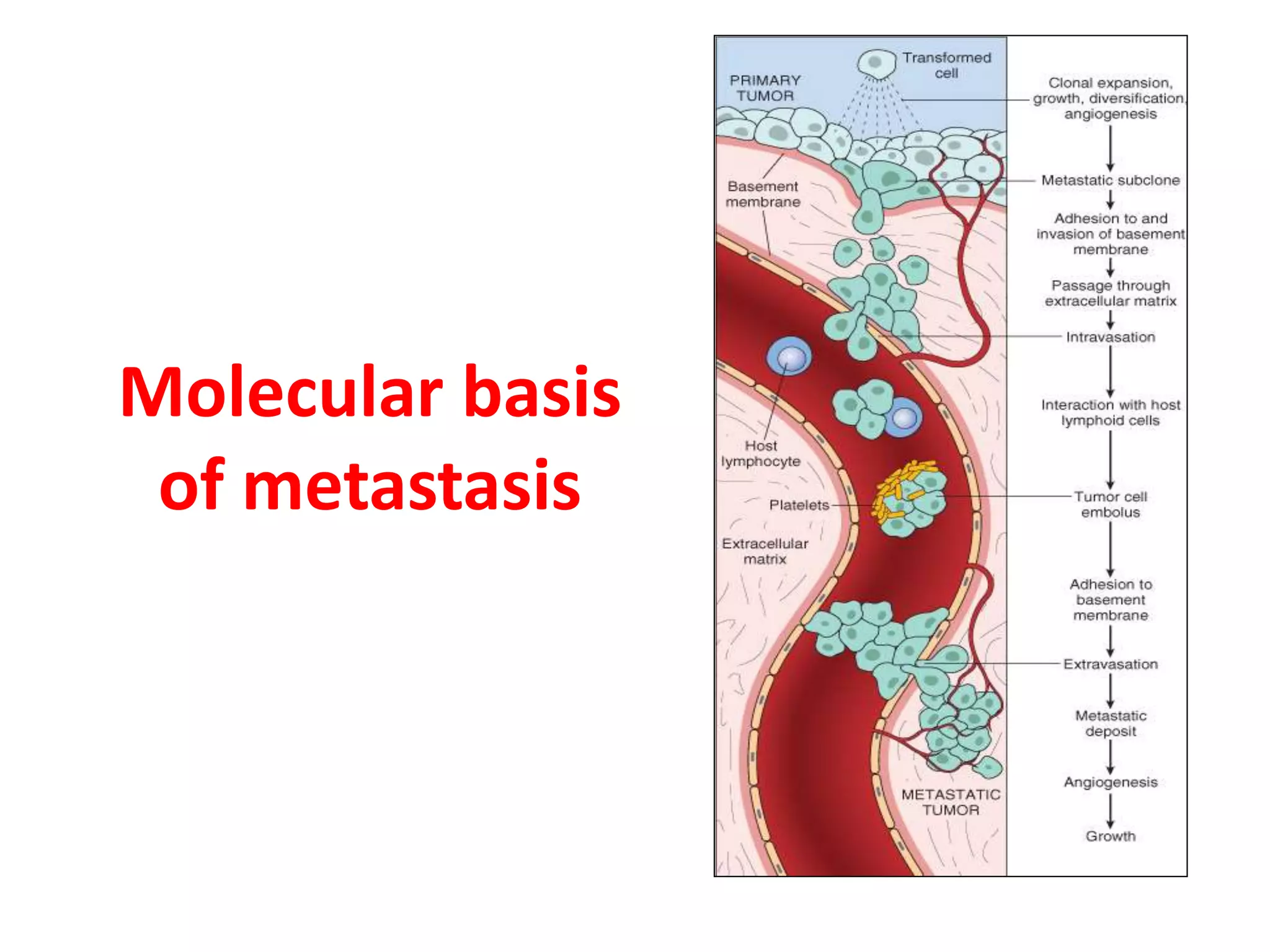
