1) Money refers to anything that is generally accepted as payment for goods and services or debt repayment. The document defines related terms like wealth, income, stock, and flow.
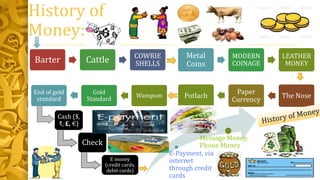
2) The functions of money are discussed - as a medium of exchange, unit of account, store of value, and standard of deferred payment. The history and evolution of money is also outlined, from barter systems to modern digital payments.
3) The advantages and disadvantages of barter systems are compared. Characteristics of good forms of money are defined as portable, acceptable, durable, divisible, scarce, recognizable, and uniform. Works cited in MLA format are listed at the end.