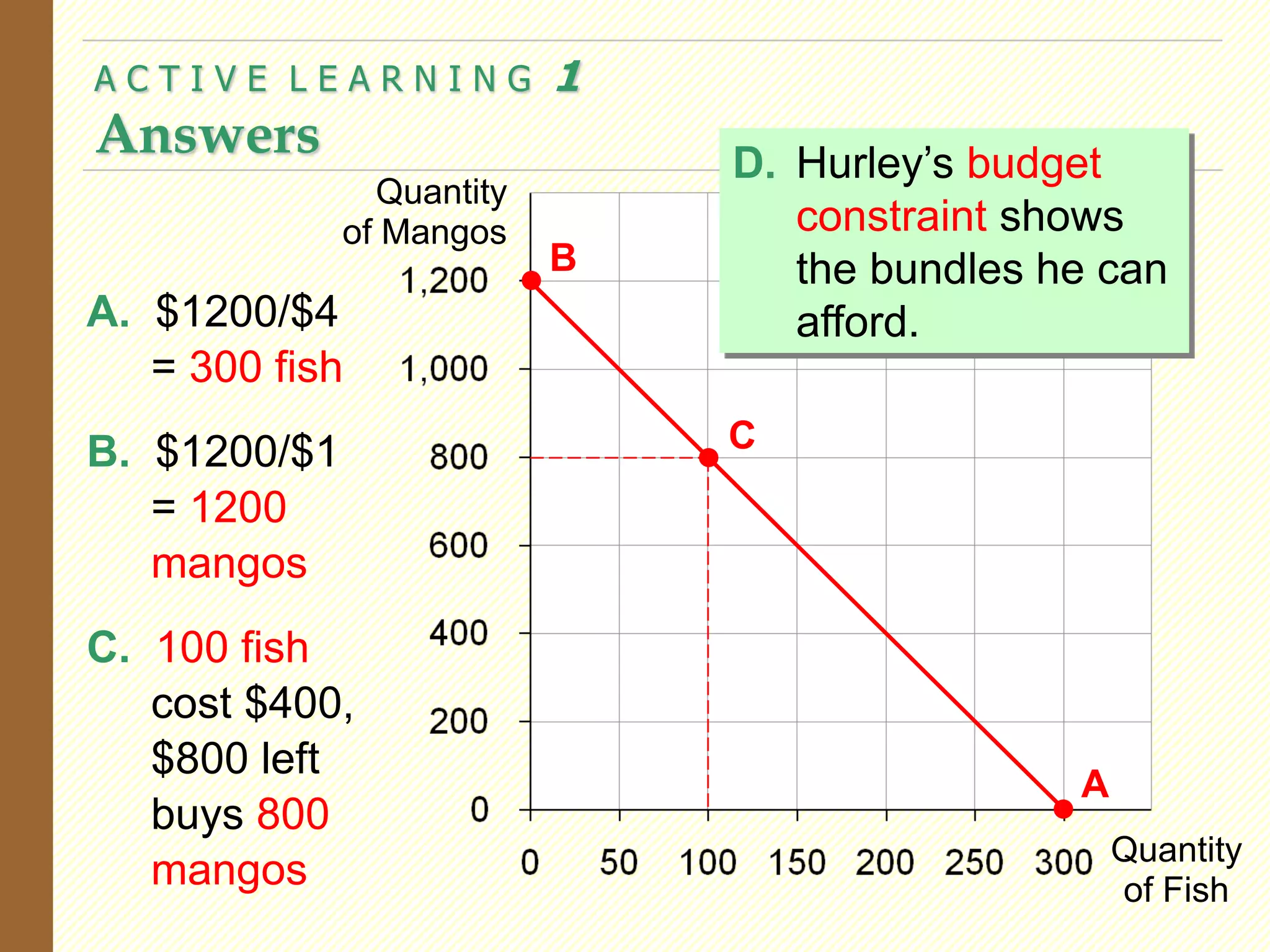
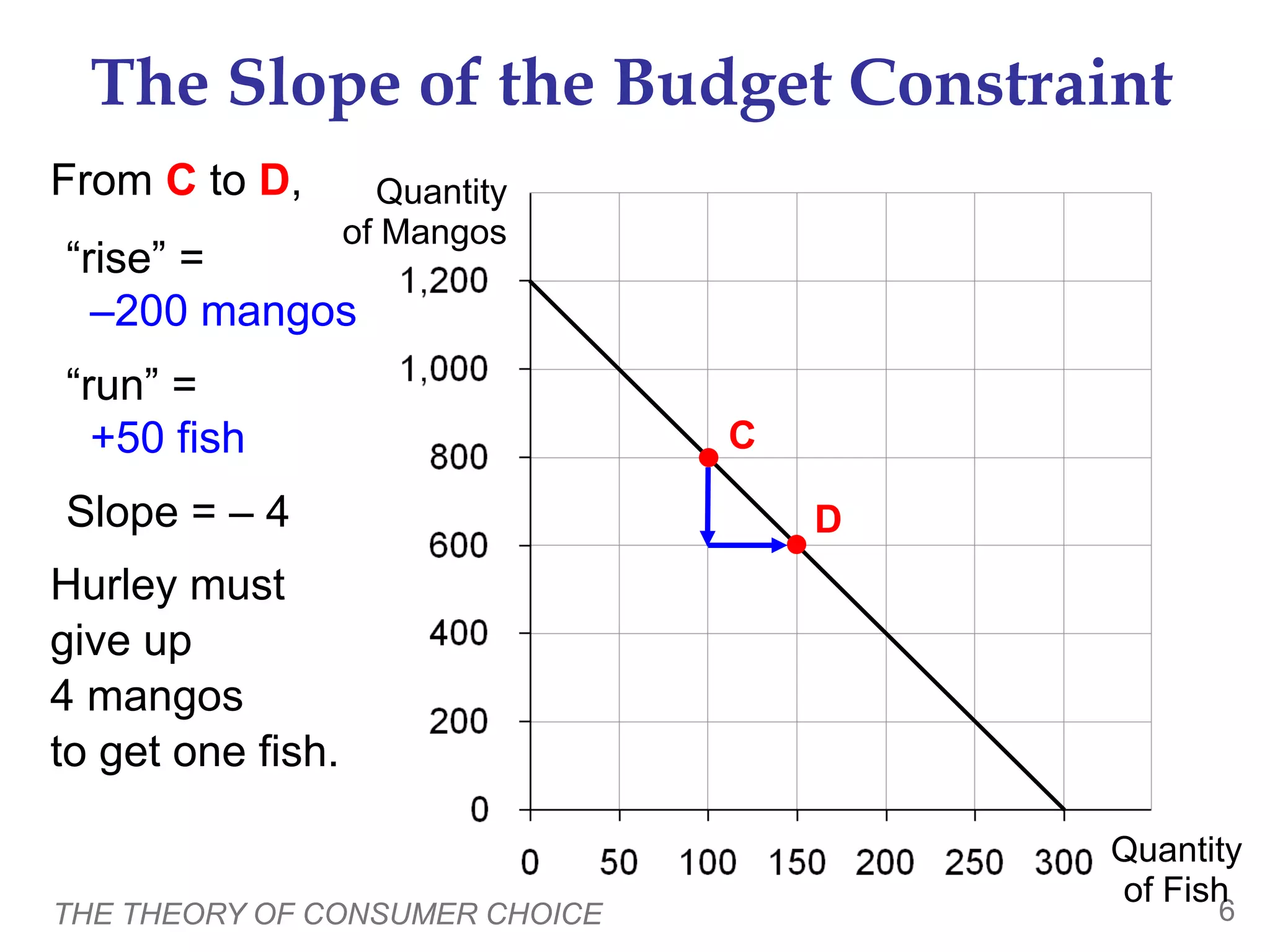
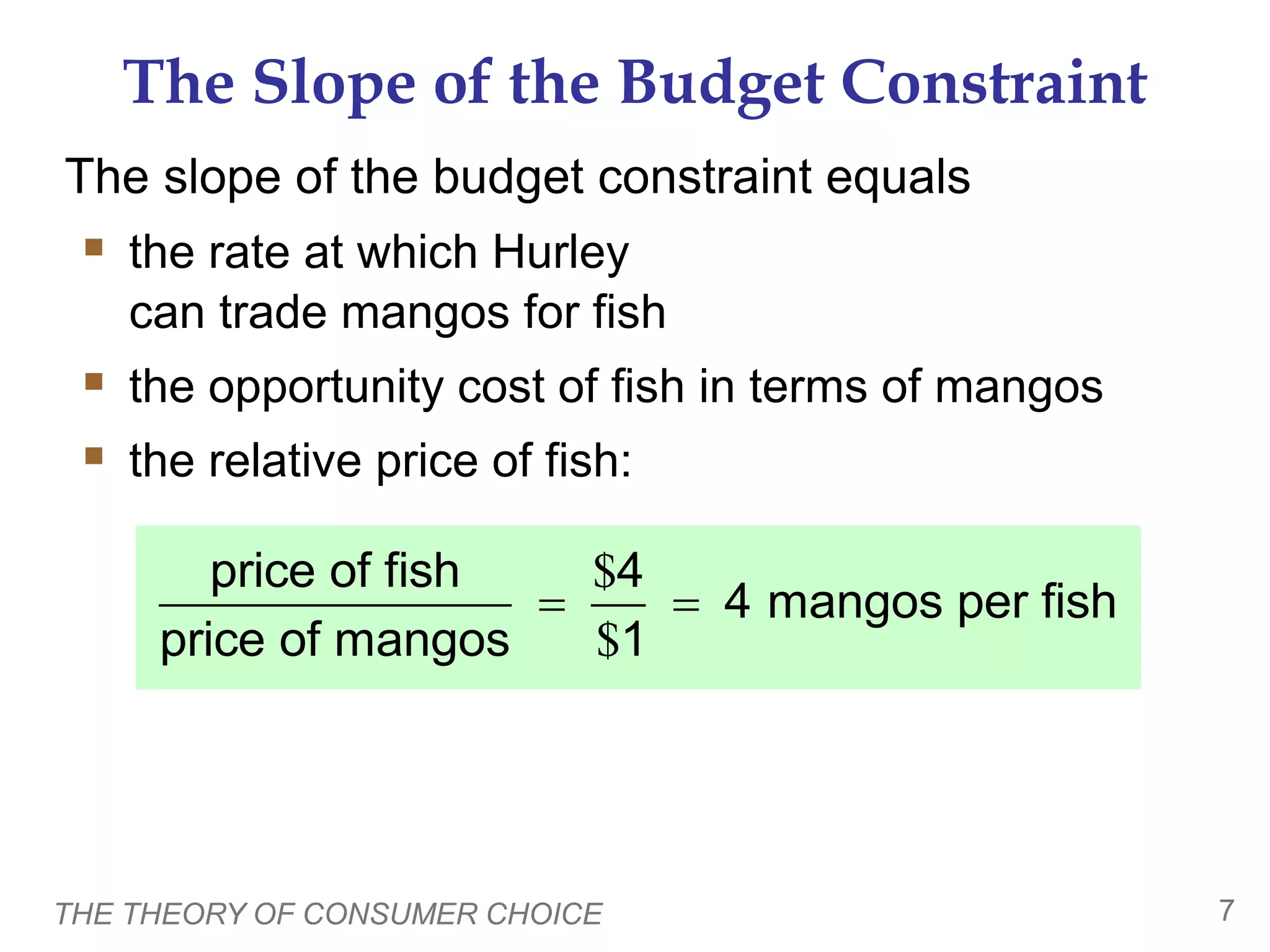
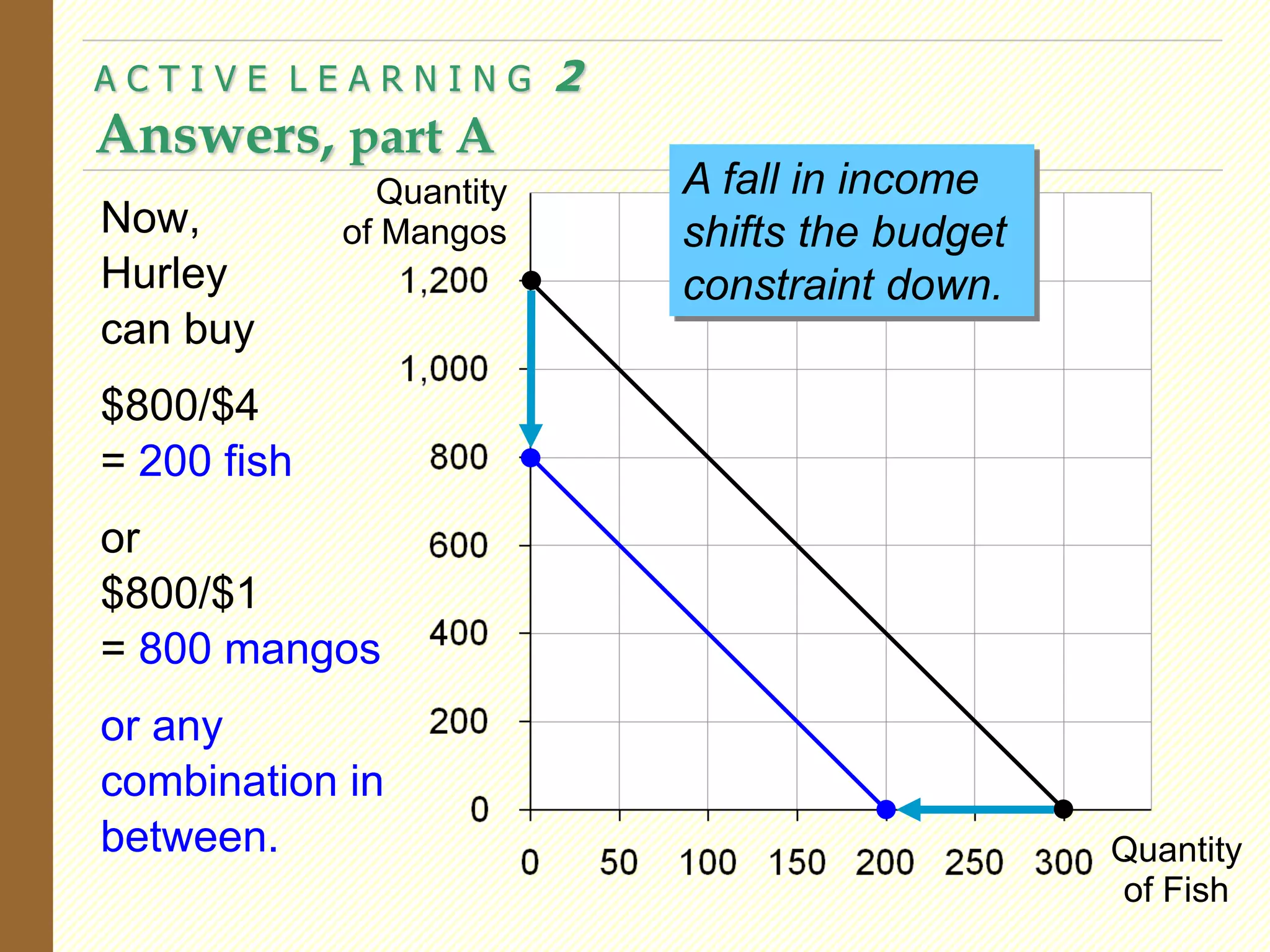
