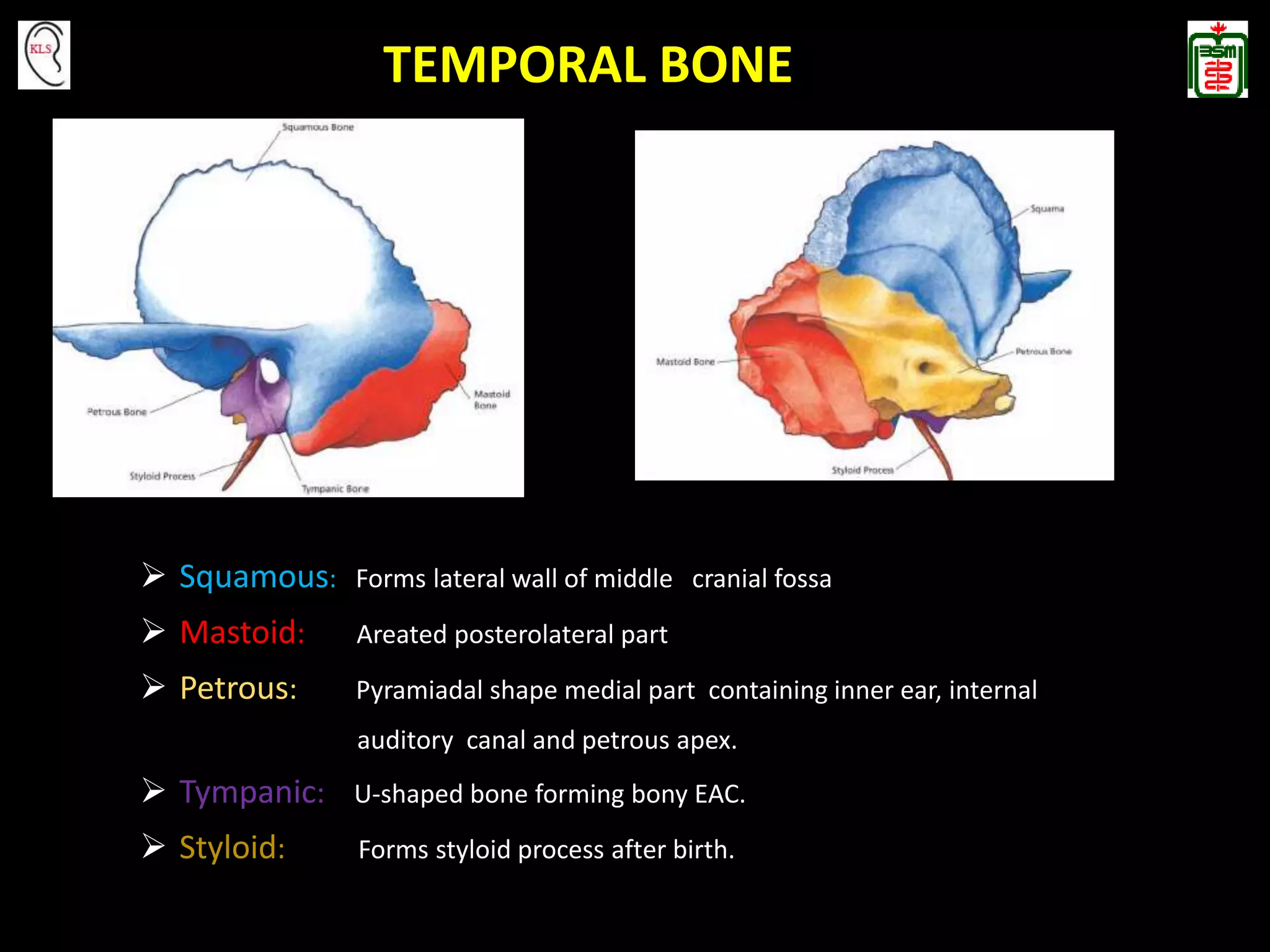
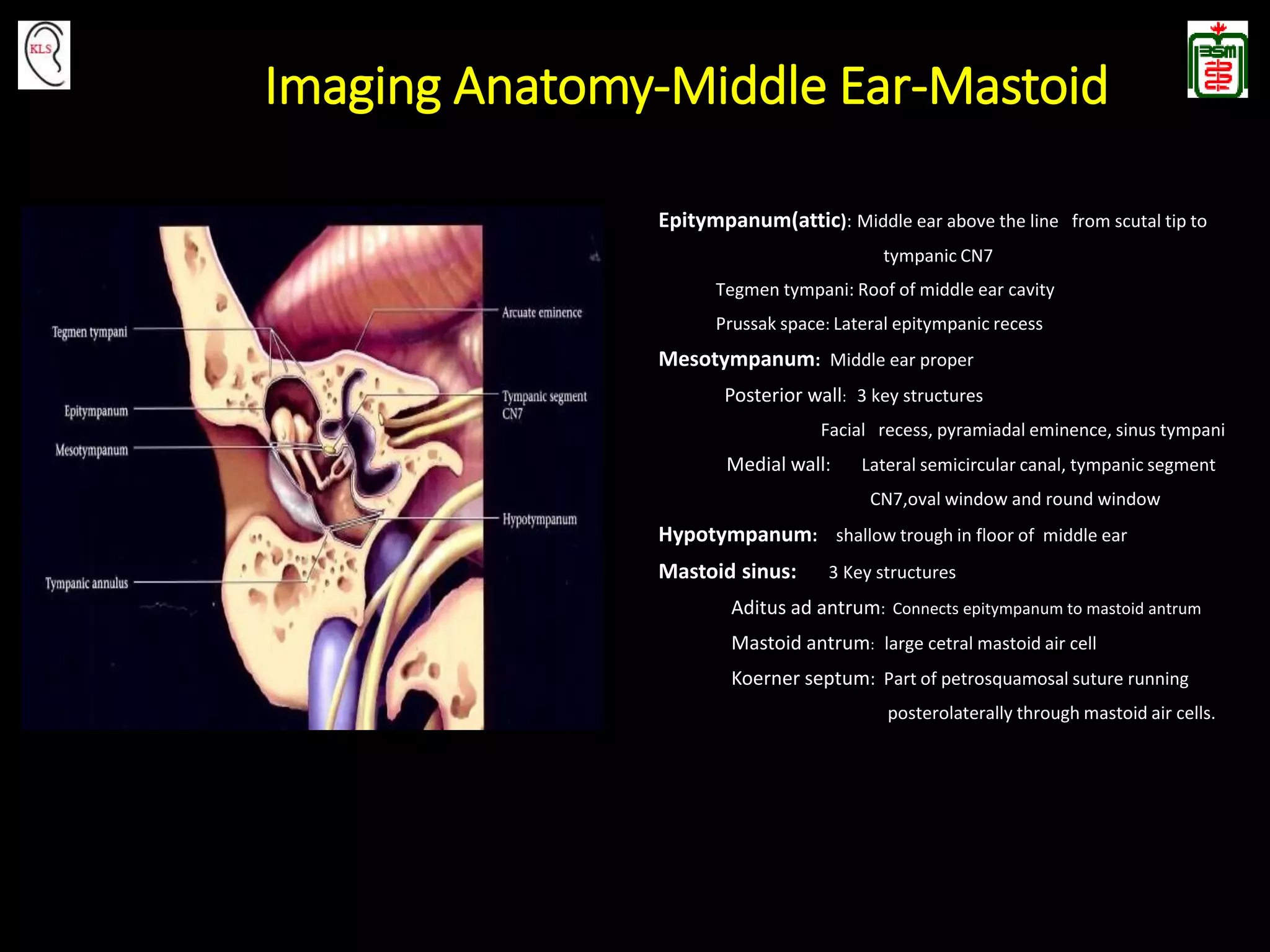
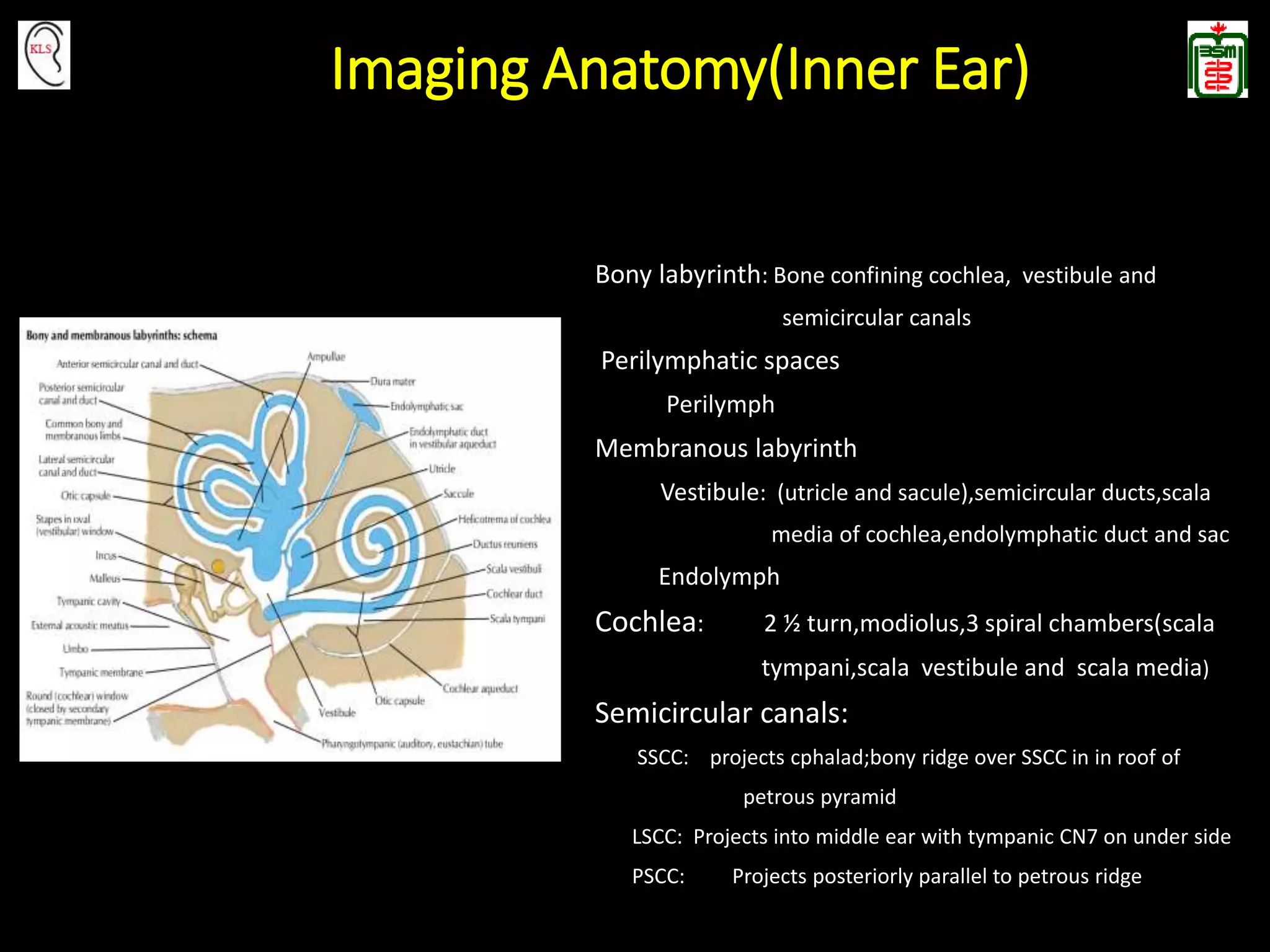
