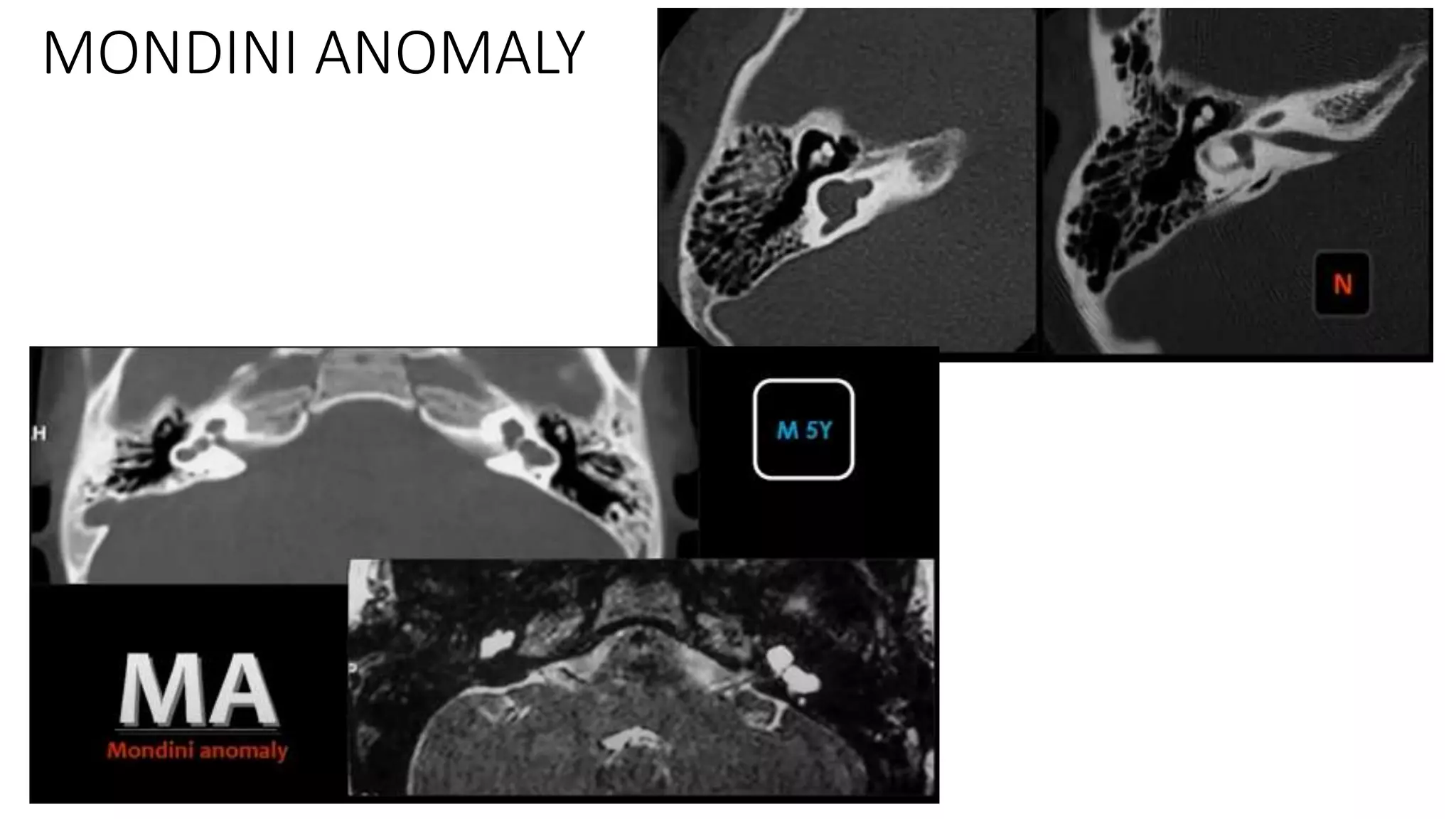
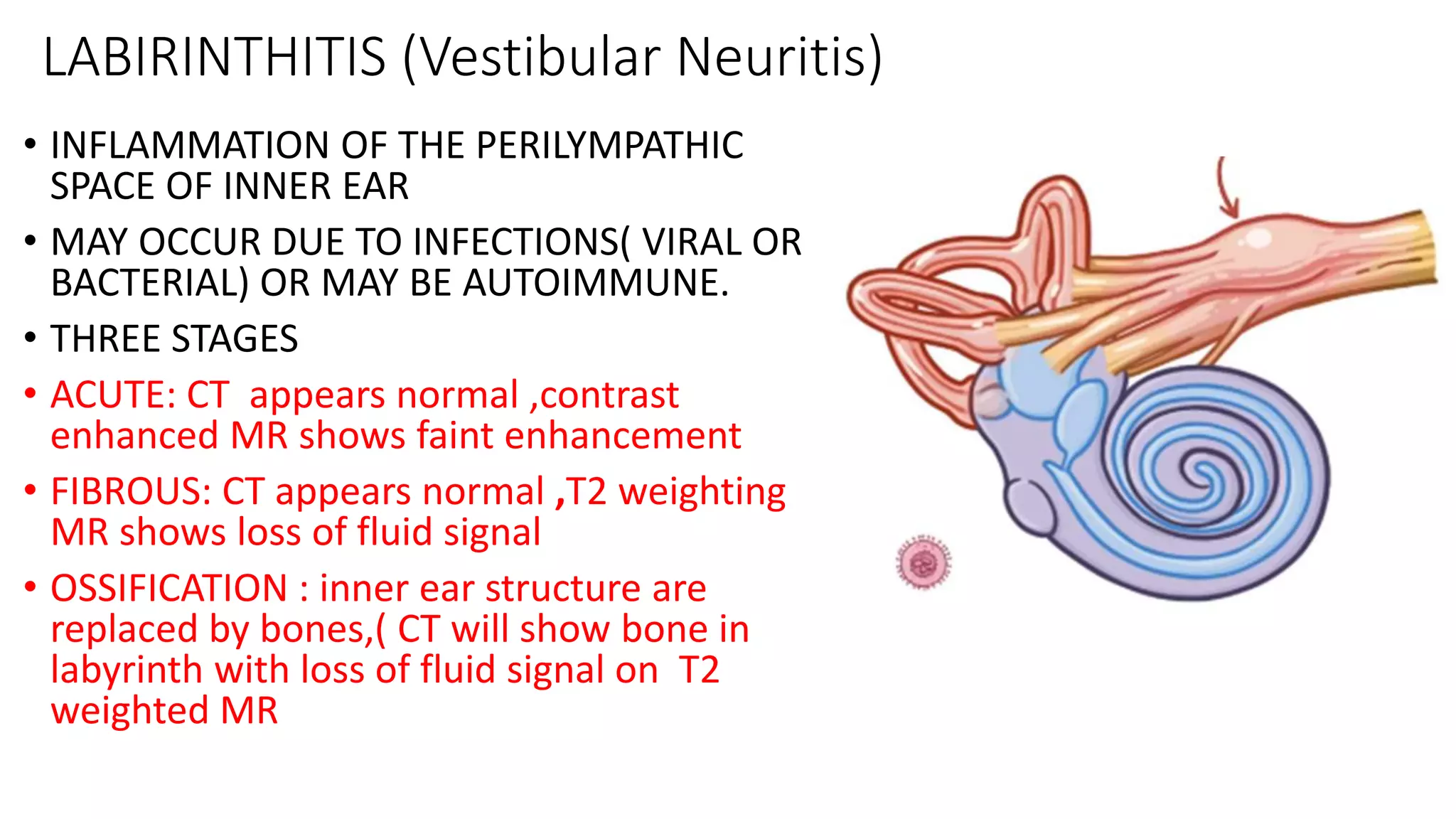
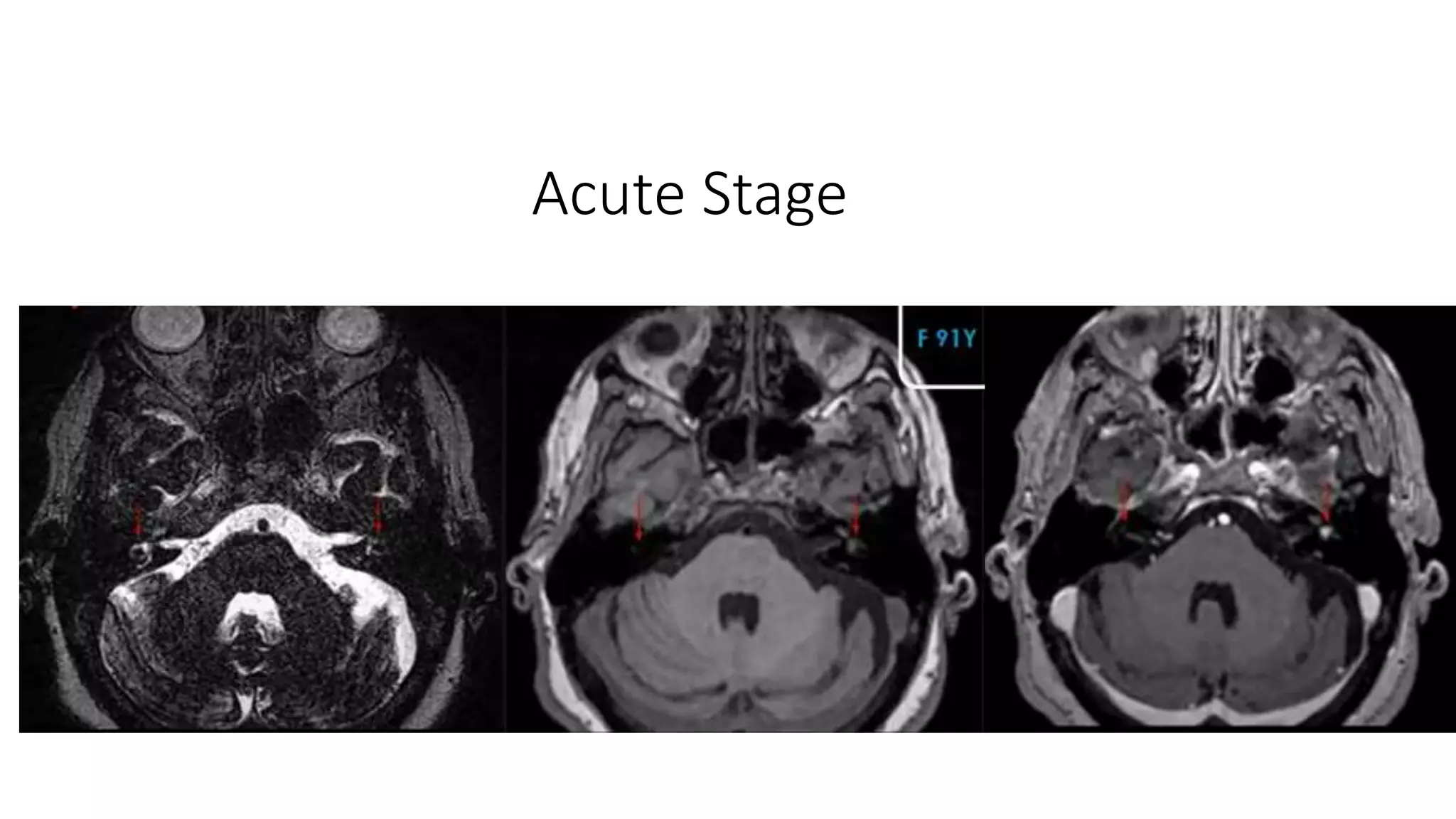
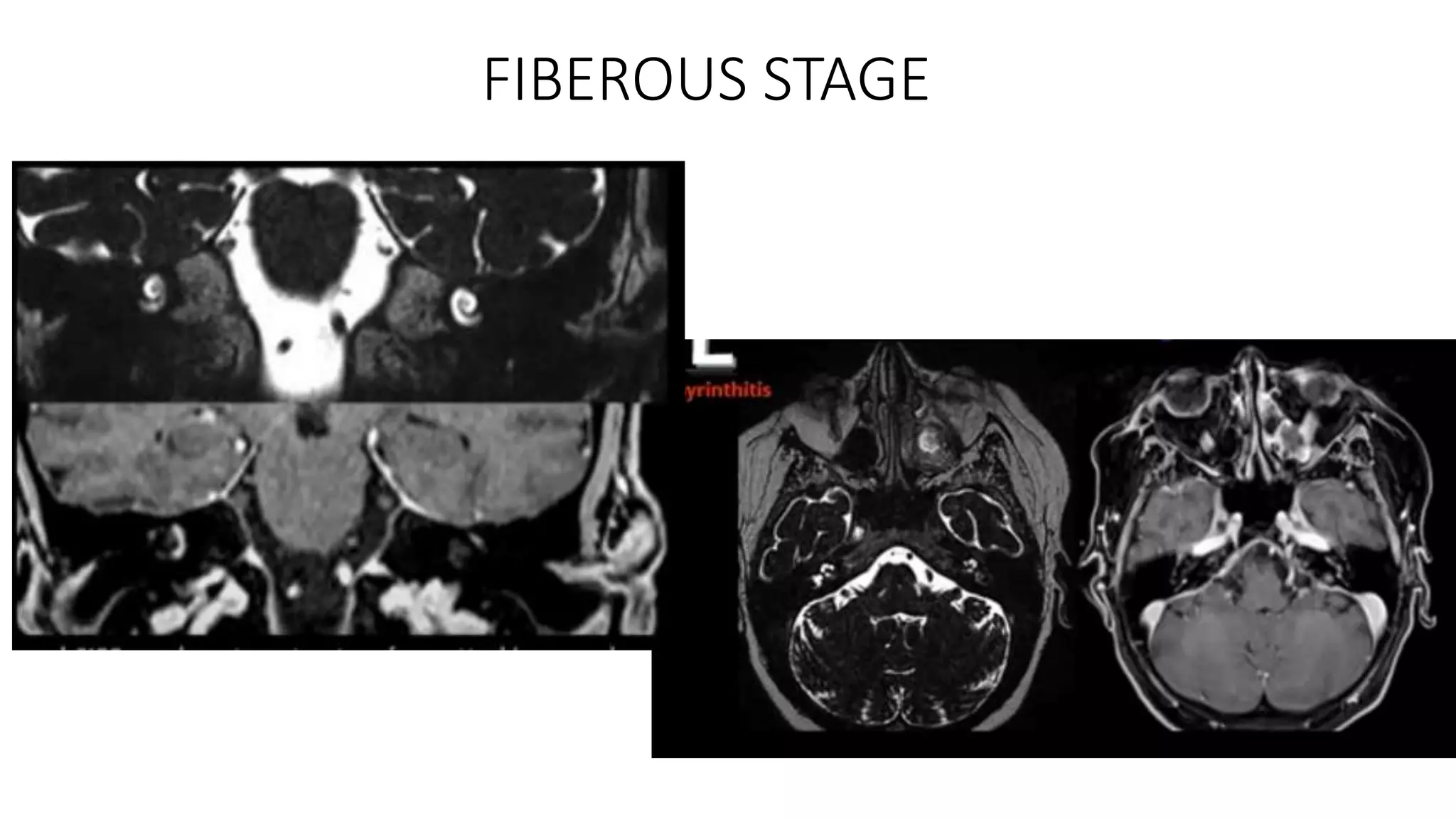
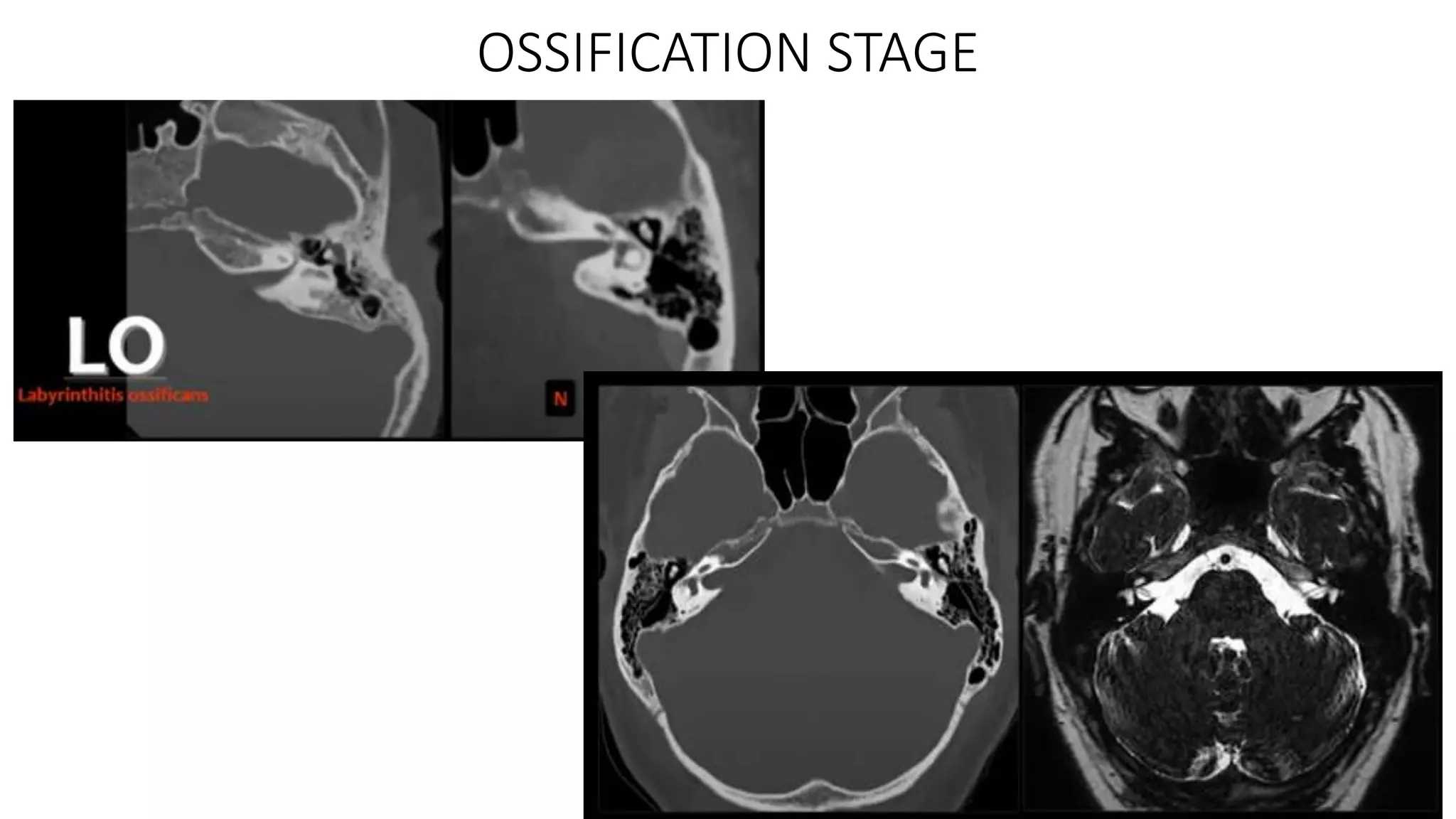