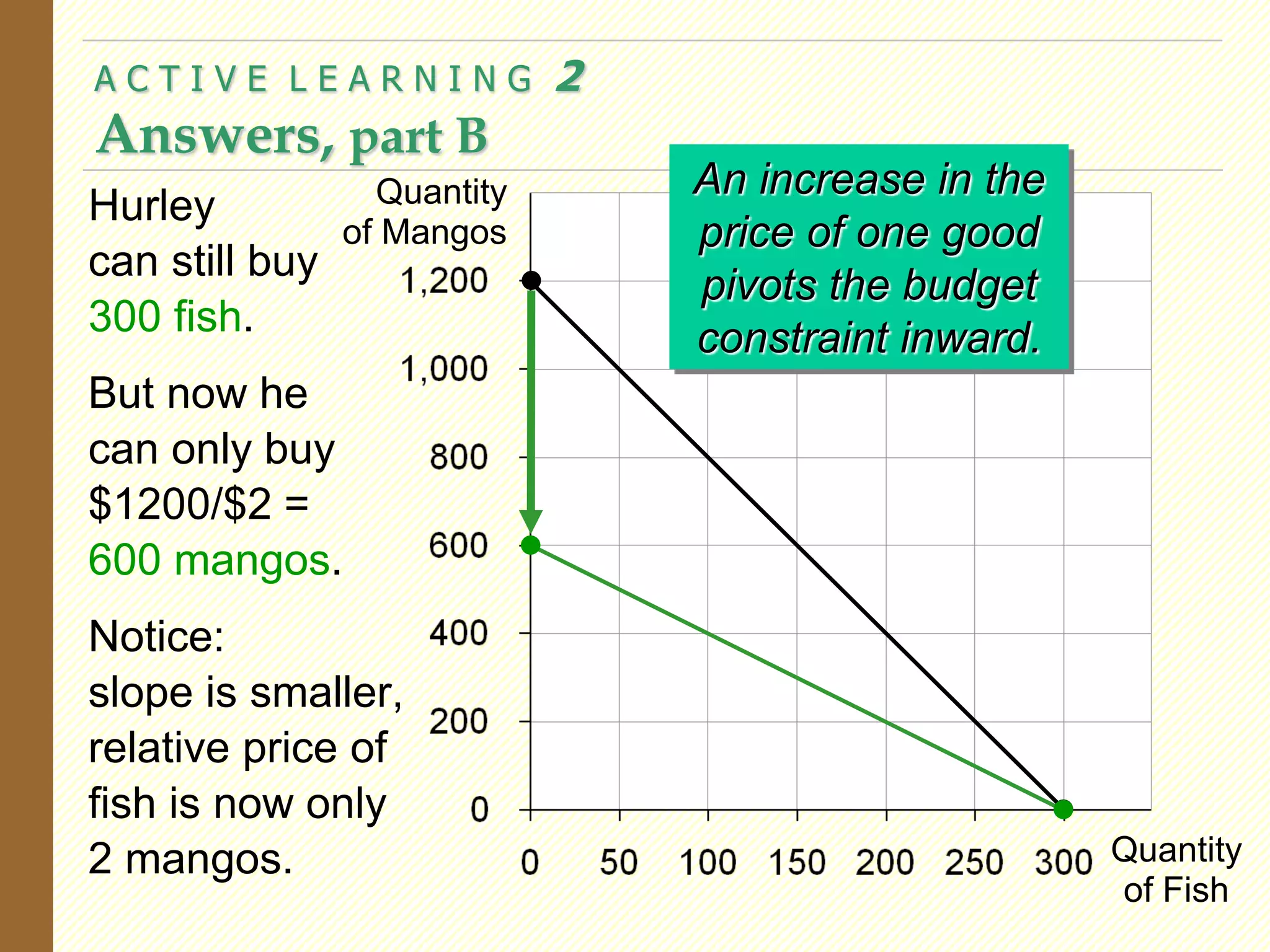
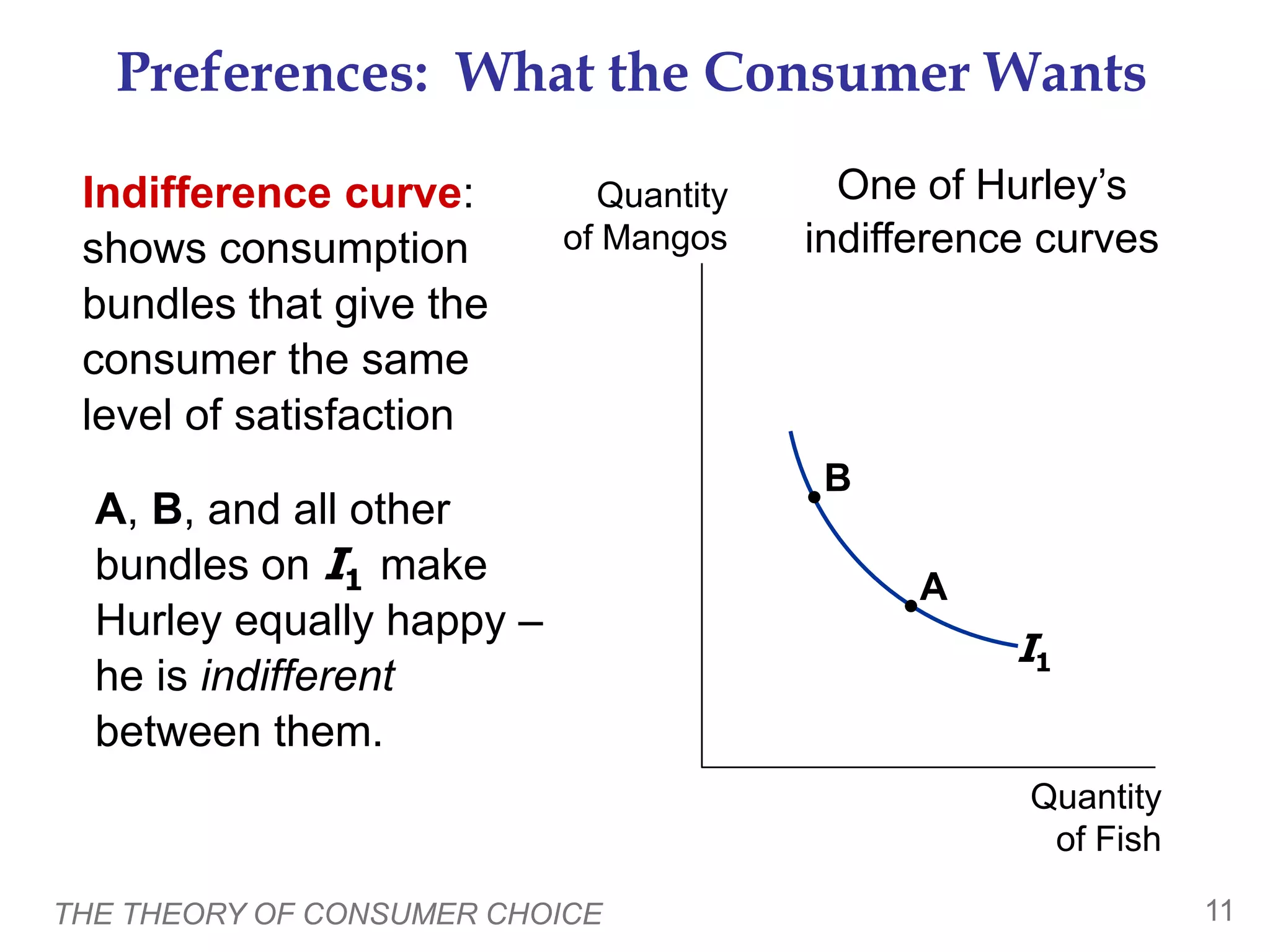
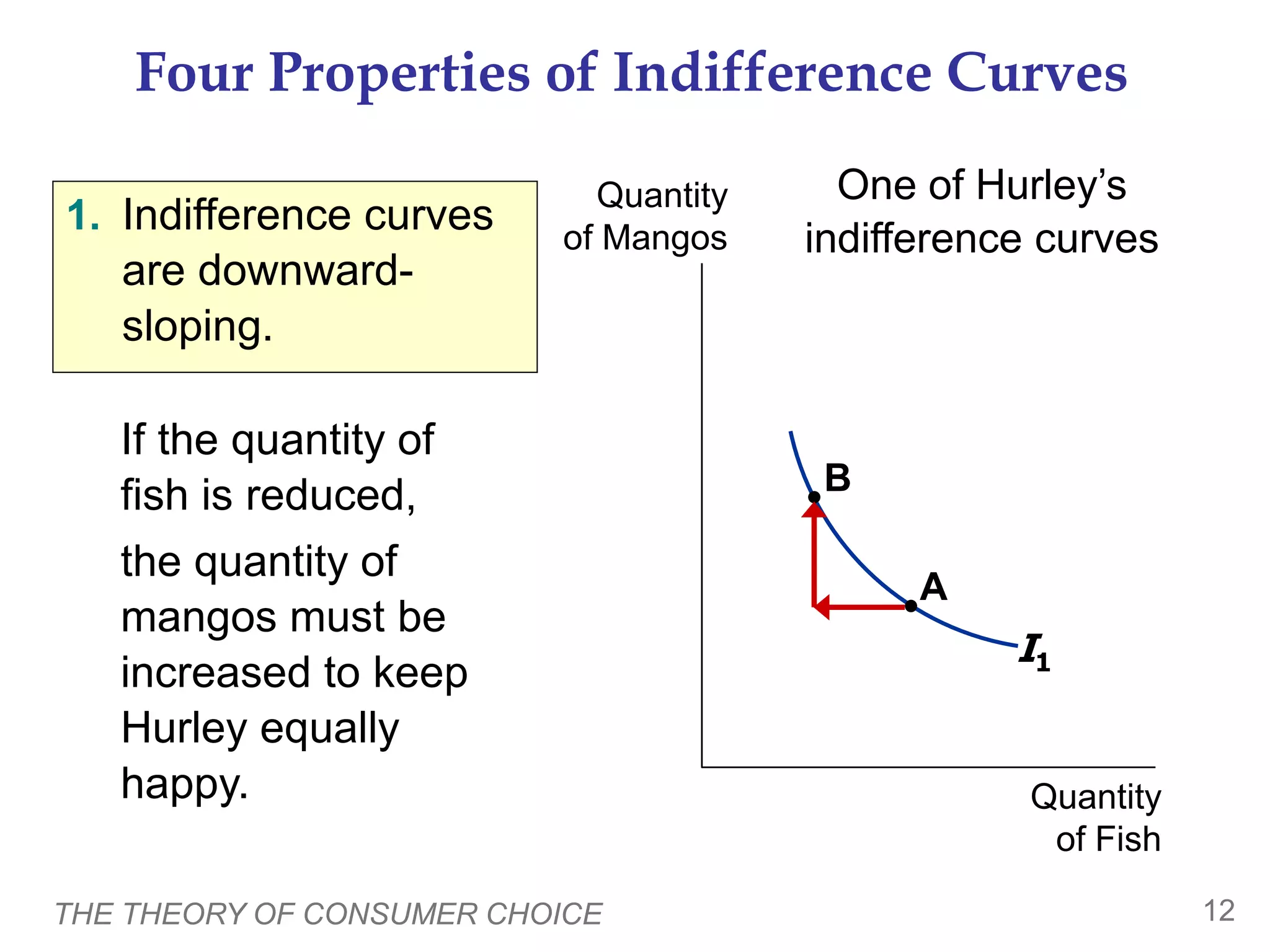
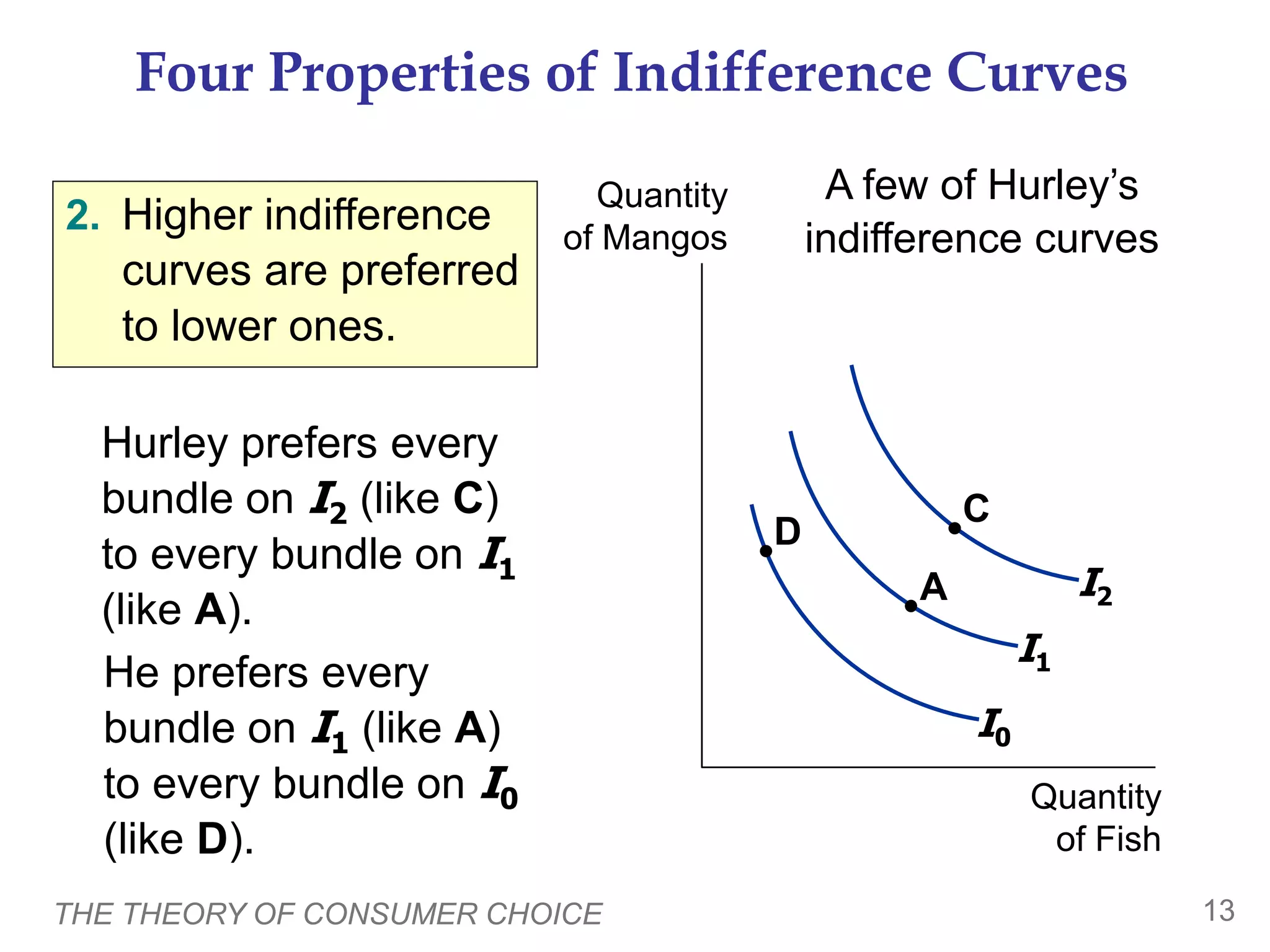
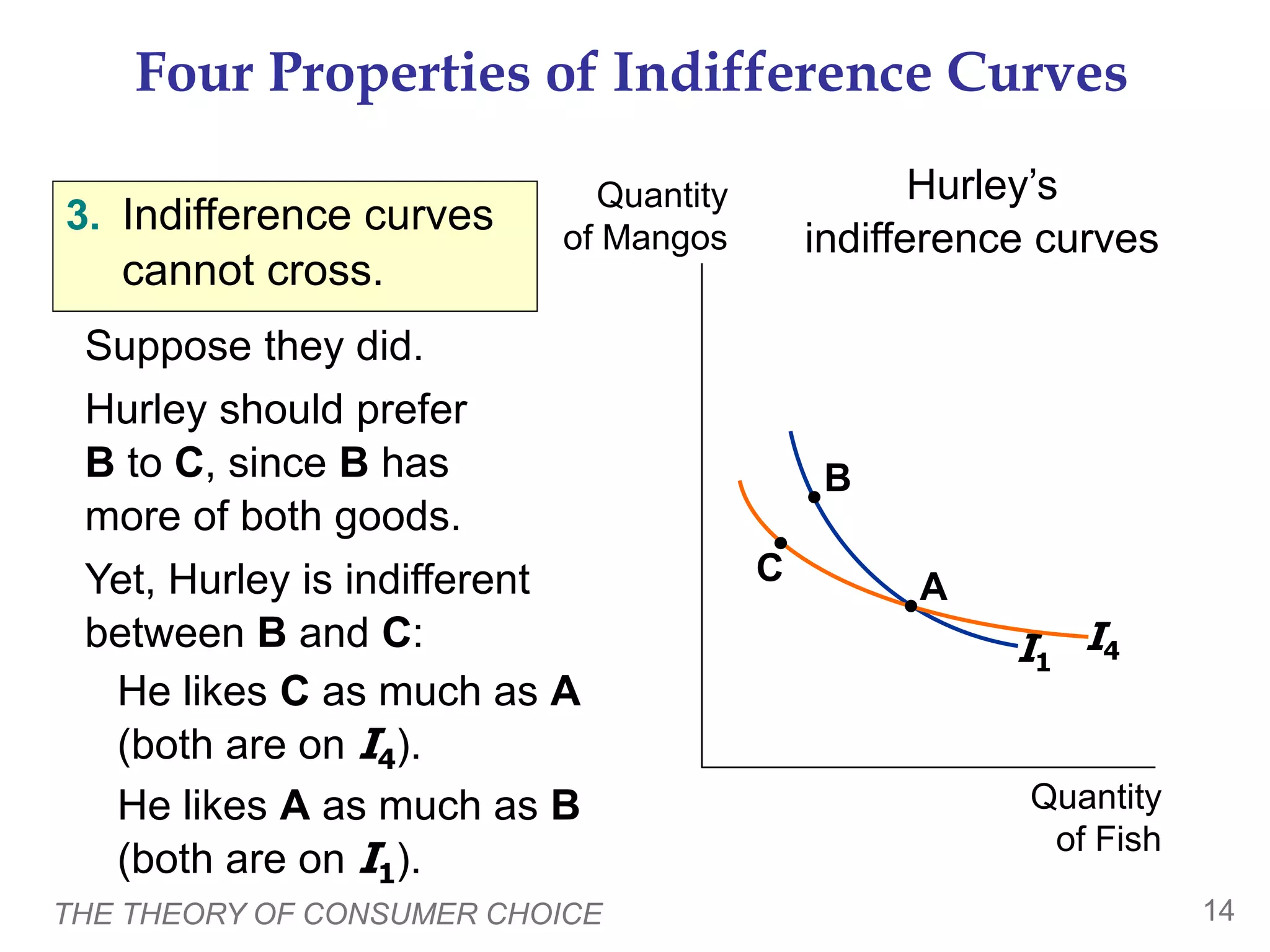
