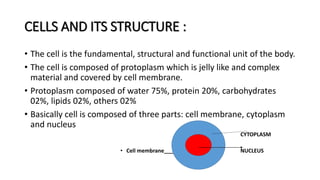
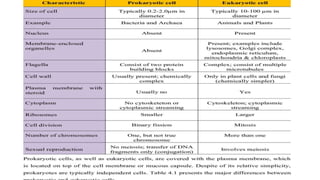
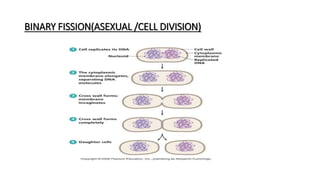
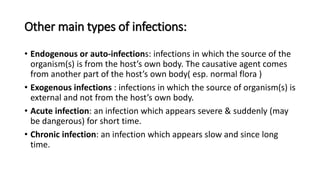
This document provides an overview of basic microbiology. It defines microbiology as the study of microorganisms that cannot be seen with the naked eye, including bacteria, viruses, protozoa, and fungi. It classifies microorganisms and describes bacterial cell structure and types, modes of bacterial reproduction, and viral replication. It also discusses factors affecting microbial growth and types of infections.