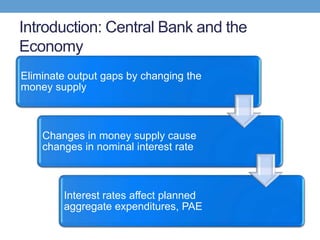
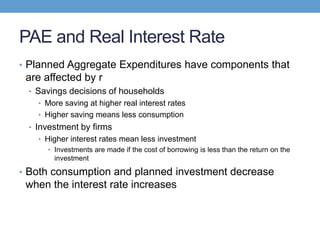
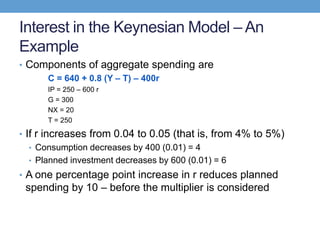
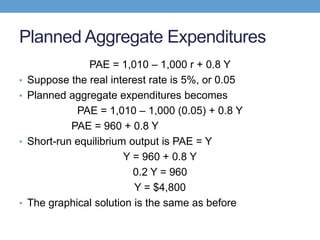
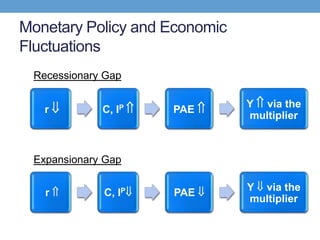
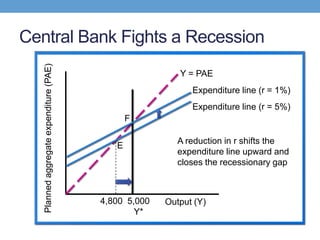
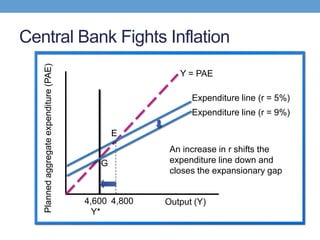
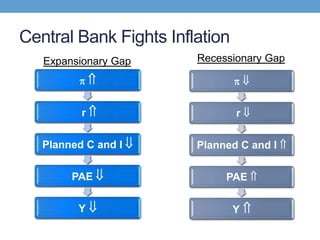
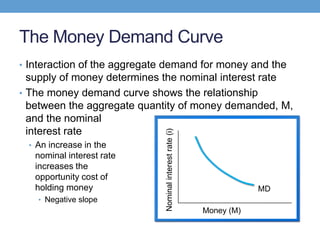
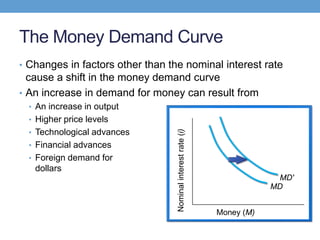
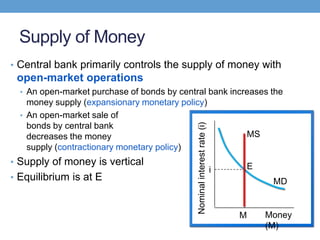
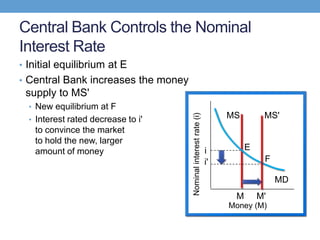
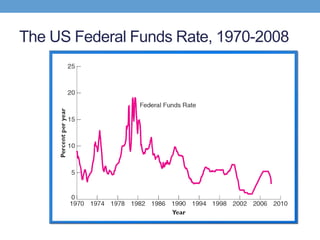
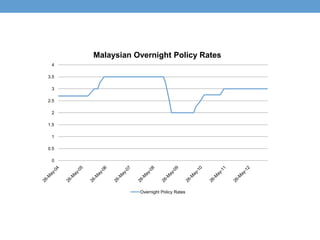
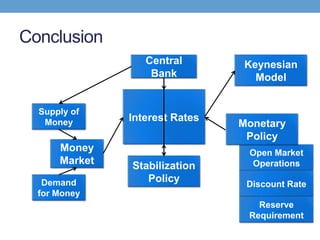
The document discusses how central banks use monetary policy to influence nominal and real interest rates and stabilize the economy. It explains that central banks primarily control the money supply through open market operations, which affect the demand for and supply of money in determining the equilibrium interest rate. Changes in interest rates then impact planned aggregate expenditures and equilibrium output. The document provides examples of how central banks can use monetary policy to address recessionary or inflationary gaps through influencing real interest rates.