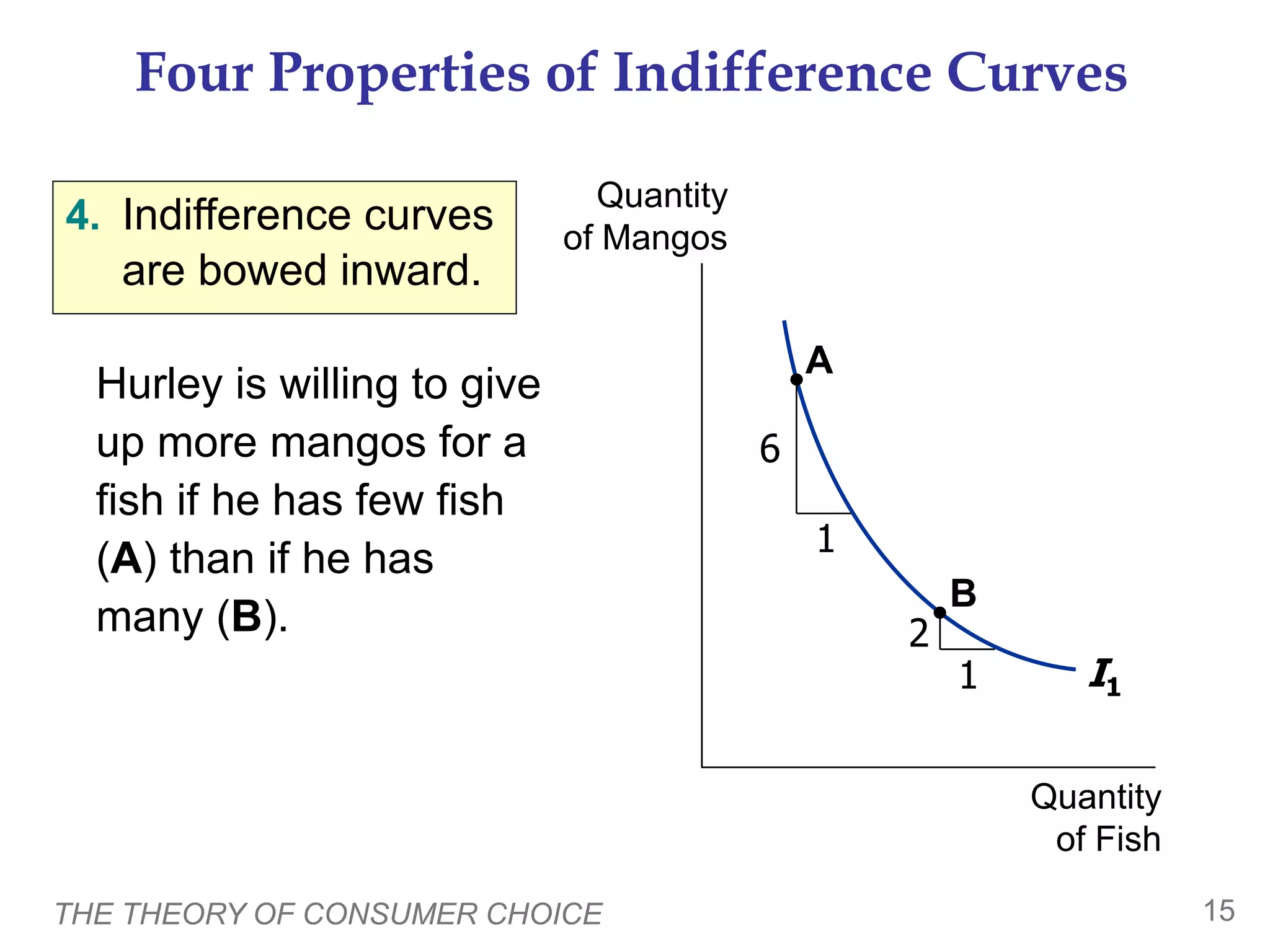
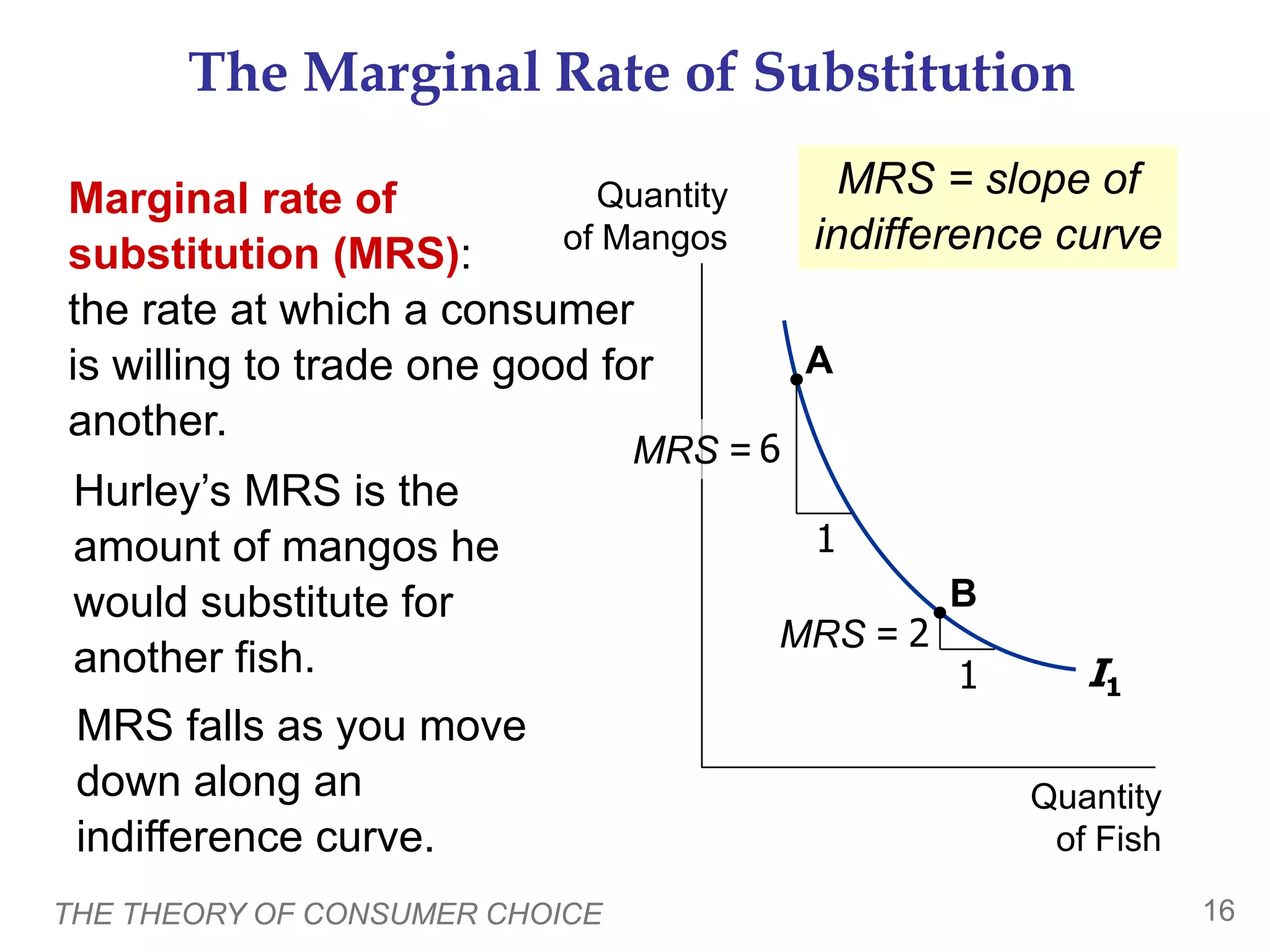
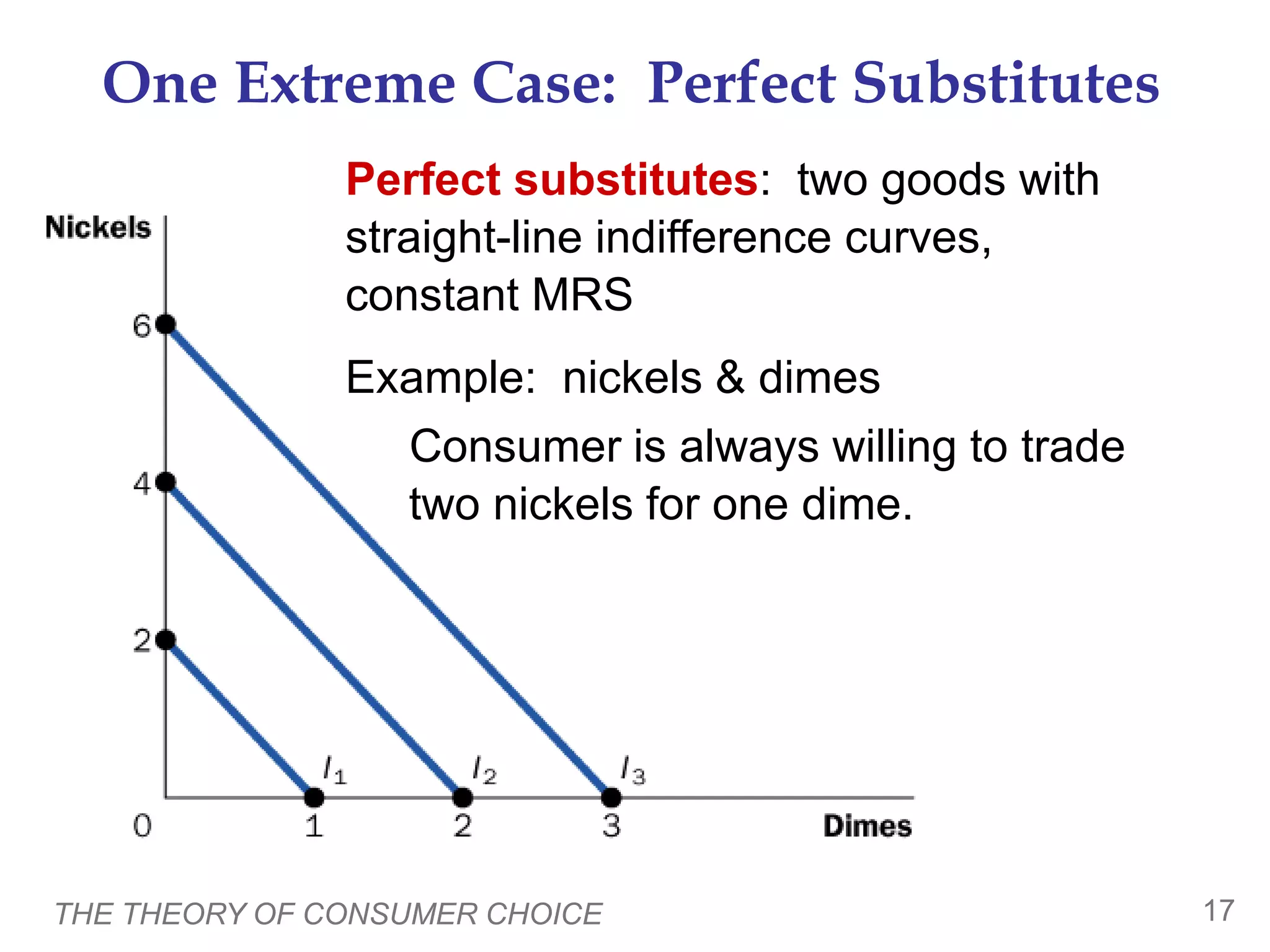
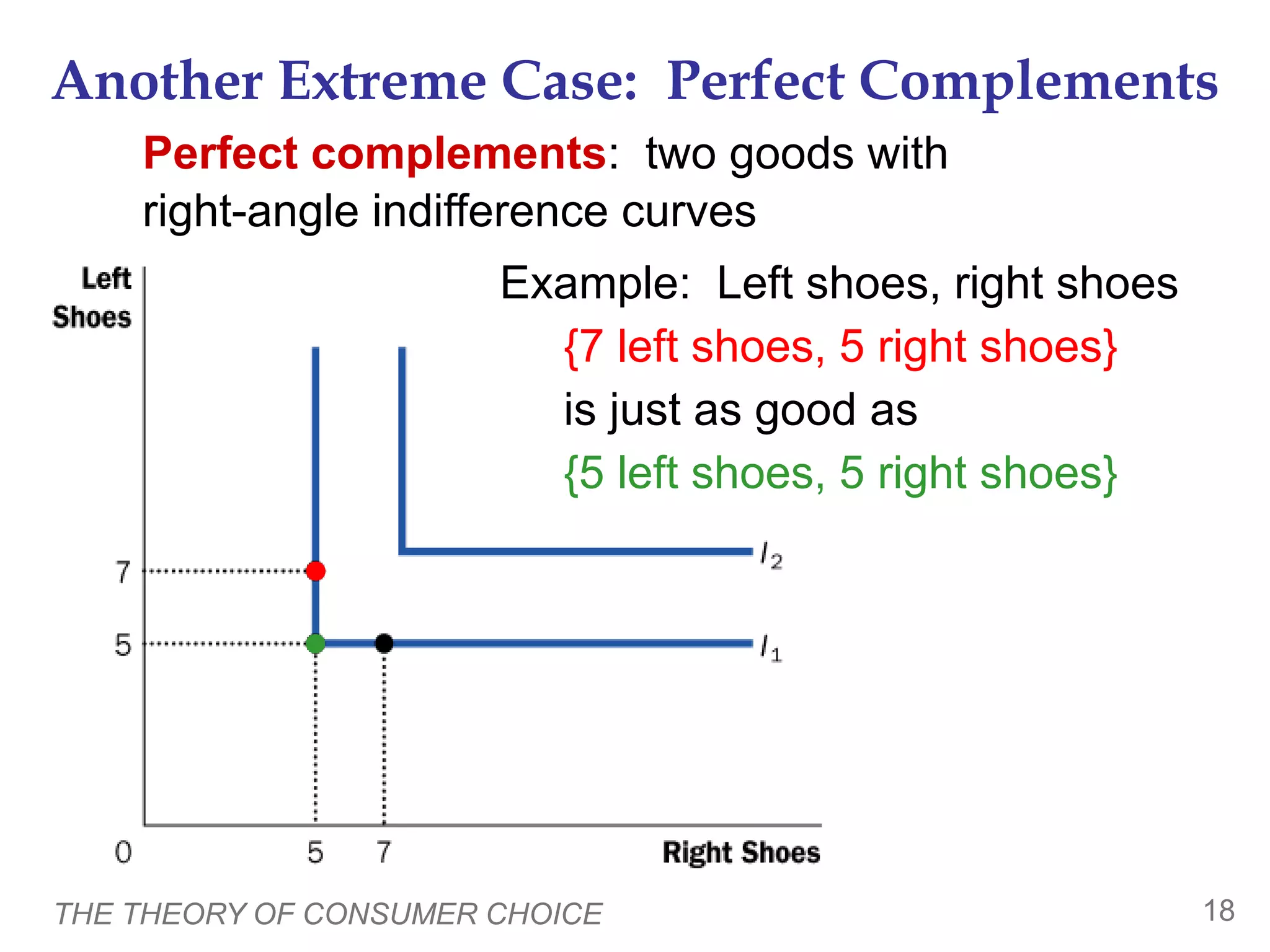