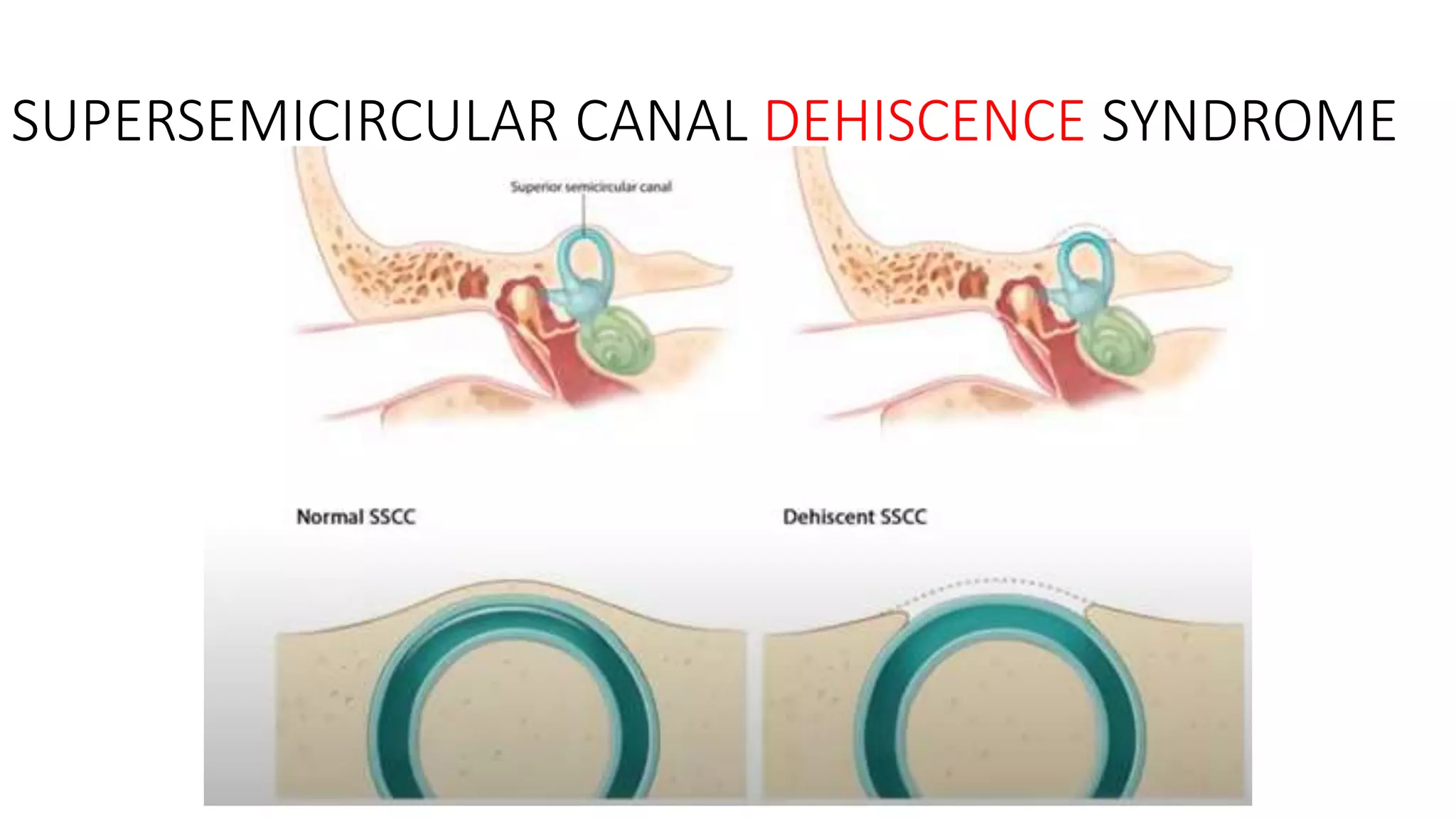
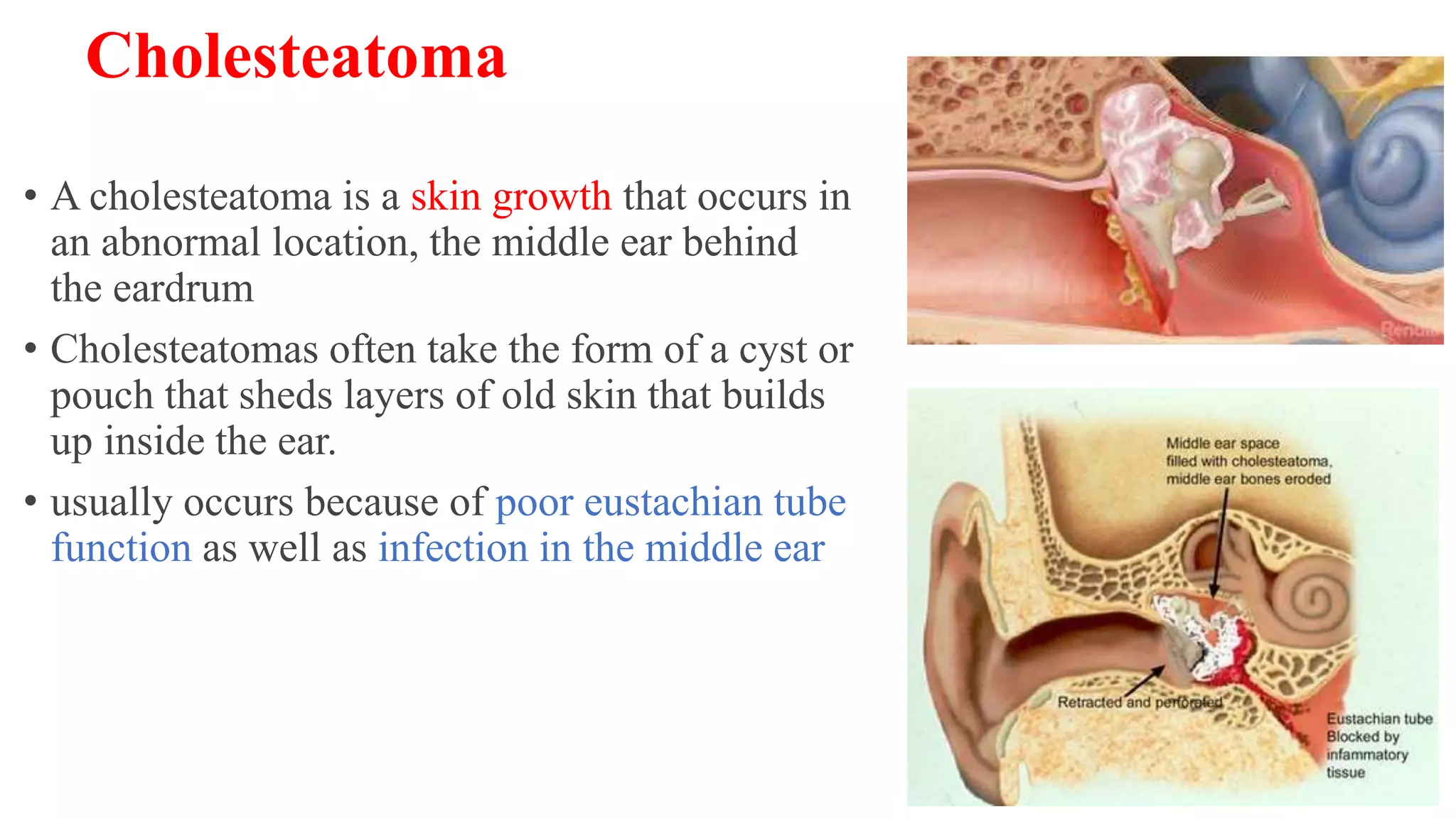
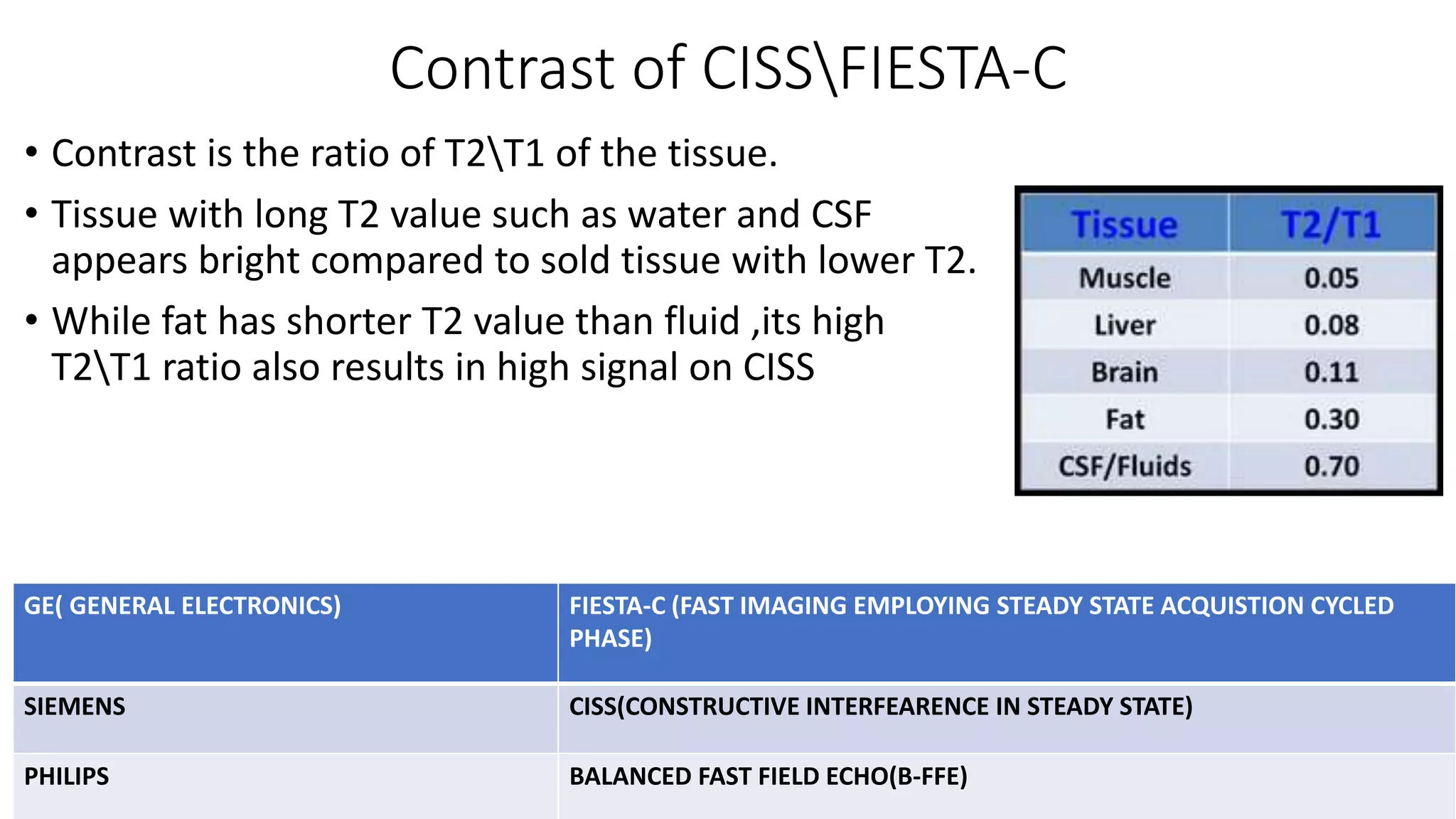
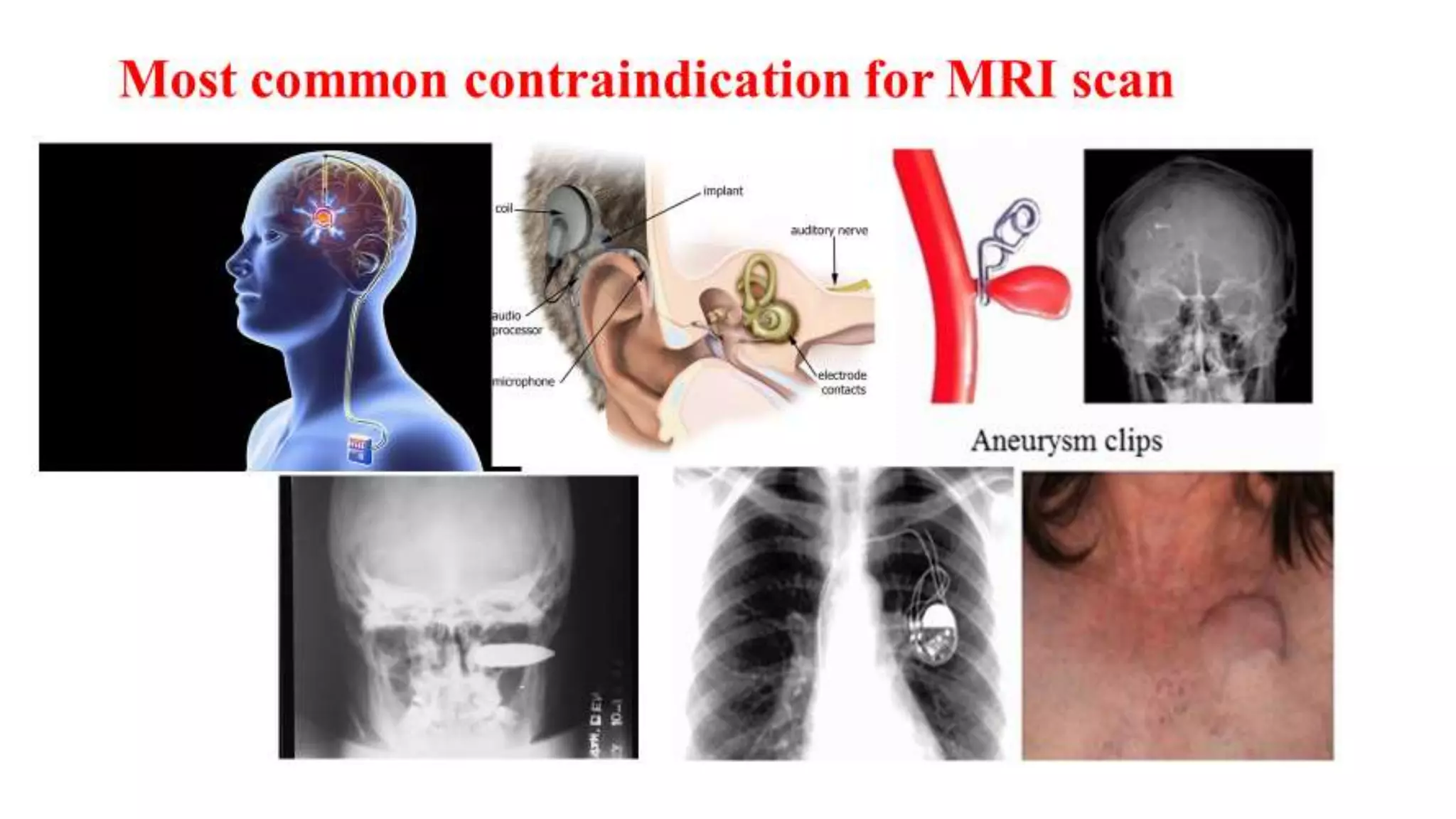
