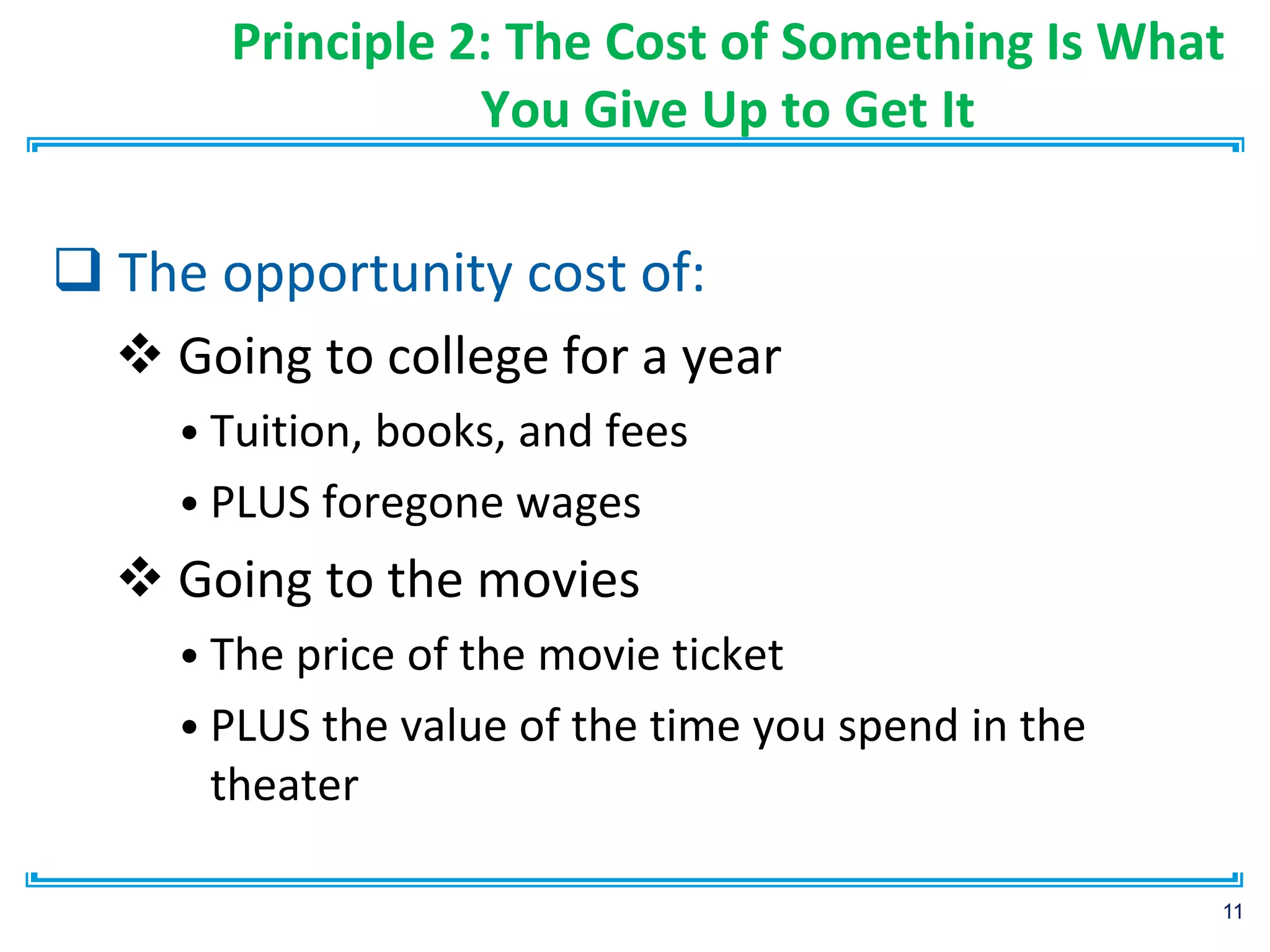
This document outlines 10 principles of economics from the textbook "Principles of Economics" by N. Gregory Mankiw. It discusses fundamental lessons about individual decision making, interactions among people, and the economy as a whole. Specifically, it summarizes that people face trade-offs and respond to incentives; markets are generally good but governments can remedy failures; productivity drives living standards; and inflation results from increasing the money supply, creating short-run trade-offs with unemployment.