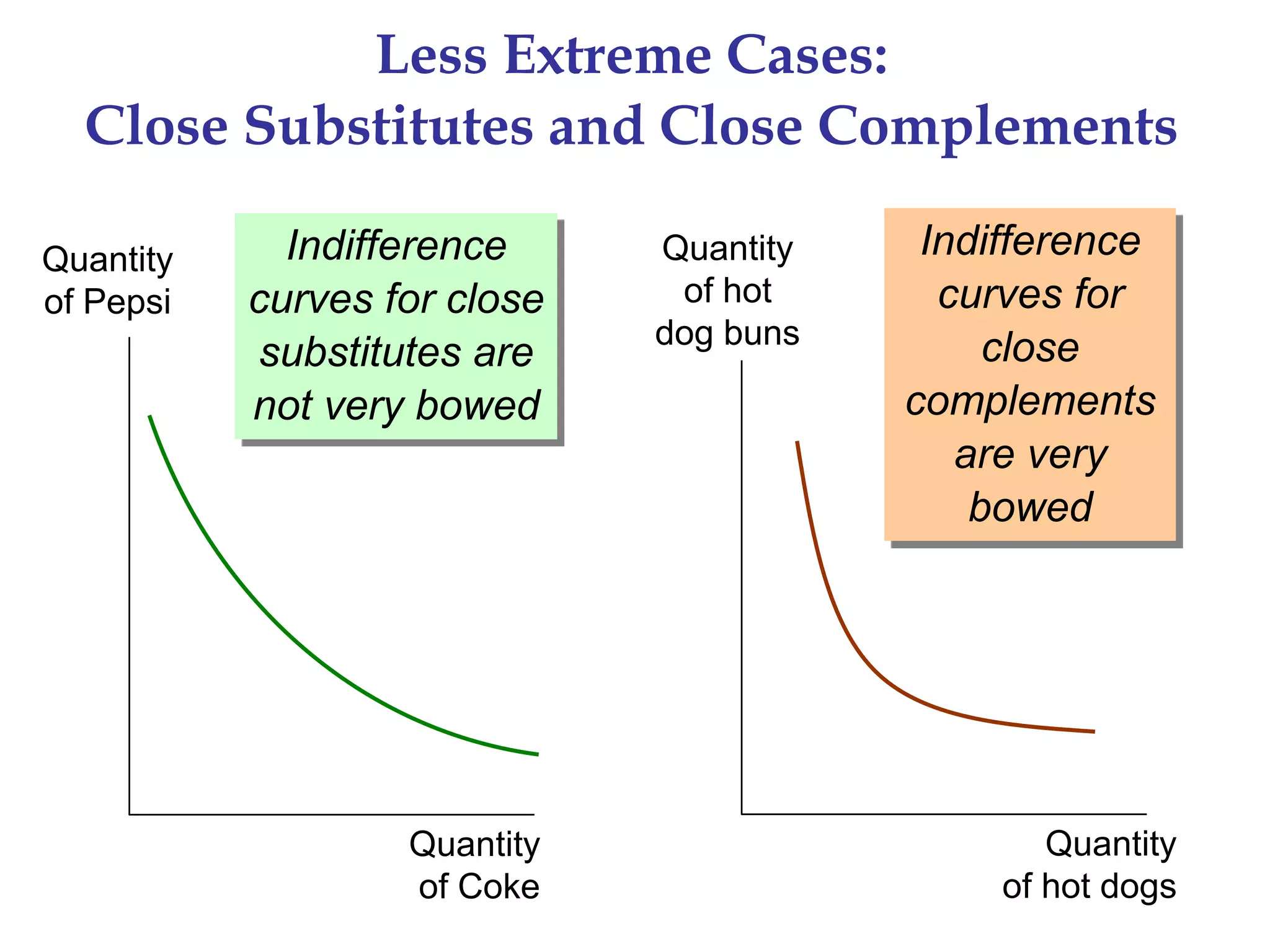
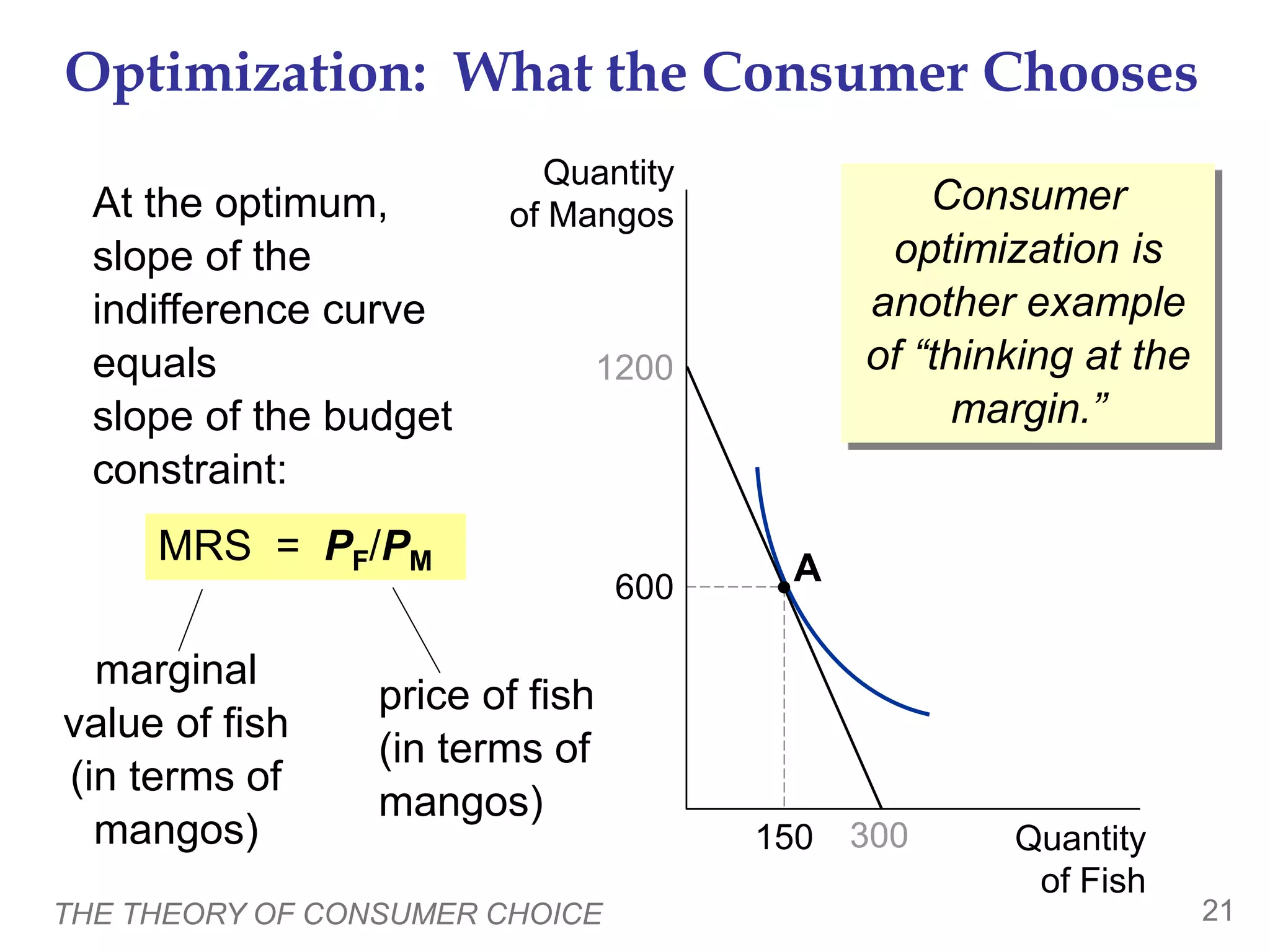
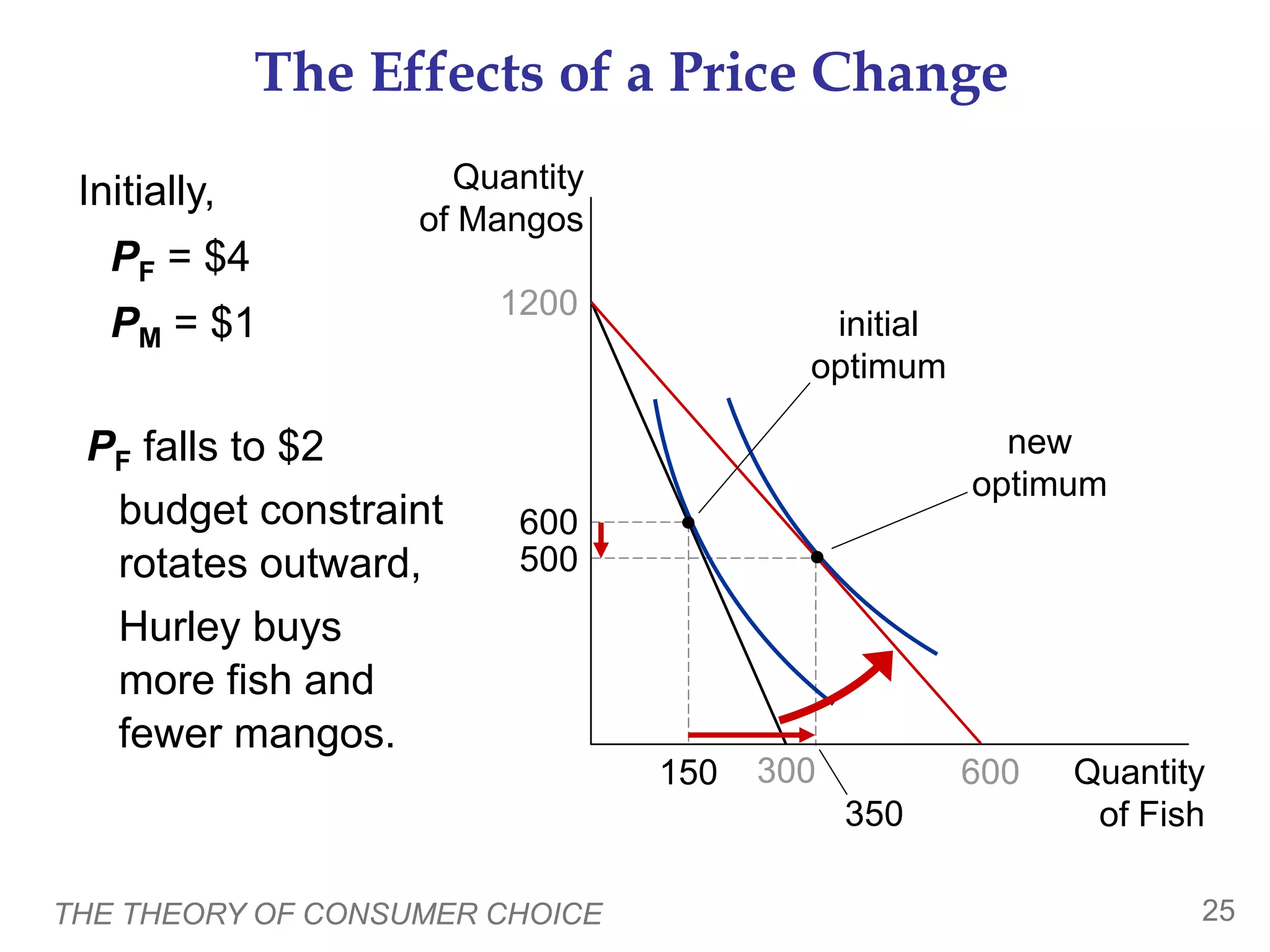
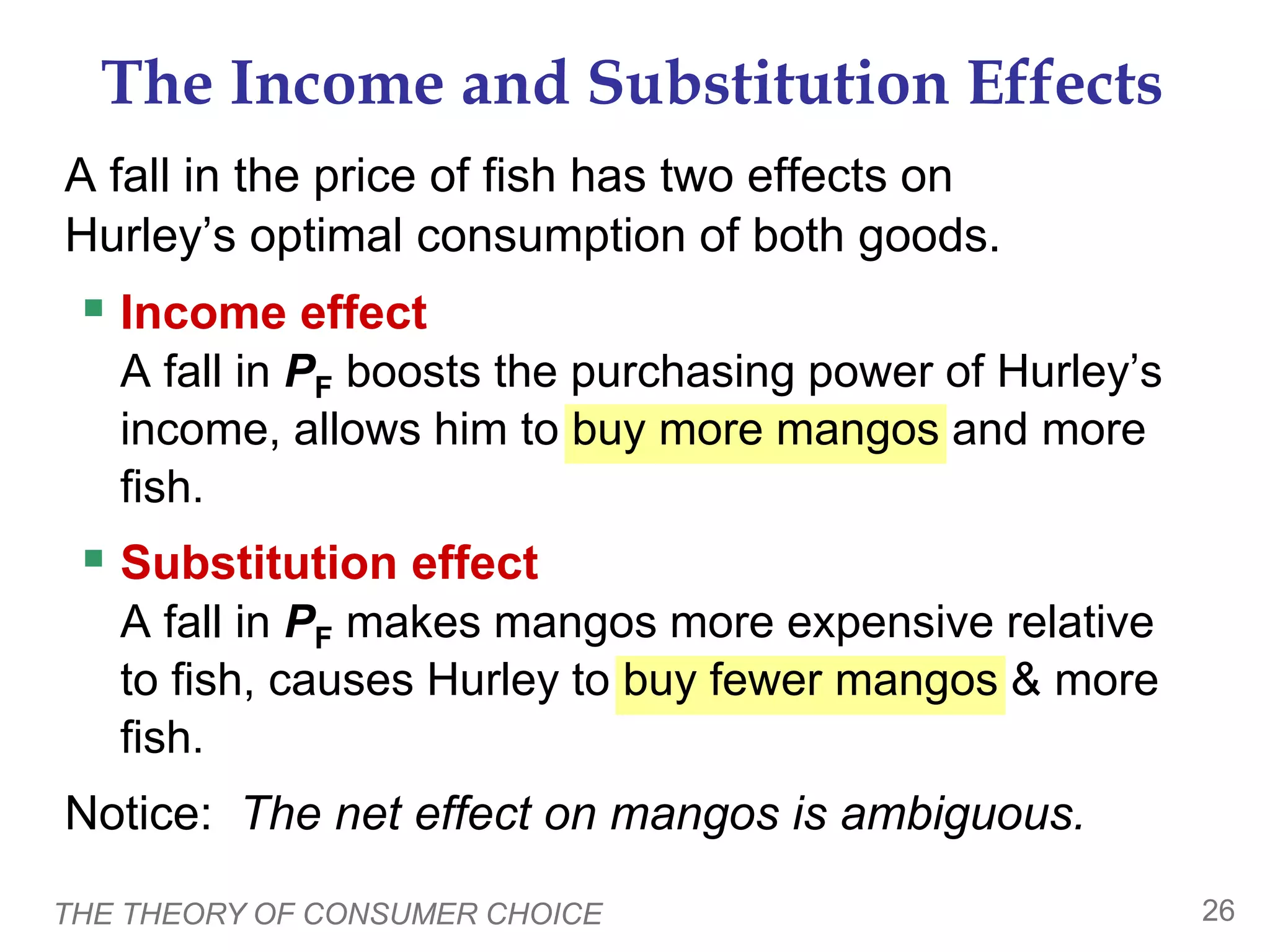
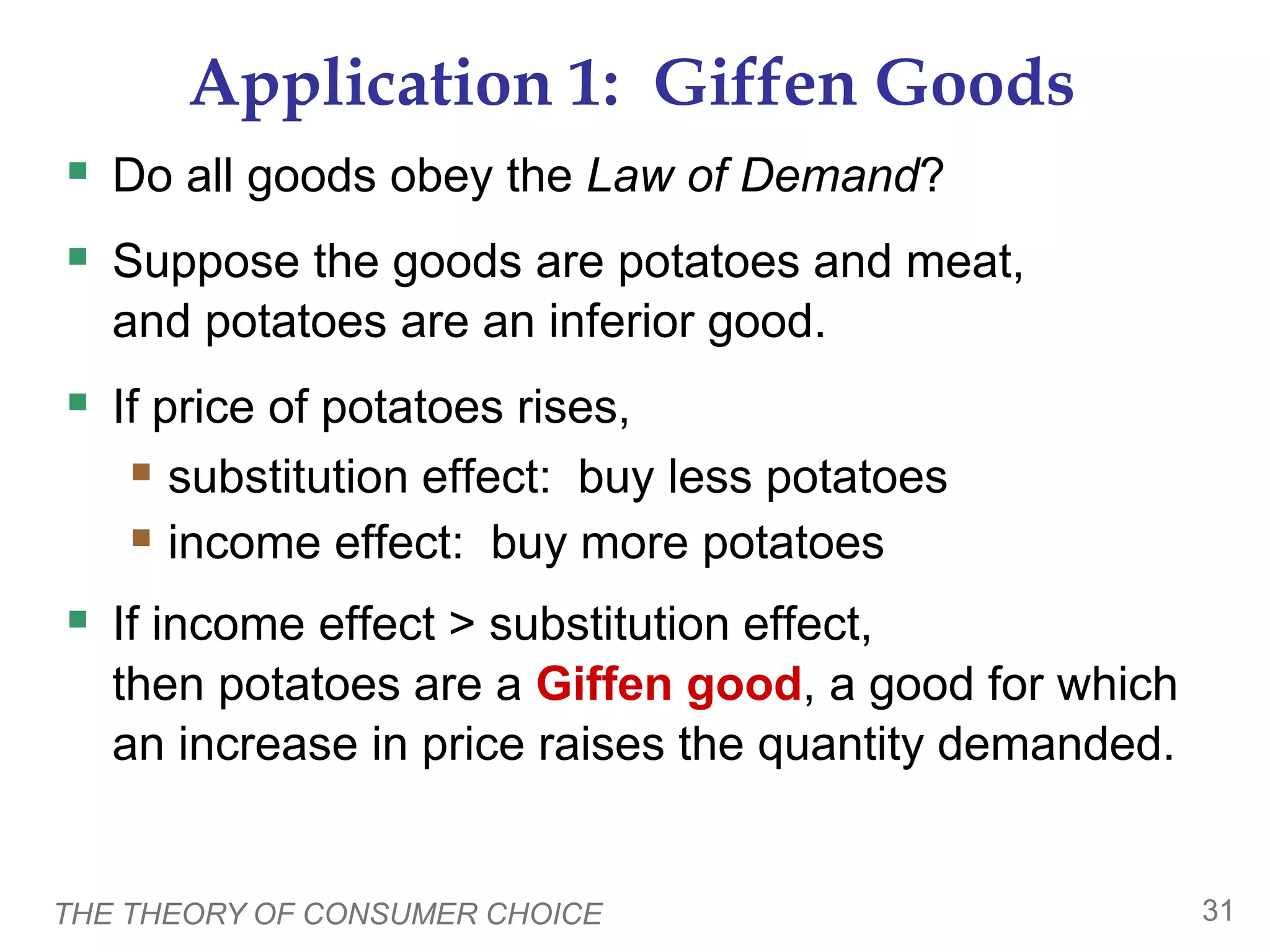
