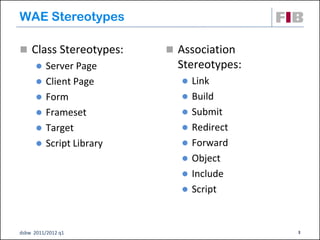
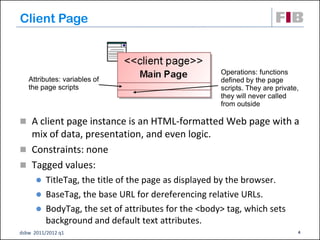
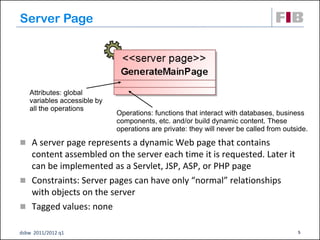
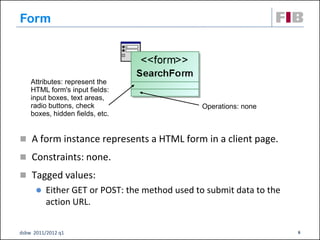
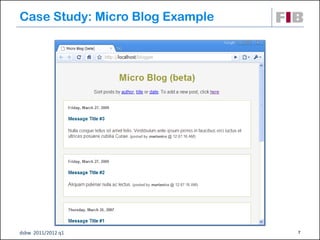
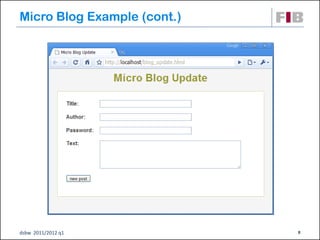
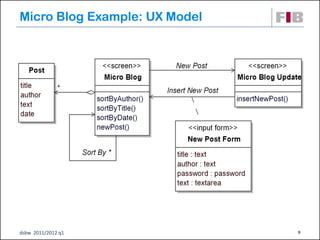
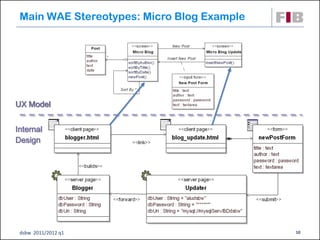
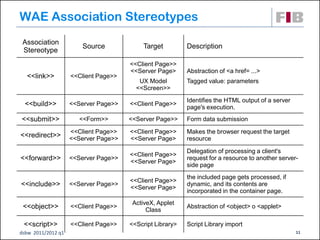
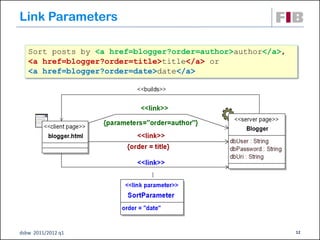
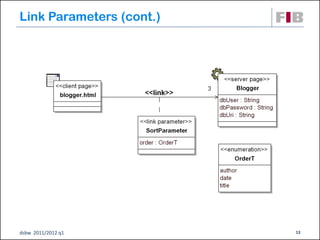
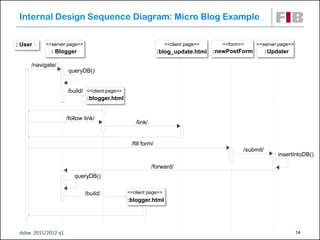
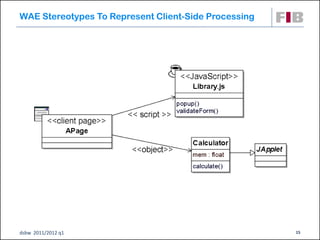
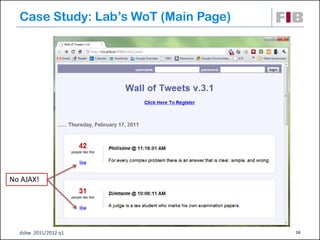
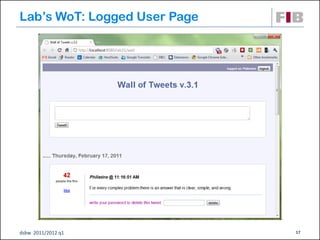
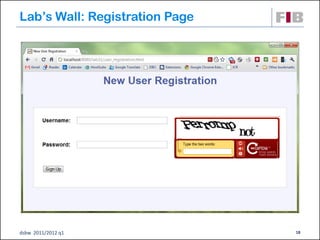
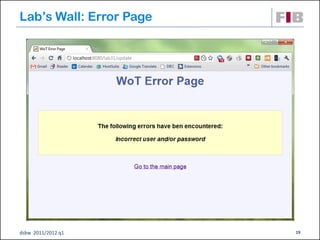
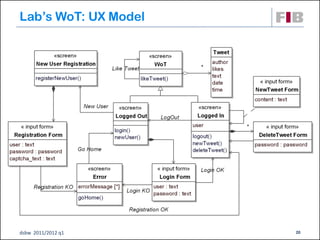
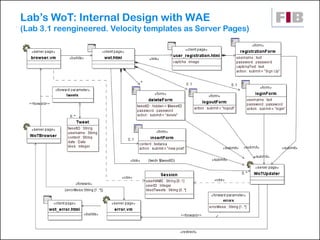
The document discusses modeling web applications using the Web Application Extension (WAE) for UML. The WAE allows web pages and other significant web elements to be represented in UML design models. It introduces stereotypes for classes like server pages and client pages to model different aspects of web pages. It also includes stereotypes for associations between model elements like links, builds, submits, and redirects. The document provides examples of using WAE stereotypes to model elements of a sample microblogging application and a lab's wall of text website.