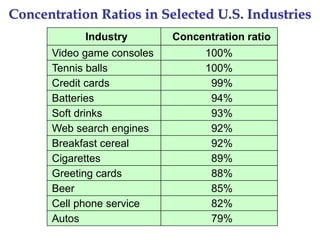
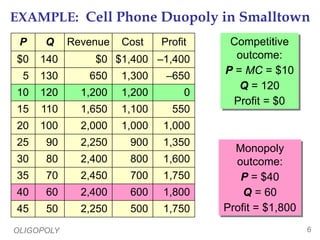
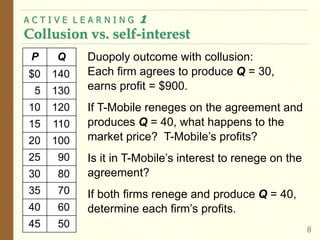
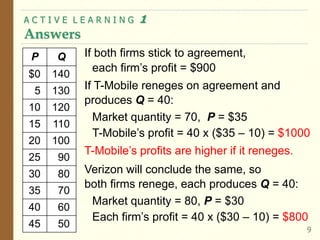
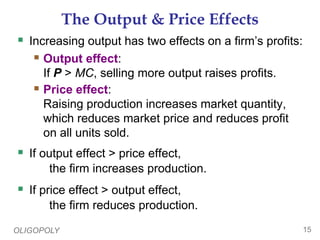
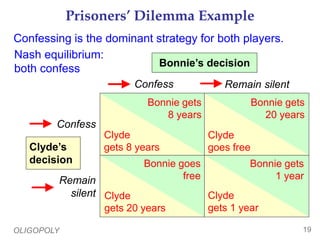
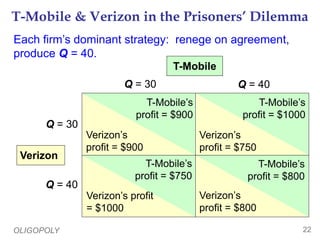
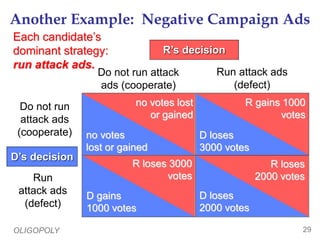
This document provides an overview of oligopoly market structures. It begins by defining key terms like concentration ratios and oligopoly. It then discusses how oligopolies differ from perfect competition and monopoly. The document uses an example of a cell phone duopoly to illustrate how firms in an oligopoly may collude but each has an incentive to lower prices on their own. It discusses how the prisoner's dilemma applies to oligopolies and makes cooperation difficult. Finally, it covers how antitrust laws aim to promote competition in oligopolies.