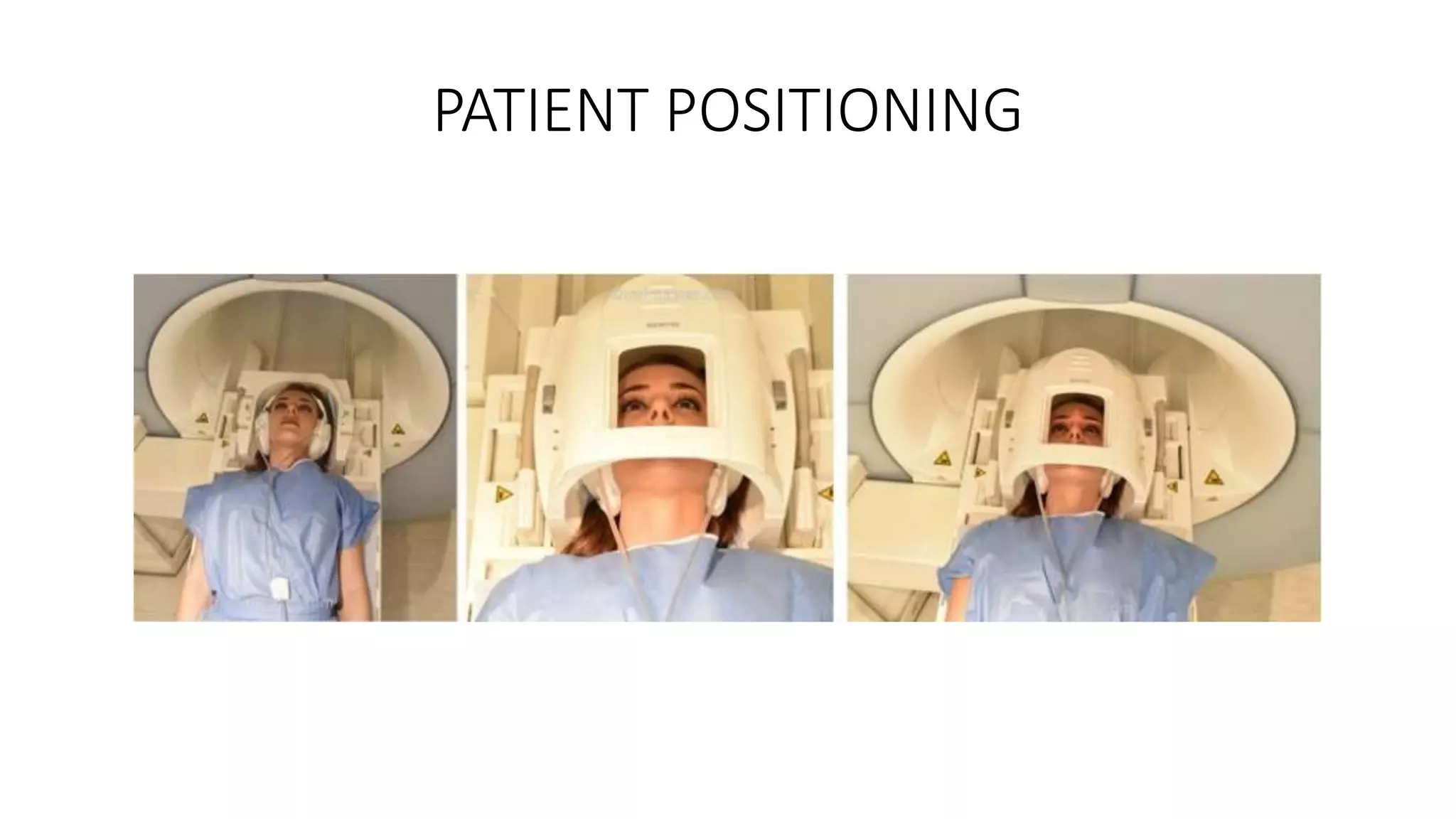
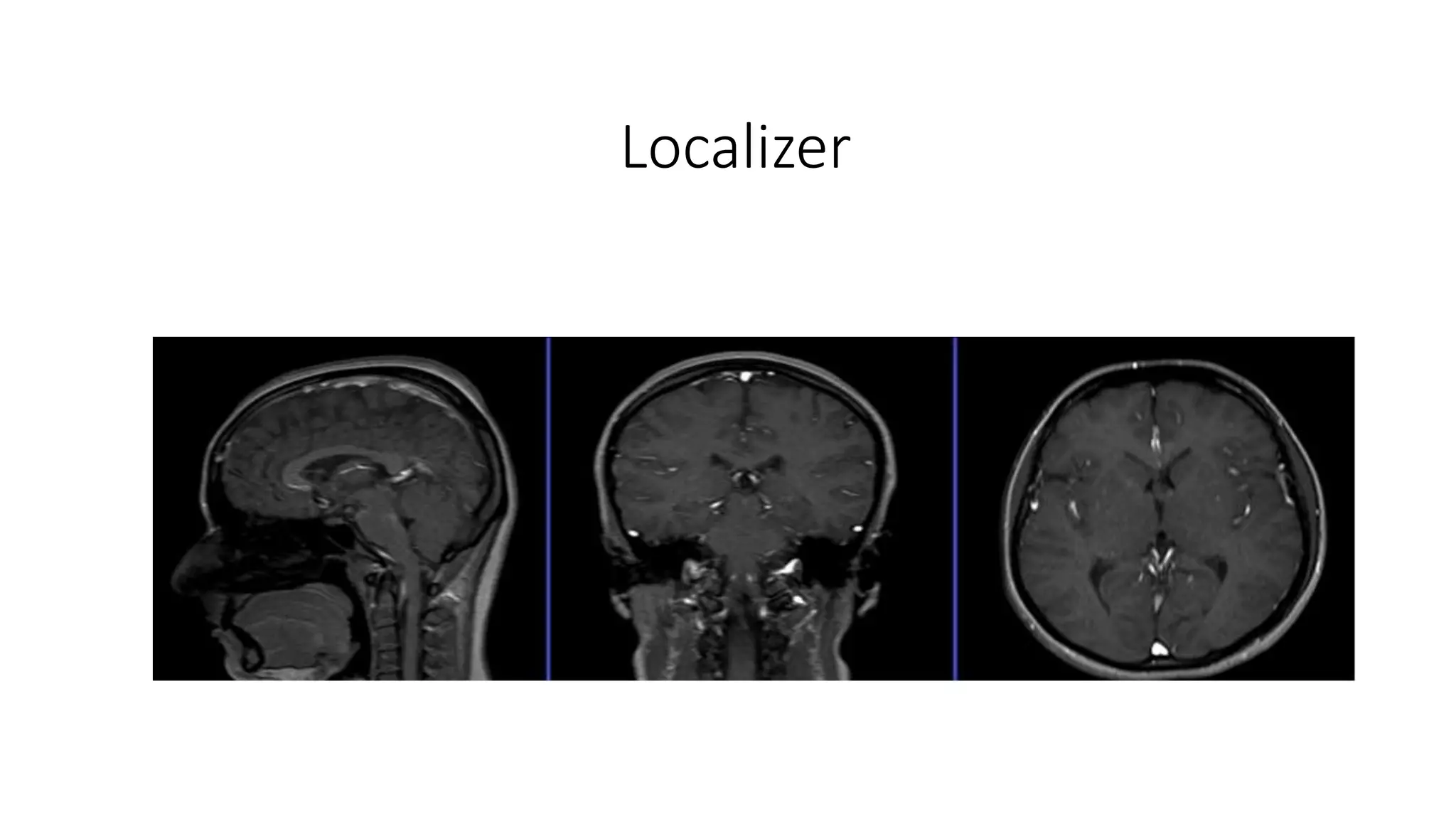
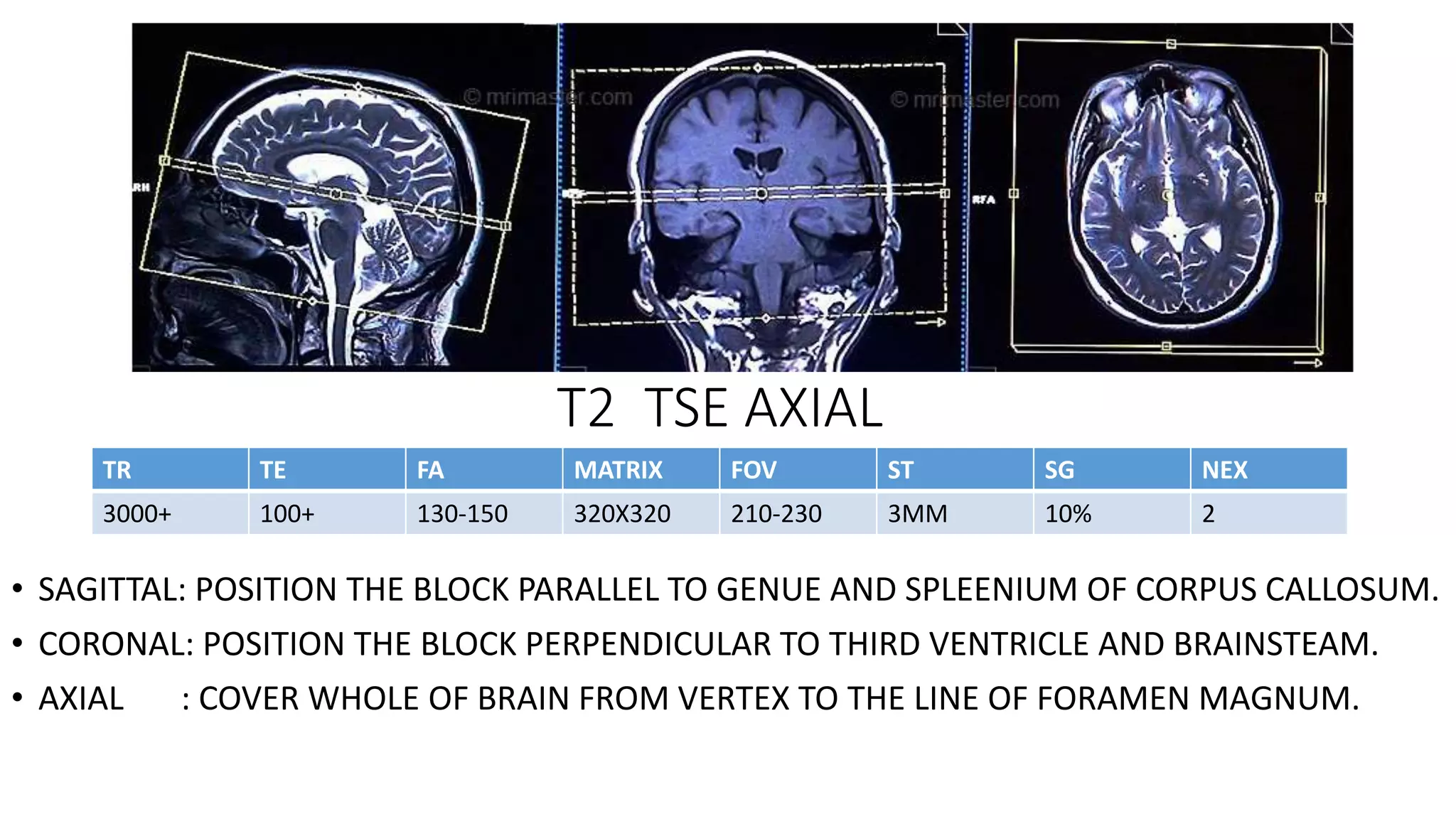
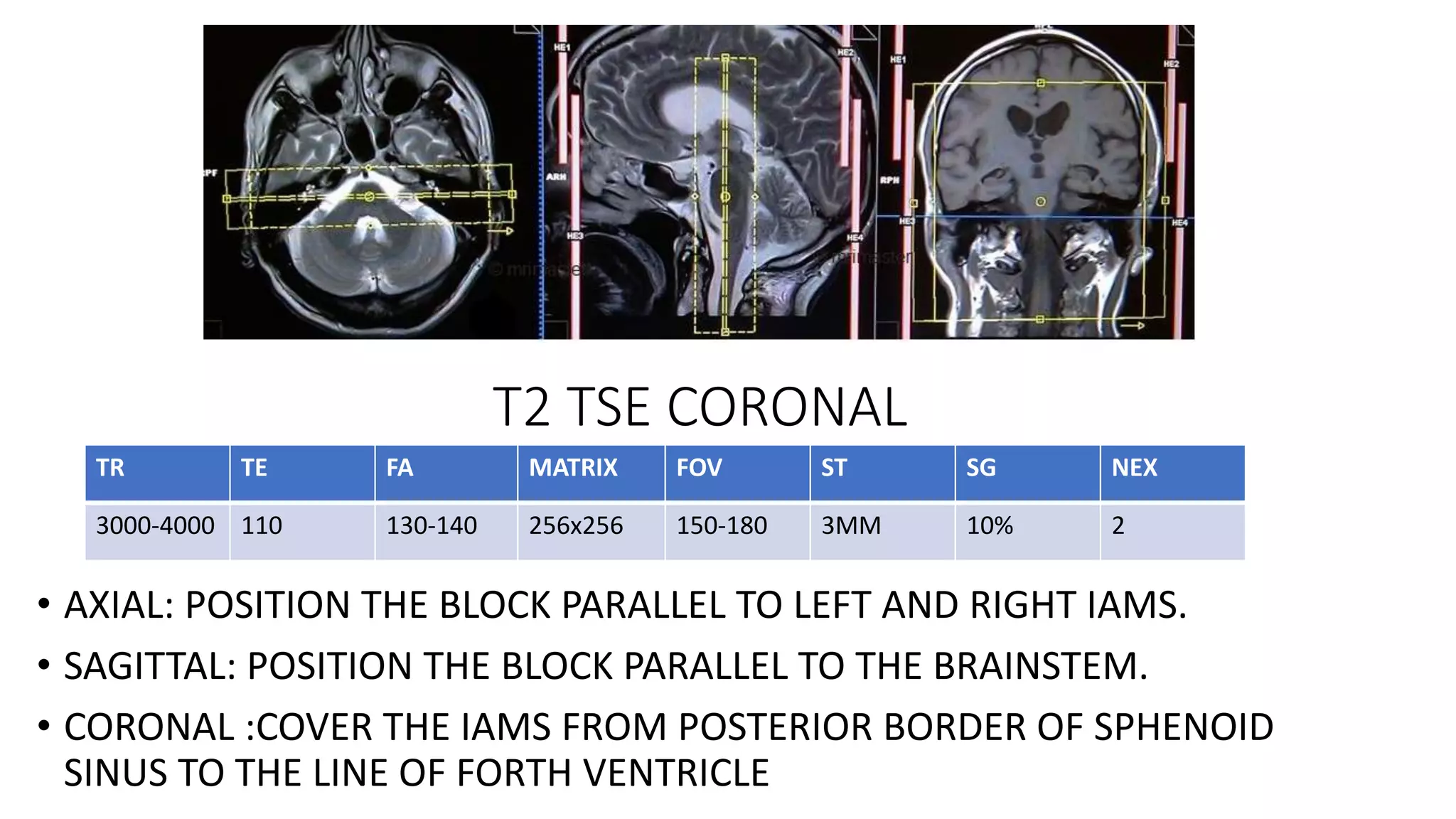
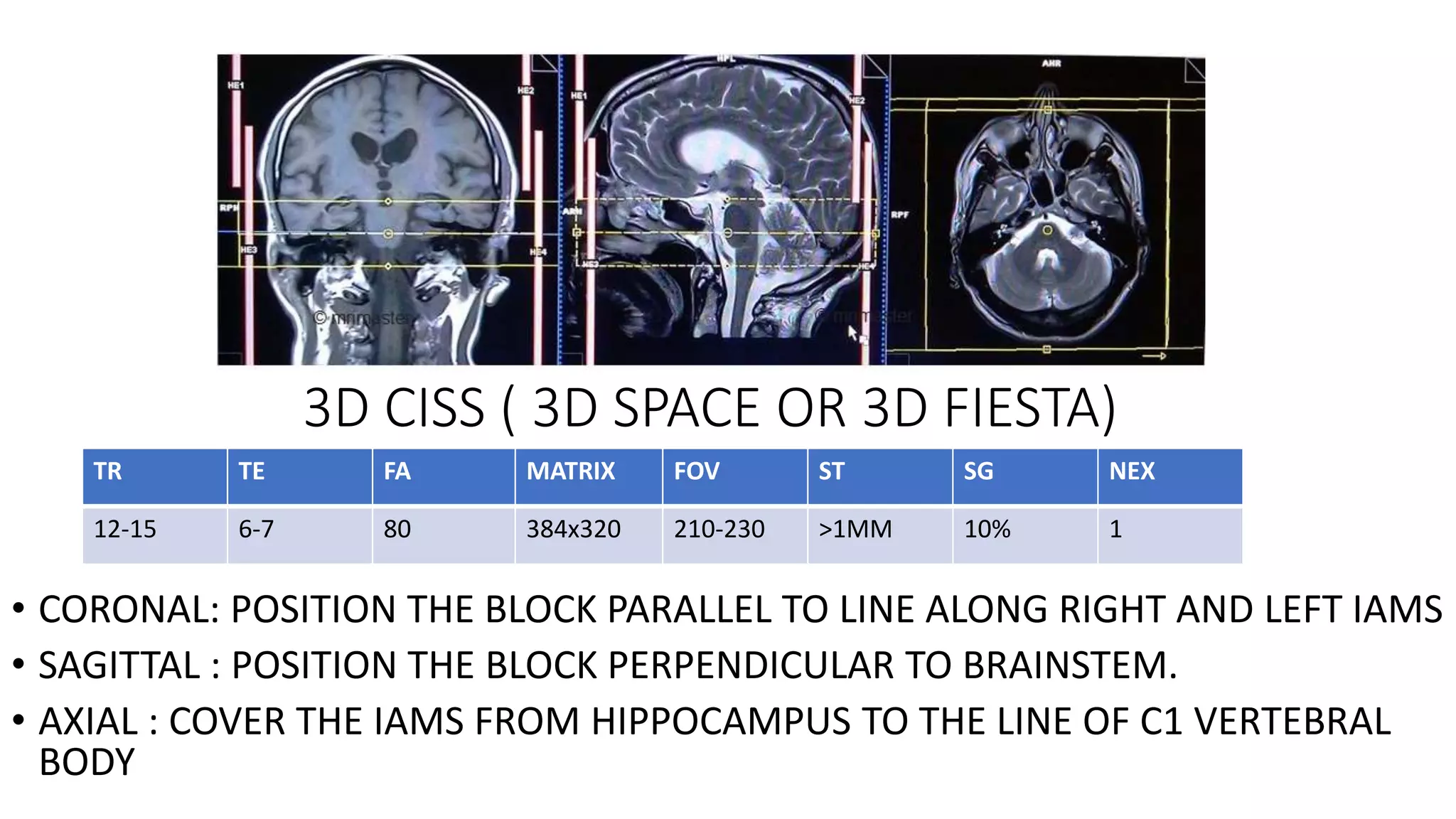
