This document discusses several key concepts related to operating systems:
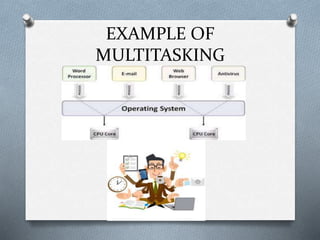
1. Multitasking allows a CPU to quickly switch between multiple programs to give the appearance that all programs are running simultaneously. There are two types: preemptive and cooperative.
2. Multiprogramming runs several programs at once using timesharing, where the operating system allocates CPU time slices to each program.
3. Buffering stores data temporarily in RAM when transferring between devices to improve efficiency. Word processors use buffers to track file changes before saving to disk.
4. Spooling places output for slower devices like printers in temporary storage so multiple applications can print concurrently without mixed output.
5. Caching uses high-