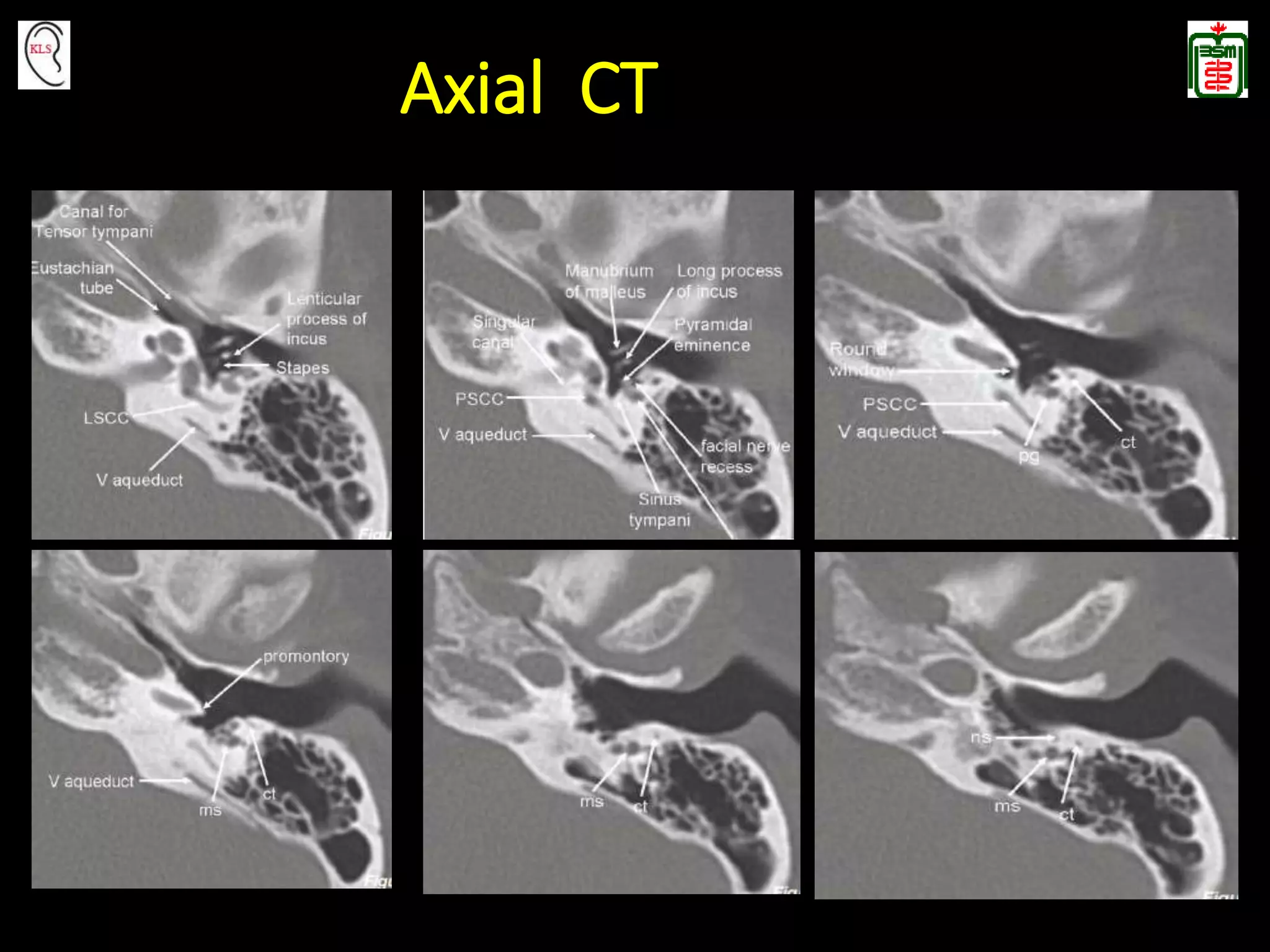
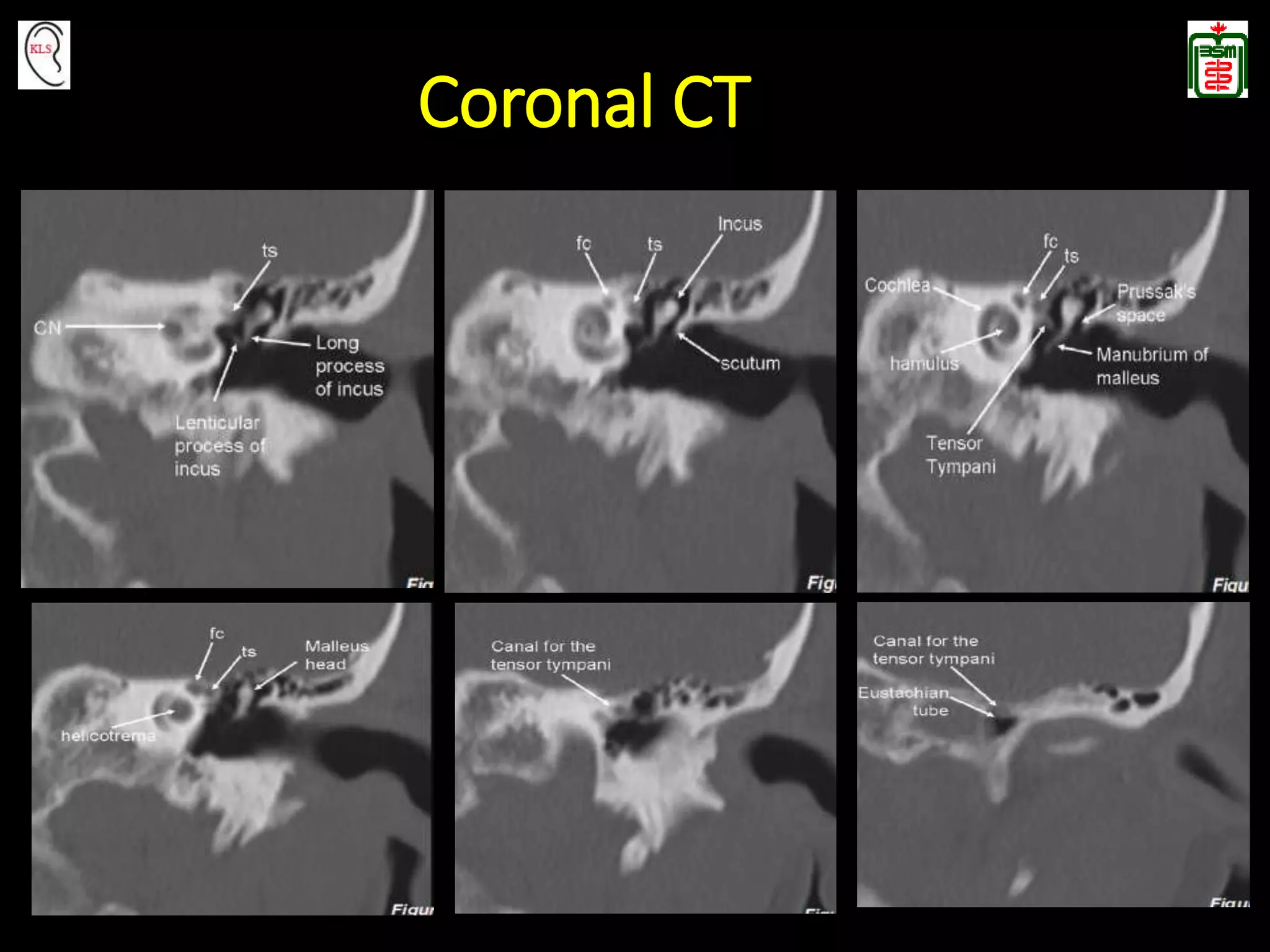
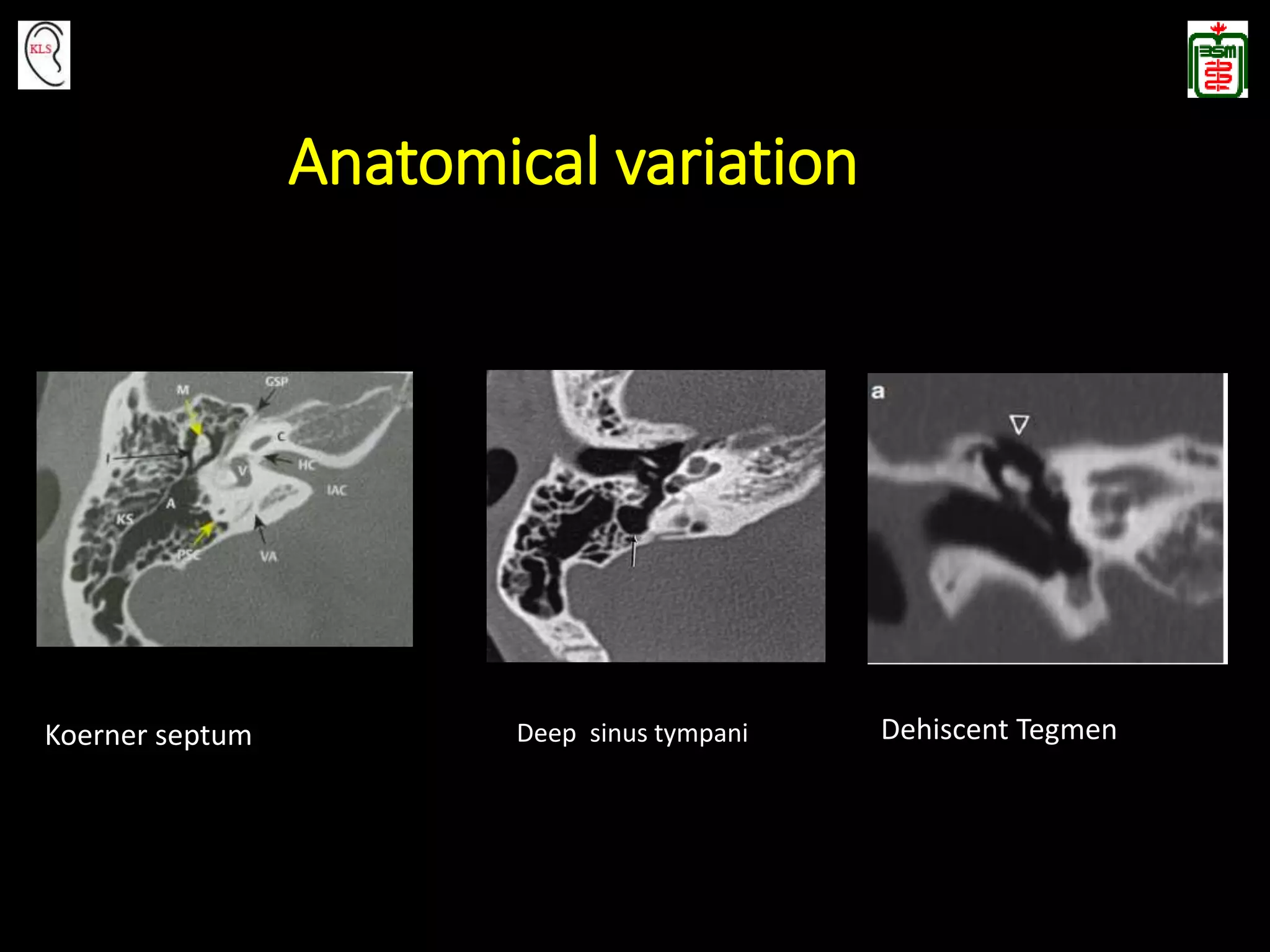
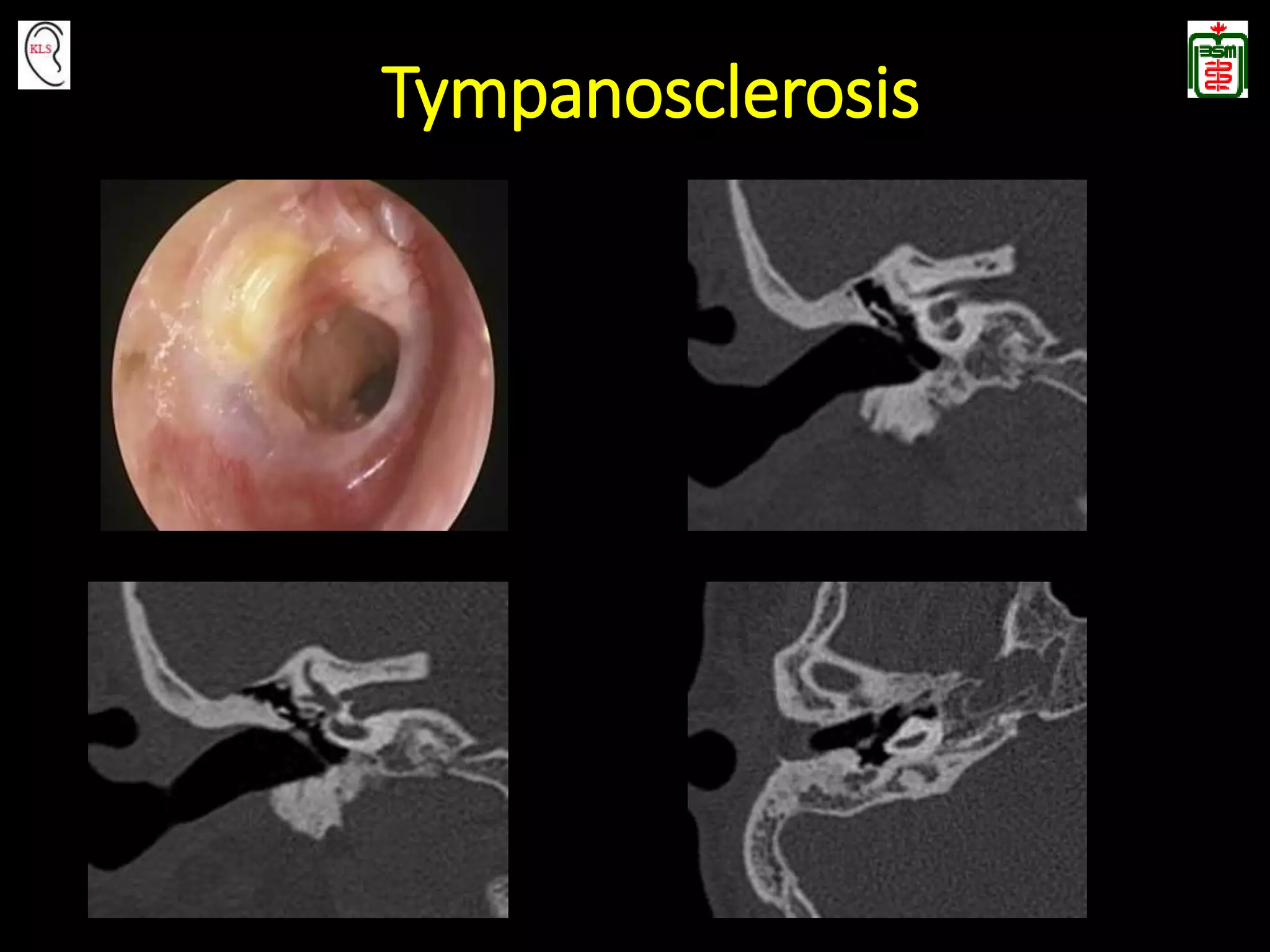
This document provides an overview of temporal bone anatomy and imaging techniques for evaluating the temporal bone. It describes the major components of the temporal bone including the external auditory canal, middle ear, inner ear, internal auditory canal, and surrounding bones. Imaging tools like CT and MRI are discussed along with techniques for each. Examples of normal anatomy, anatomical variations, and various pathological conditions are shown through CT and MRI images with explanations. The importance of understanding temporal bone imaging for otologists and radiologists is emphasized to accurately diagnose and treat temporal bone diseases.