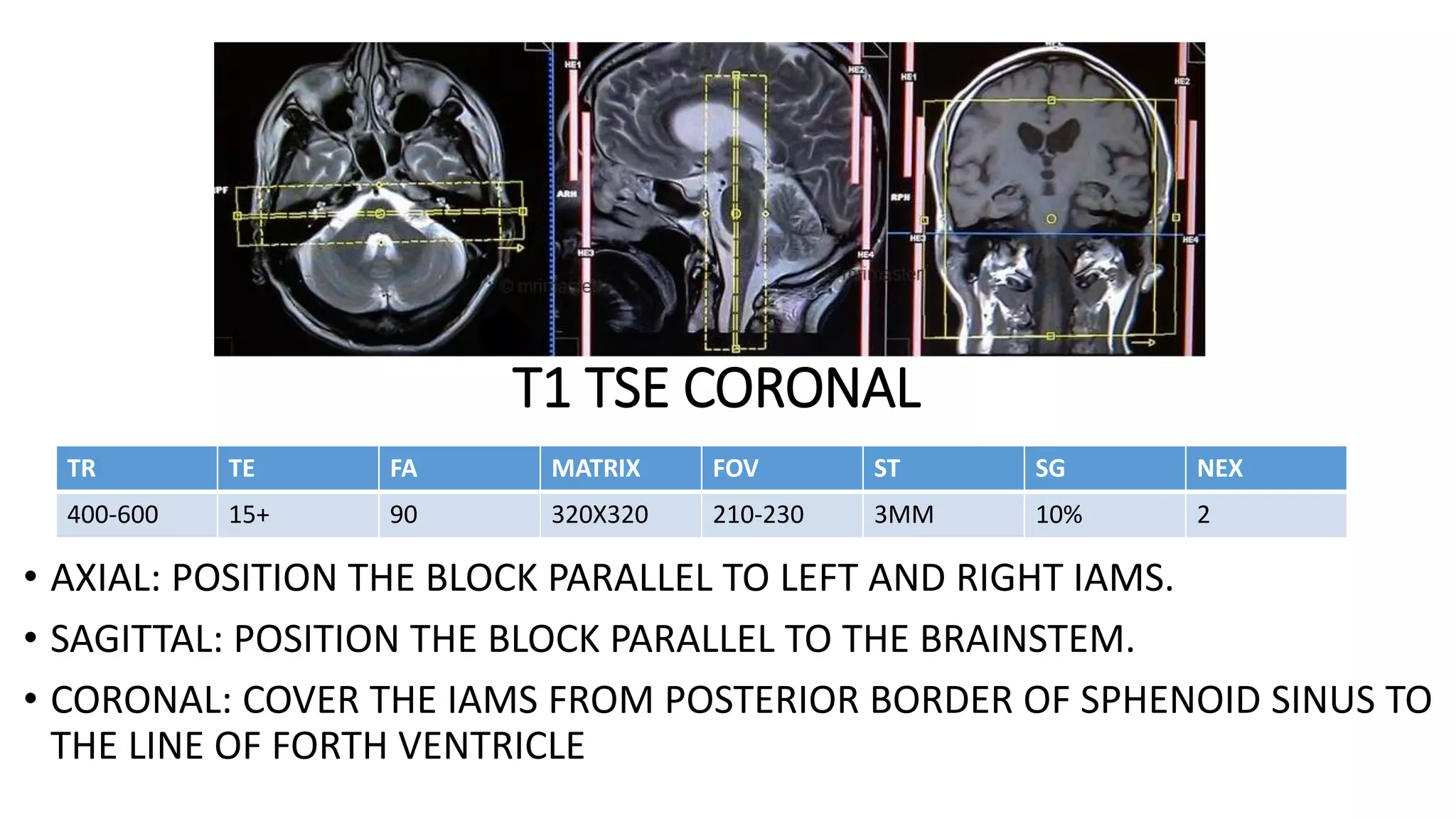
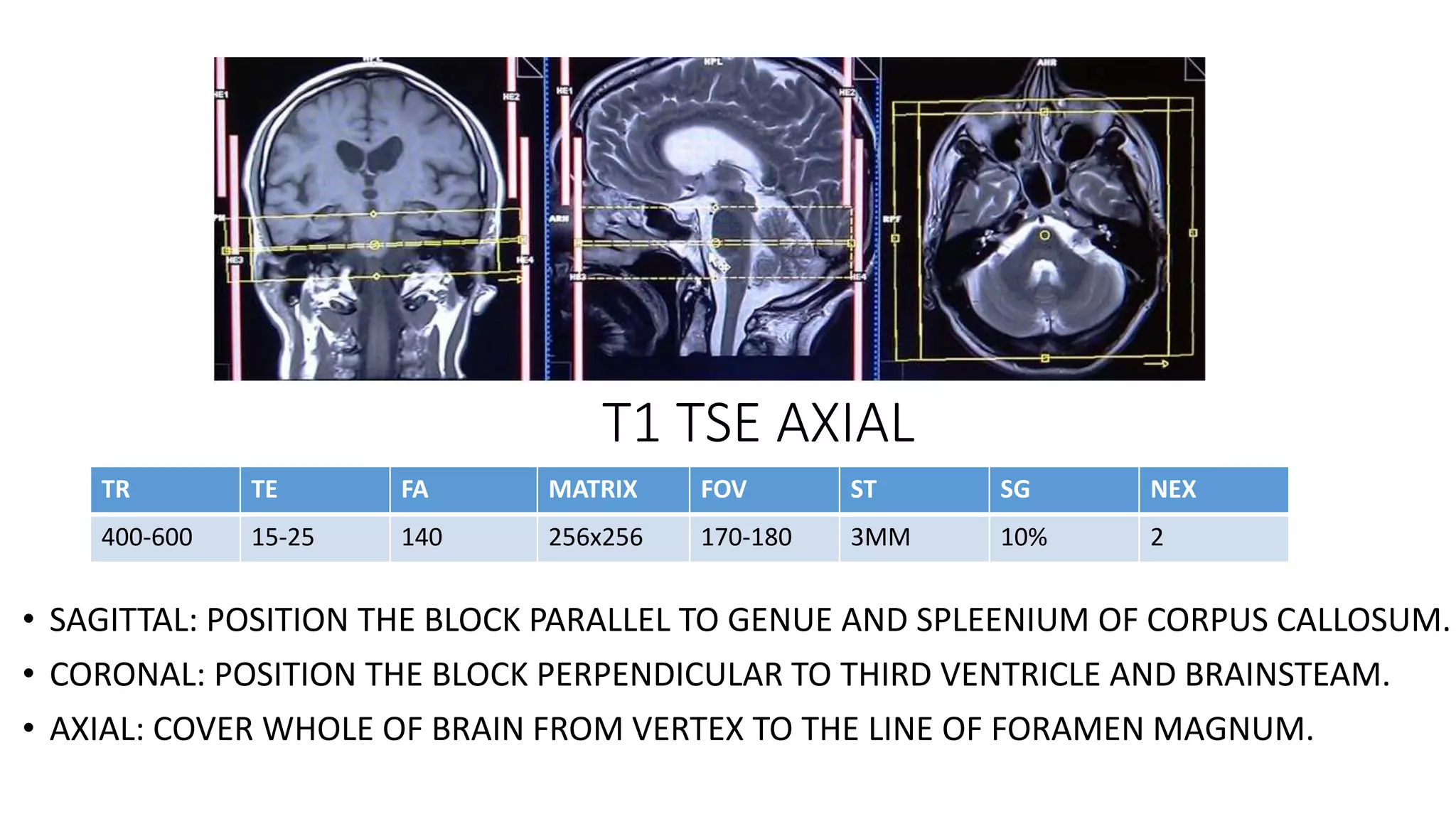
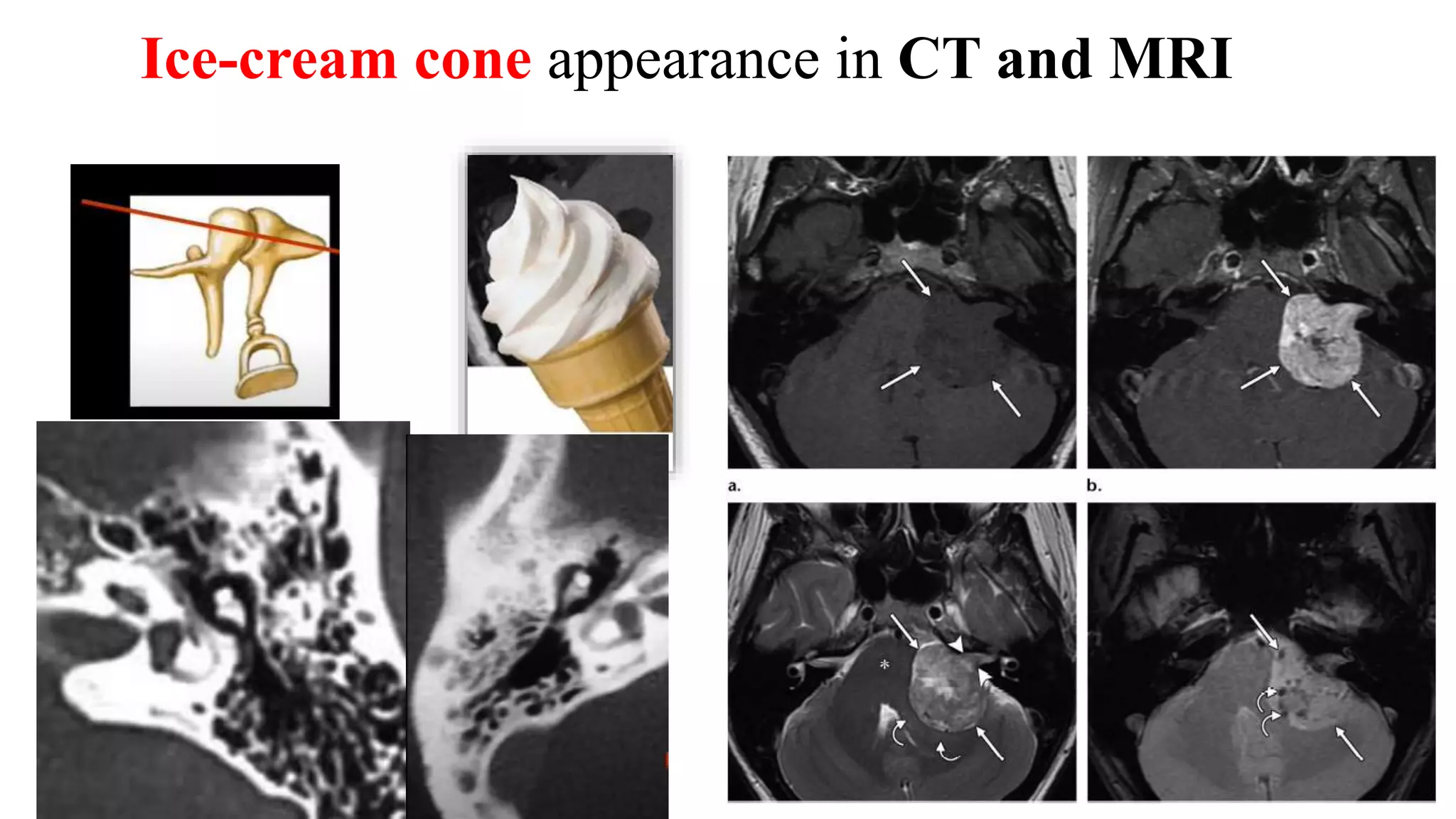
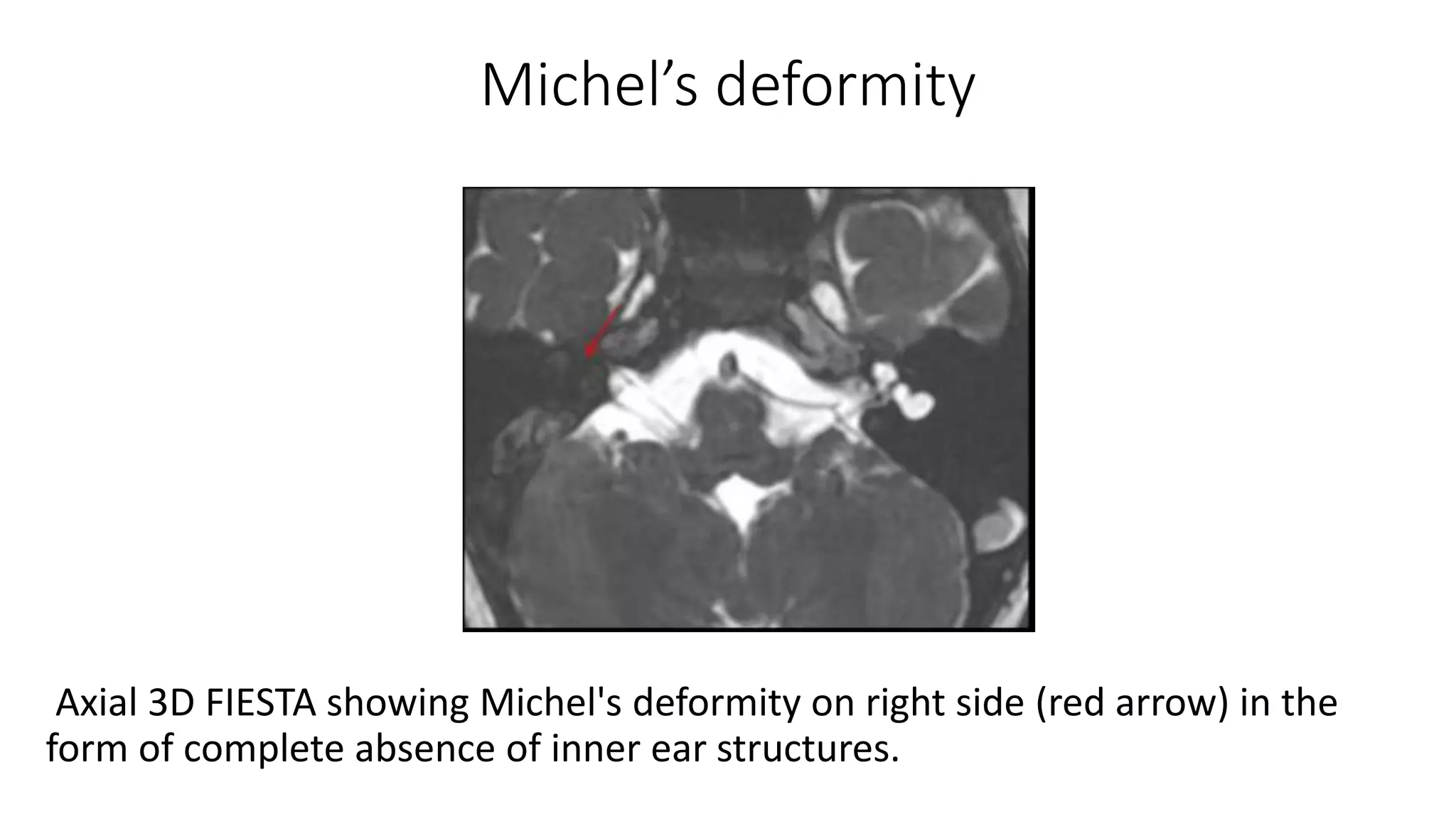
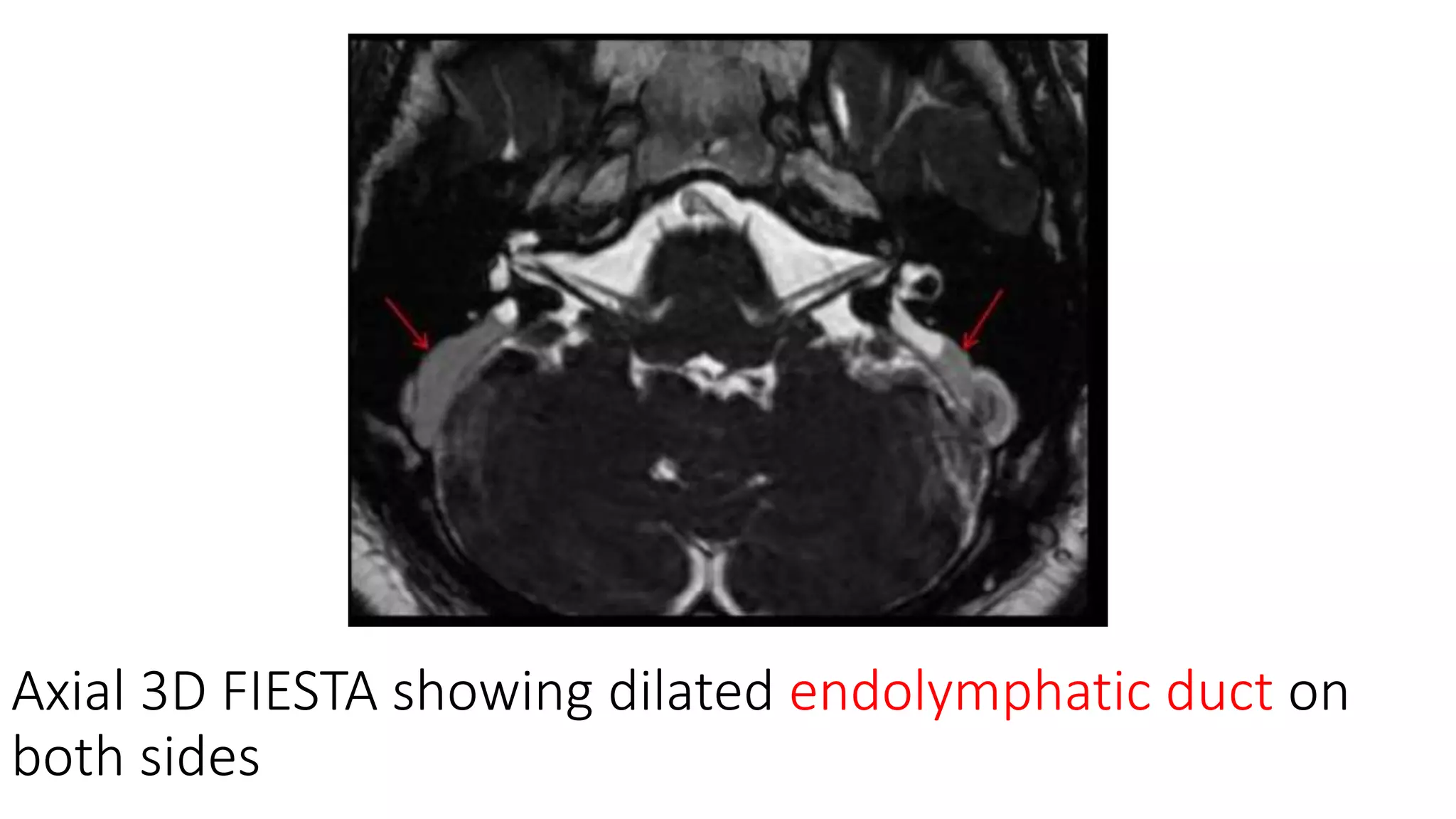