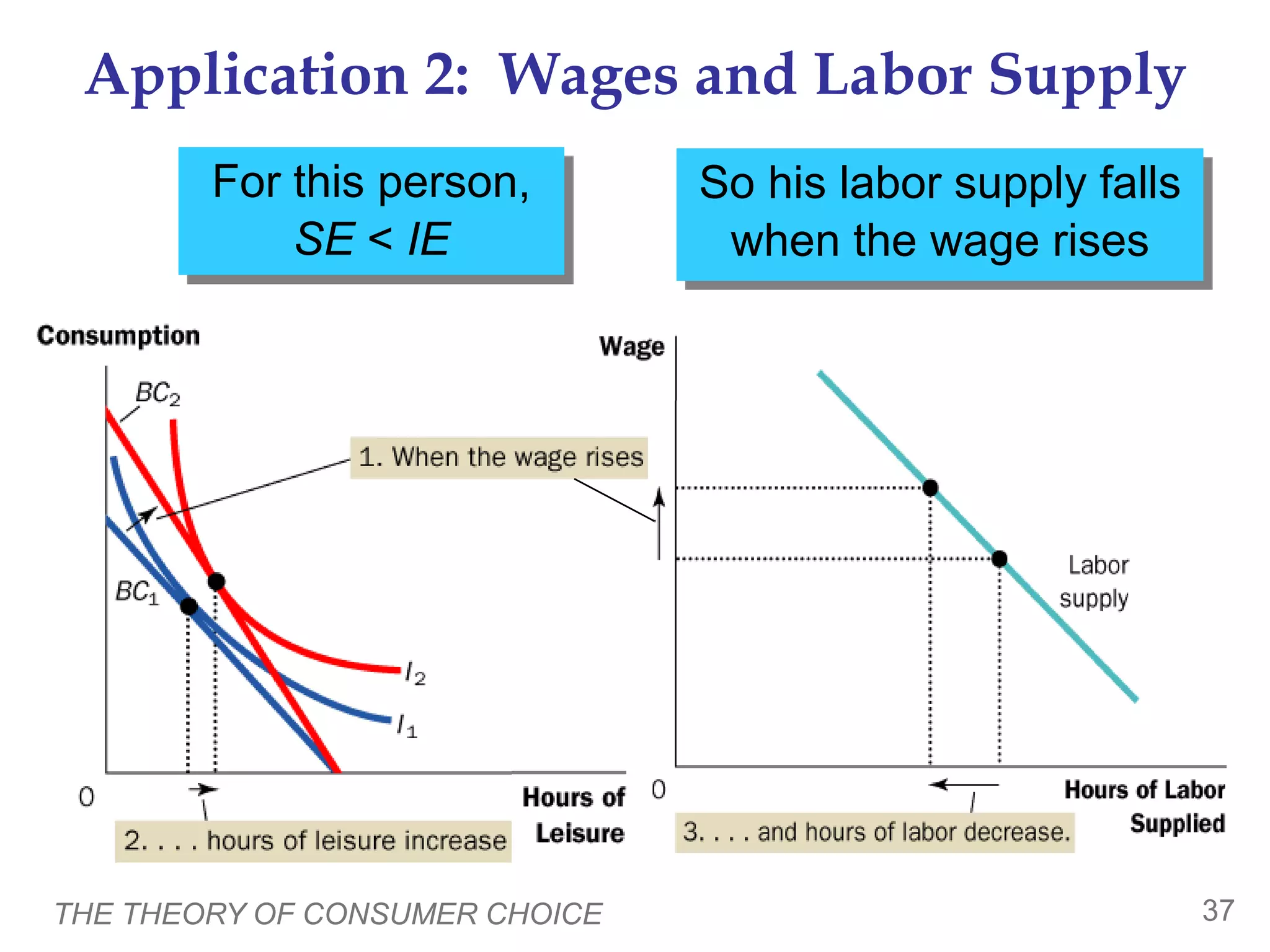
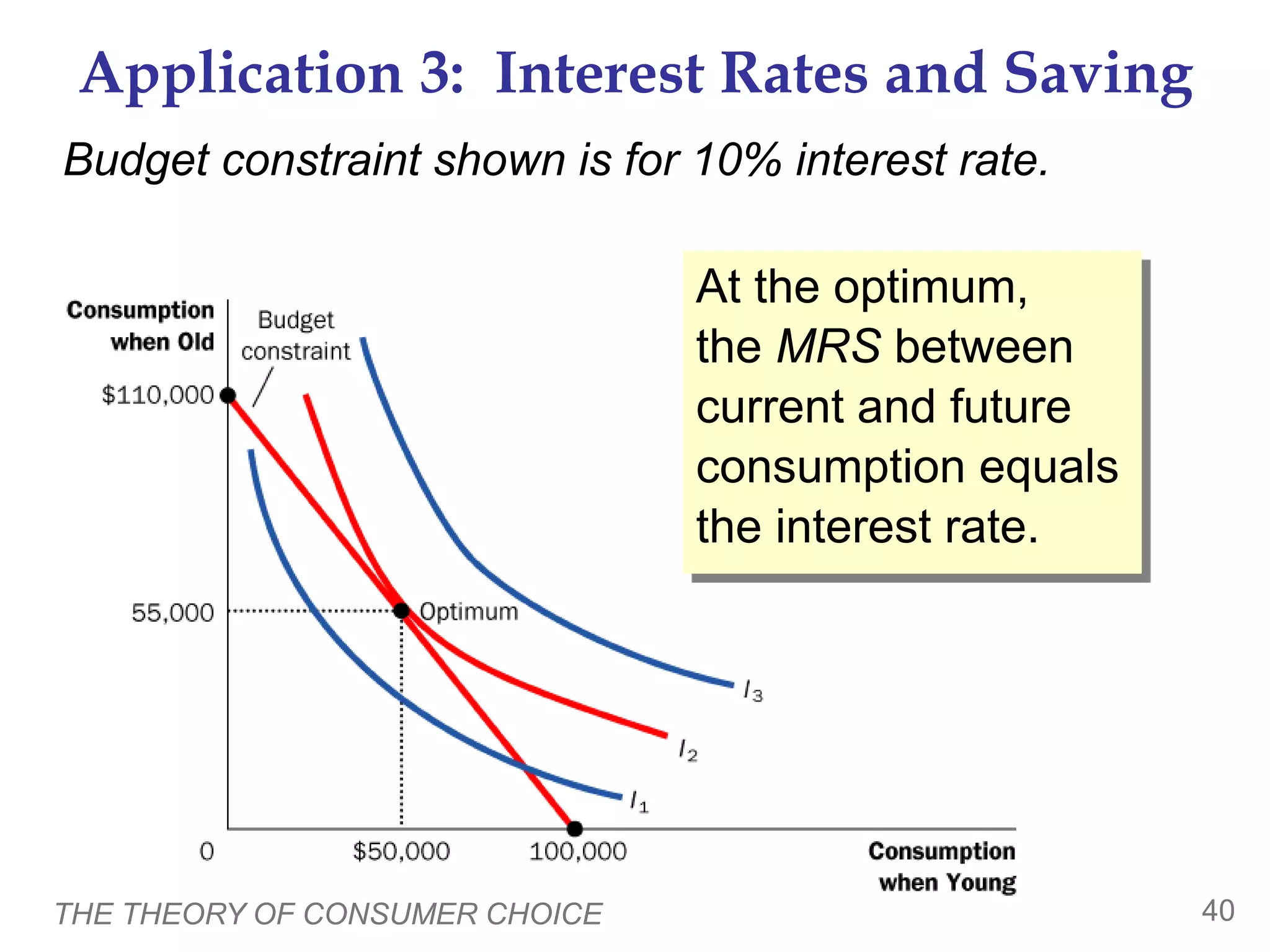
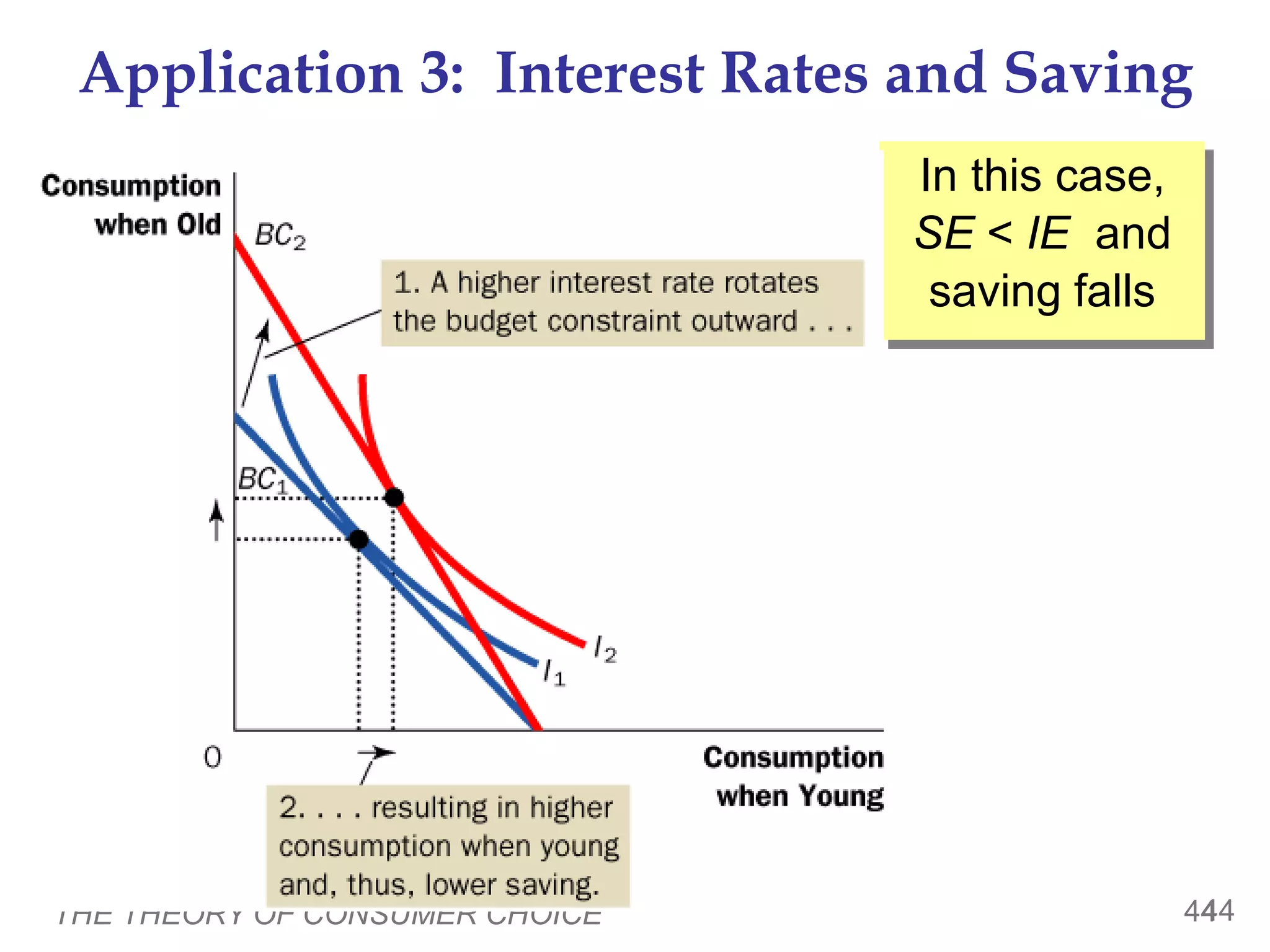
This document provides an overview of the theory of consumer choice. It introduces key concepts like the budget constraint, indifference curves, marginal rate of substitution, and consumer optimization. The budget constraint represents the combinations of goods a consumer can afford based on prices and income. Indifference curves represent combinations of goods that provide equal utility. Consumers optimize by choosing the highest indifference curve possible given their budget constraint. The theory is then applied to explain consumer decisions around income and price changes, labor supply, and saving.