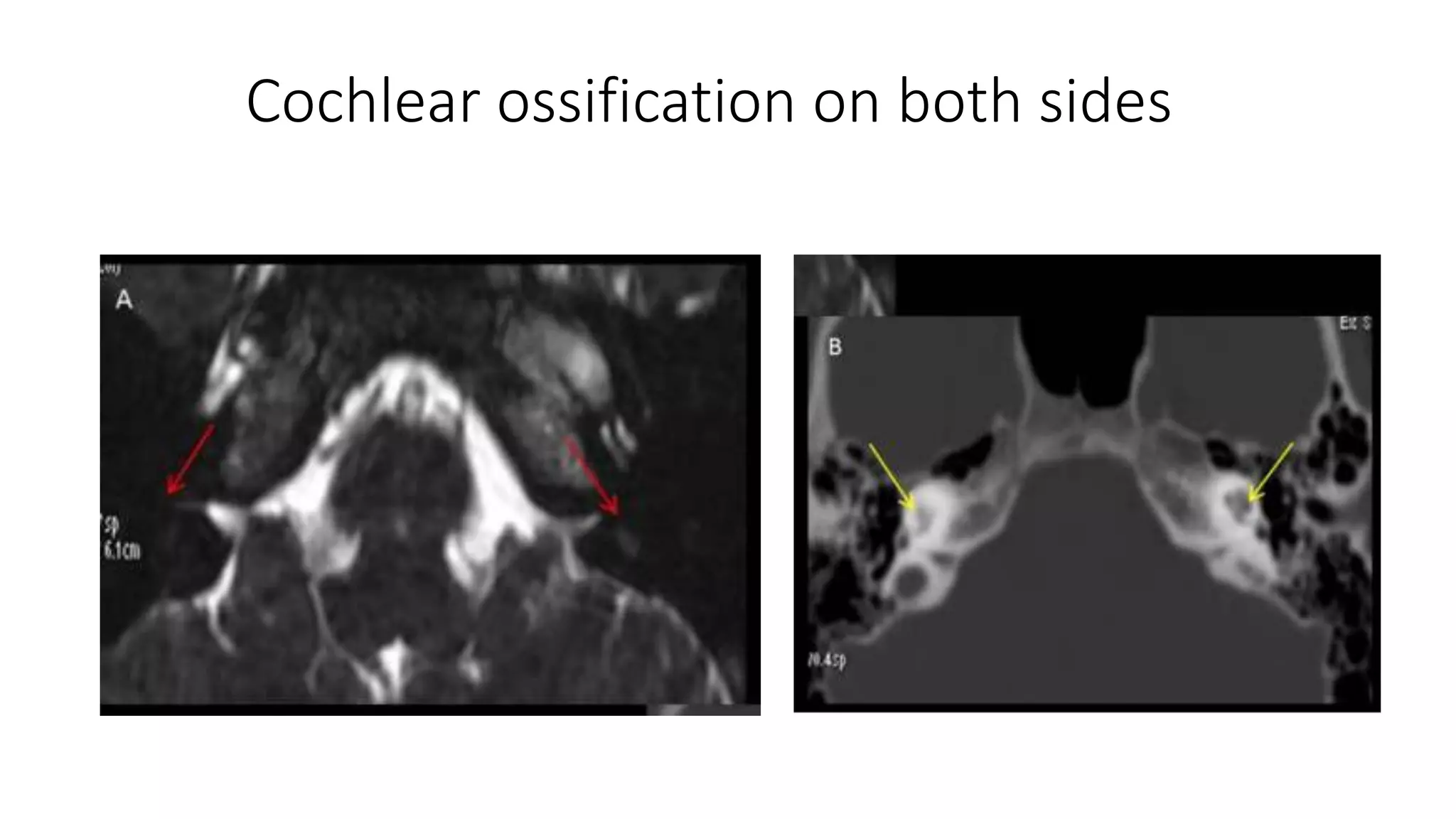
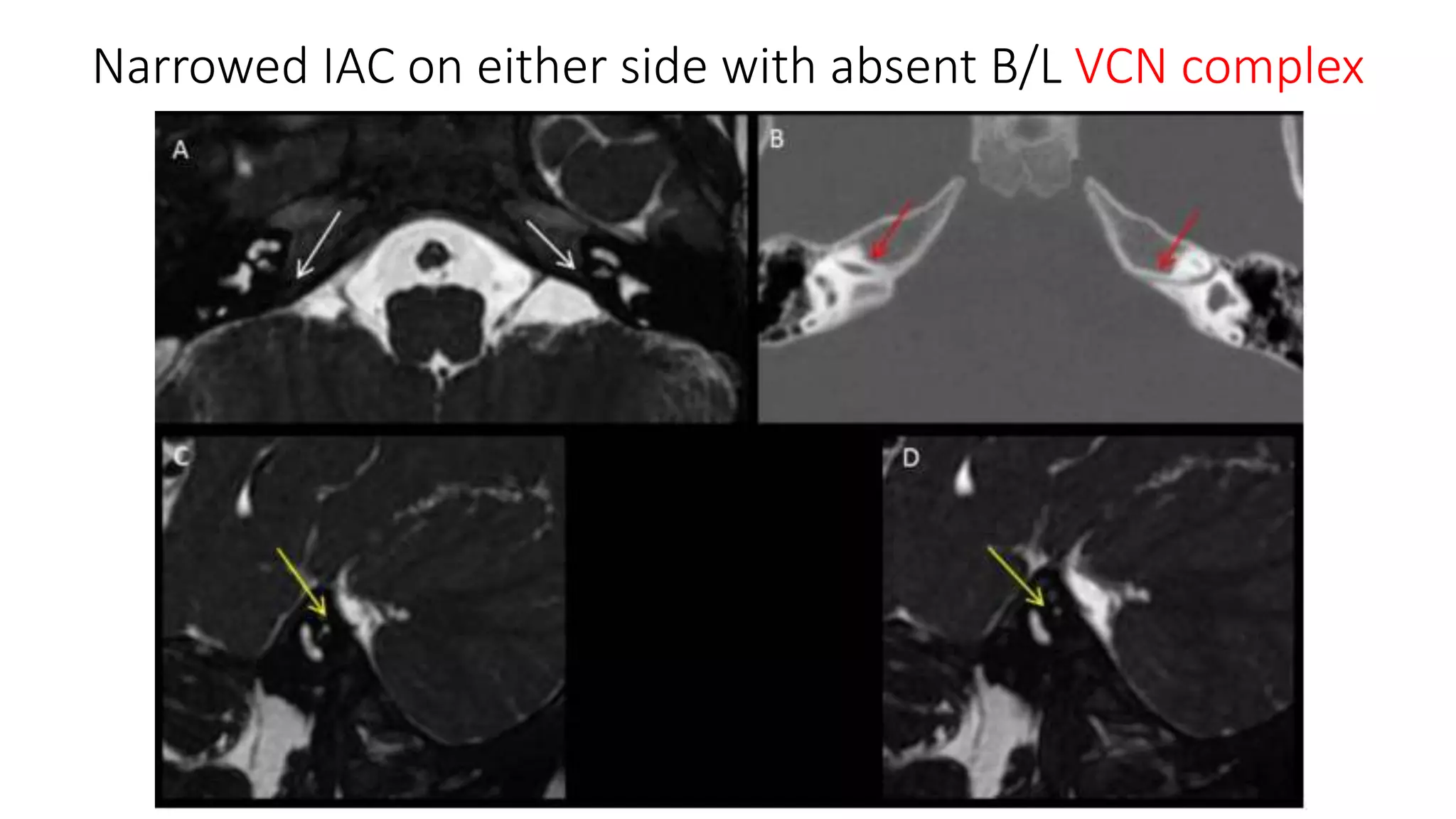
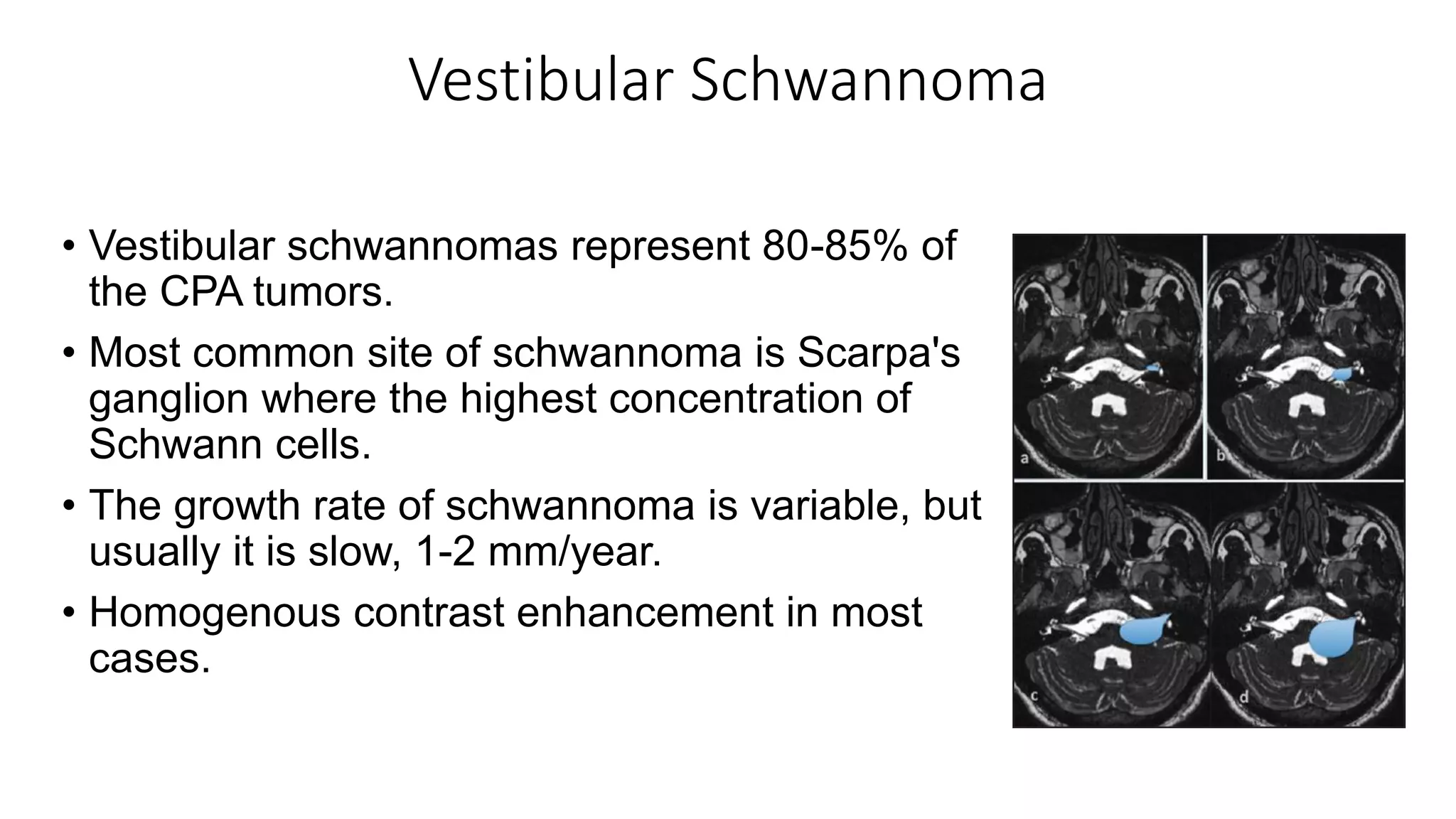
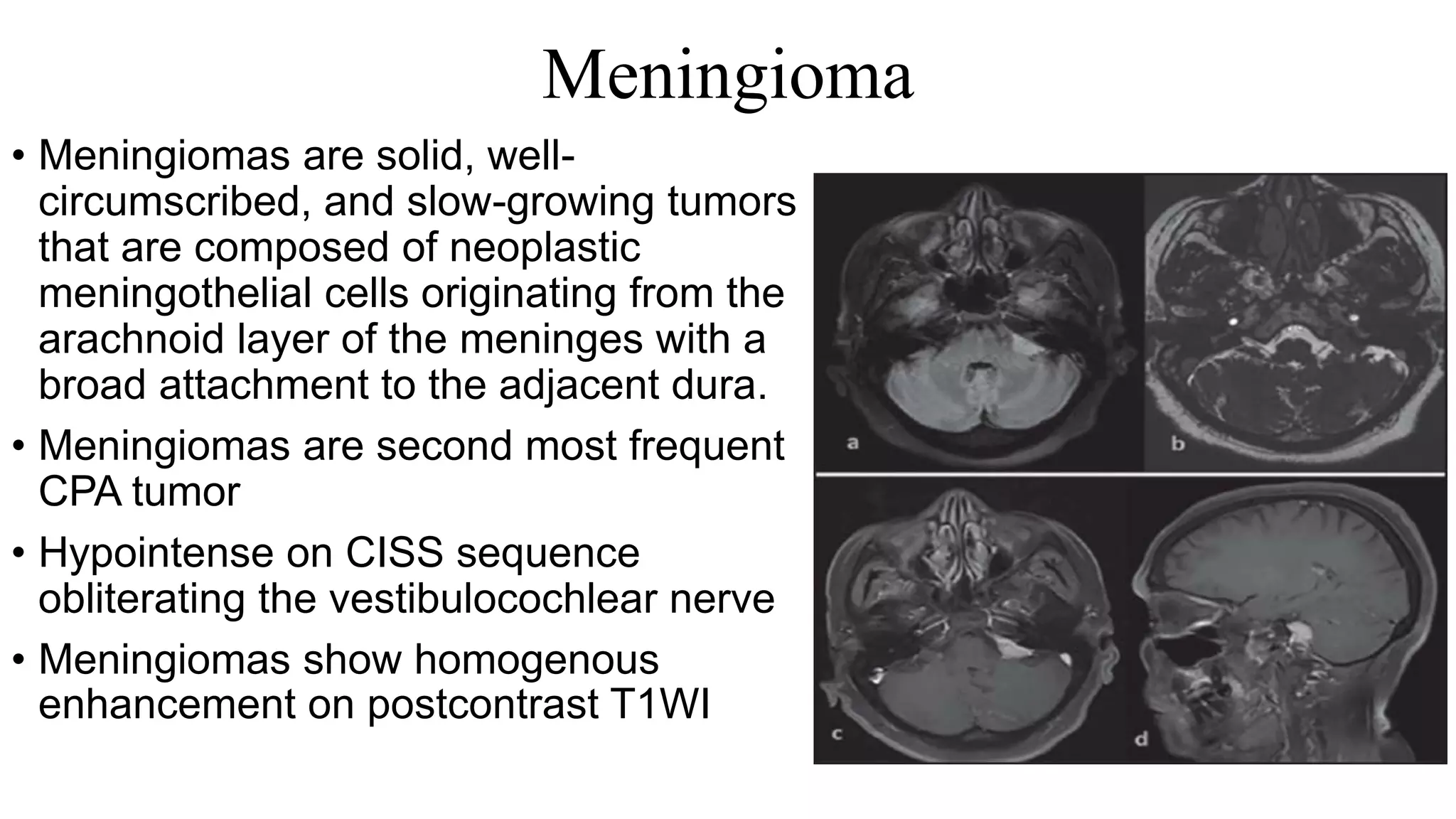
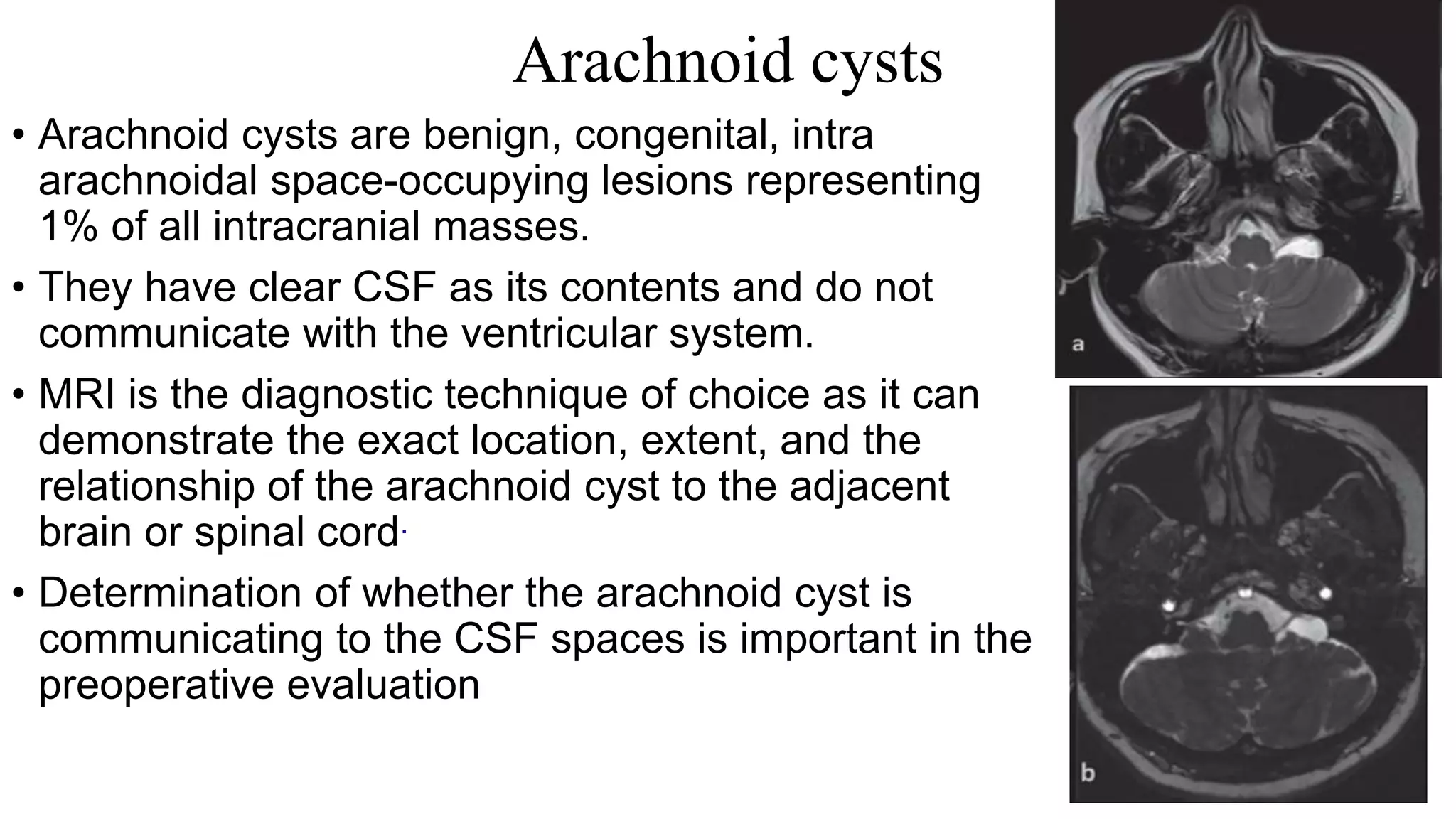
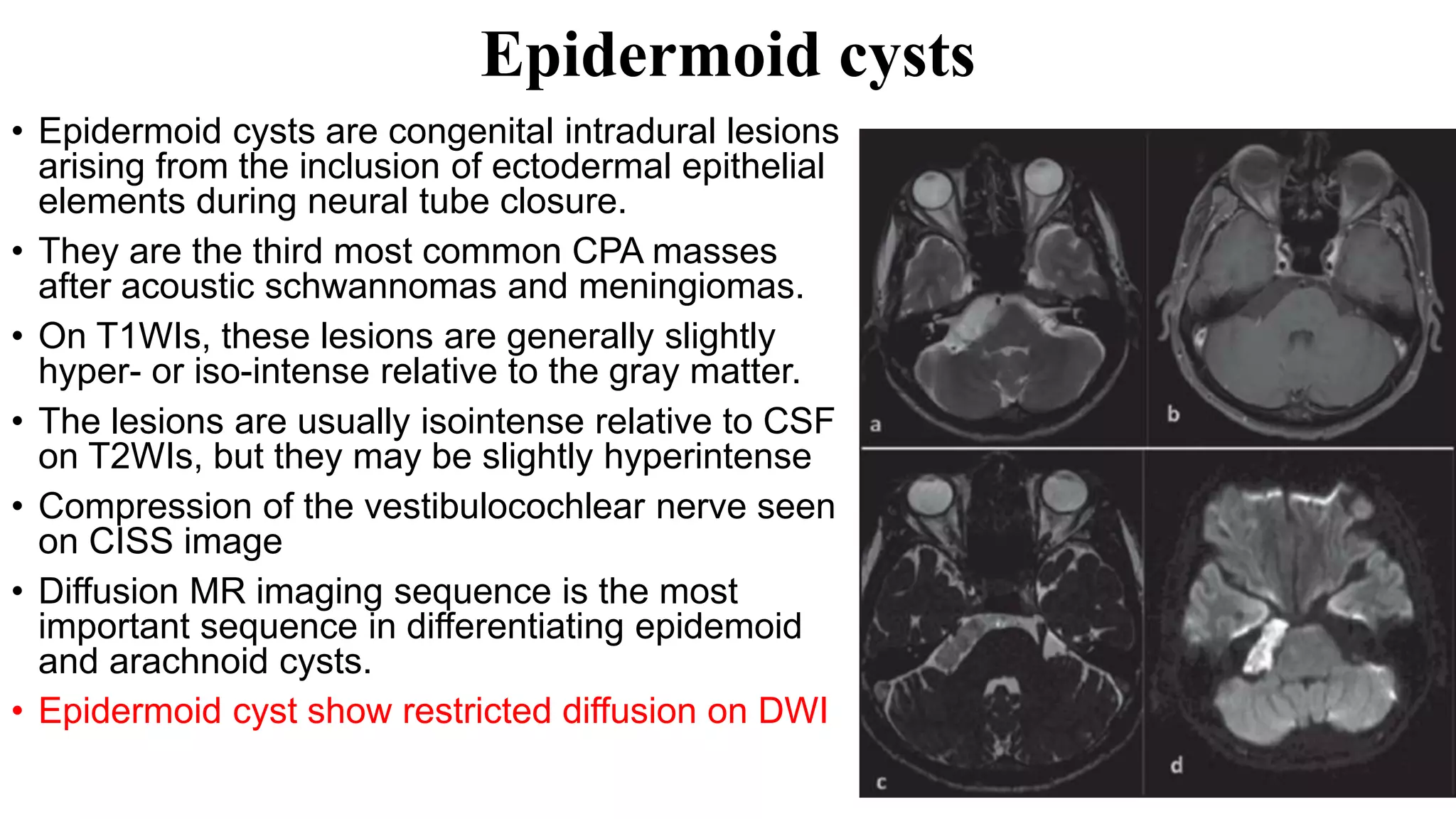
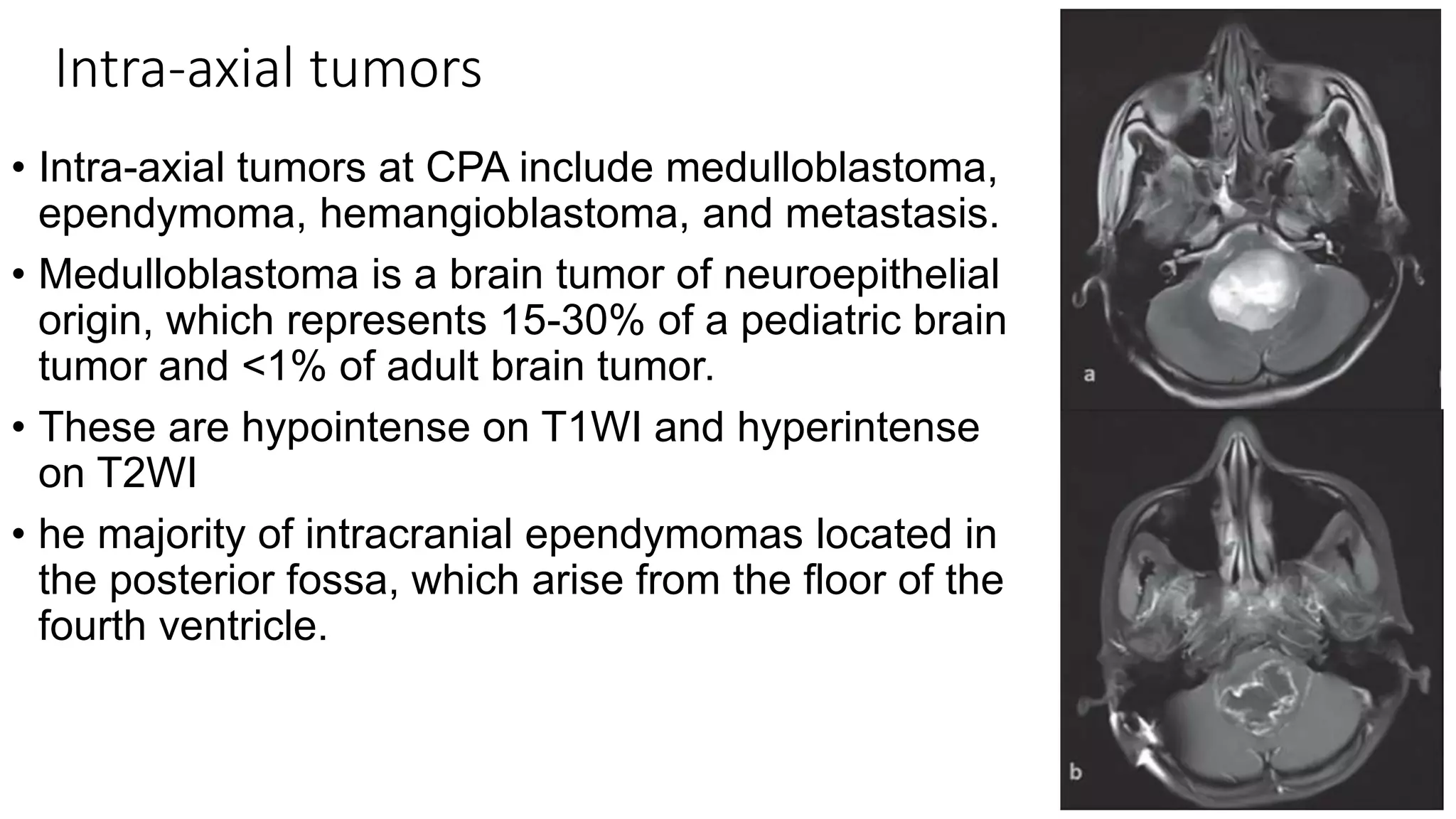
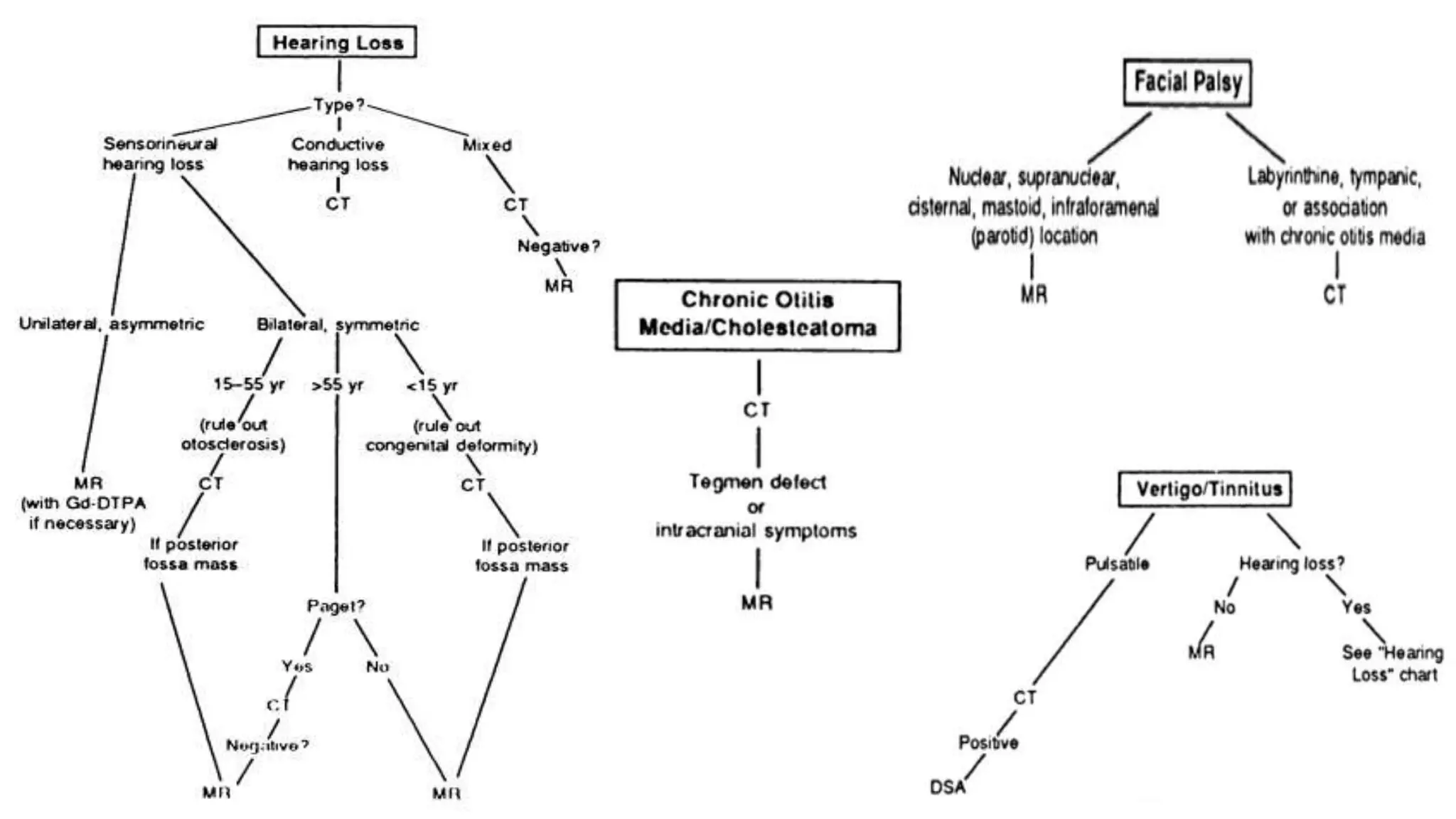
MRI is used to image the fluid spaces, vascular structures, and nerves of the inner ear. It can evaluate the oval and round windows, facial nerve, vestibulocochlear nerve, and identify pathologies like acoustic neuromas, Bell's palsy, vertigo, sensorineural hearing loss, tinnitus, Meniere's disease, inner ear anomalies, and cholesteatoma. Proper patient preparation and positioning is important for high quality MRI of the inner ear.