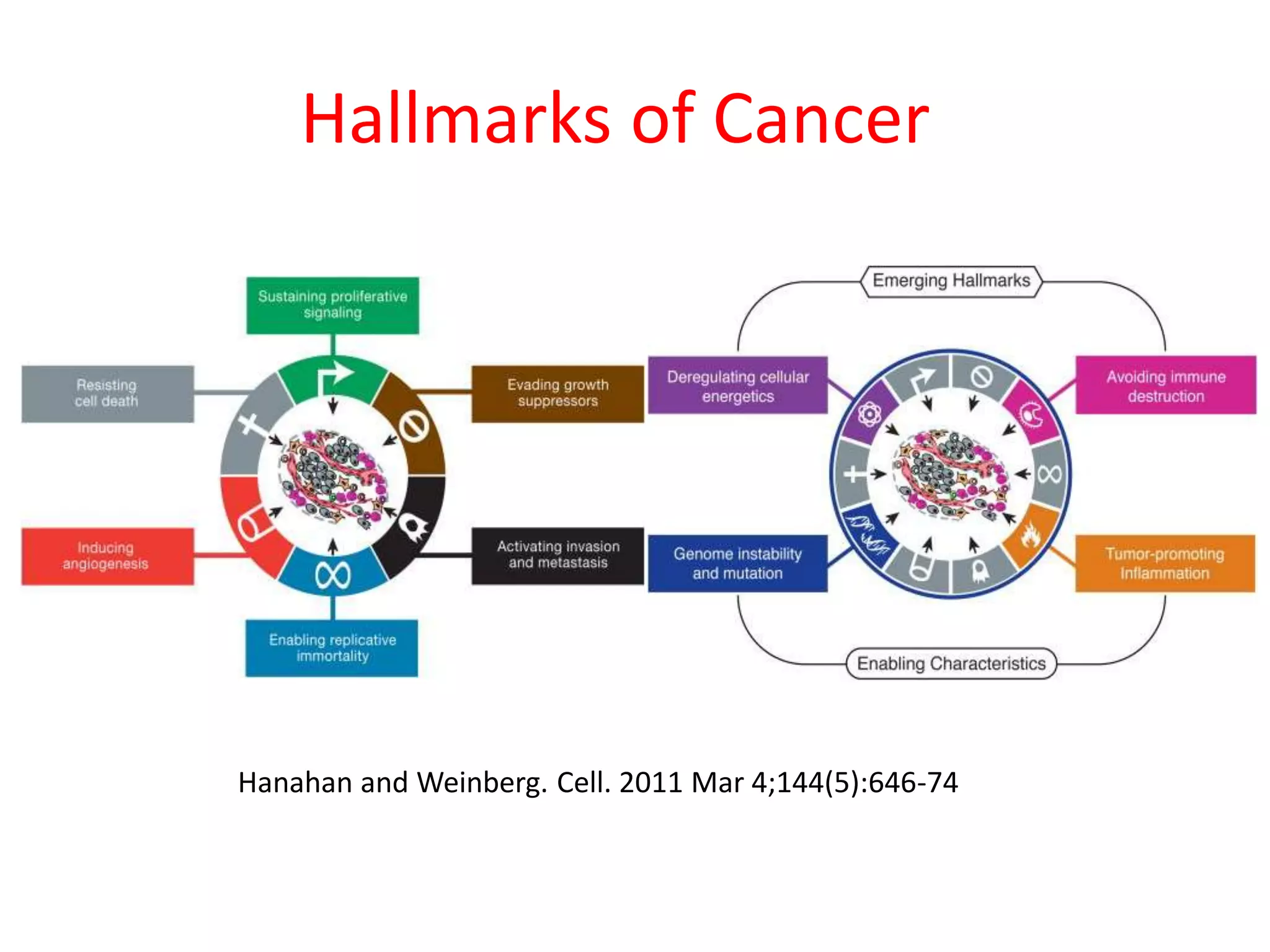
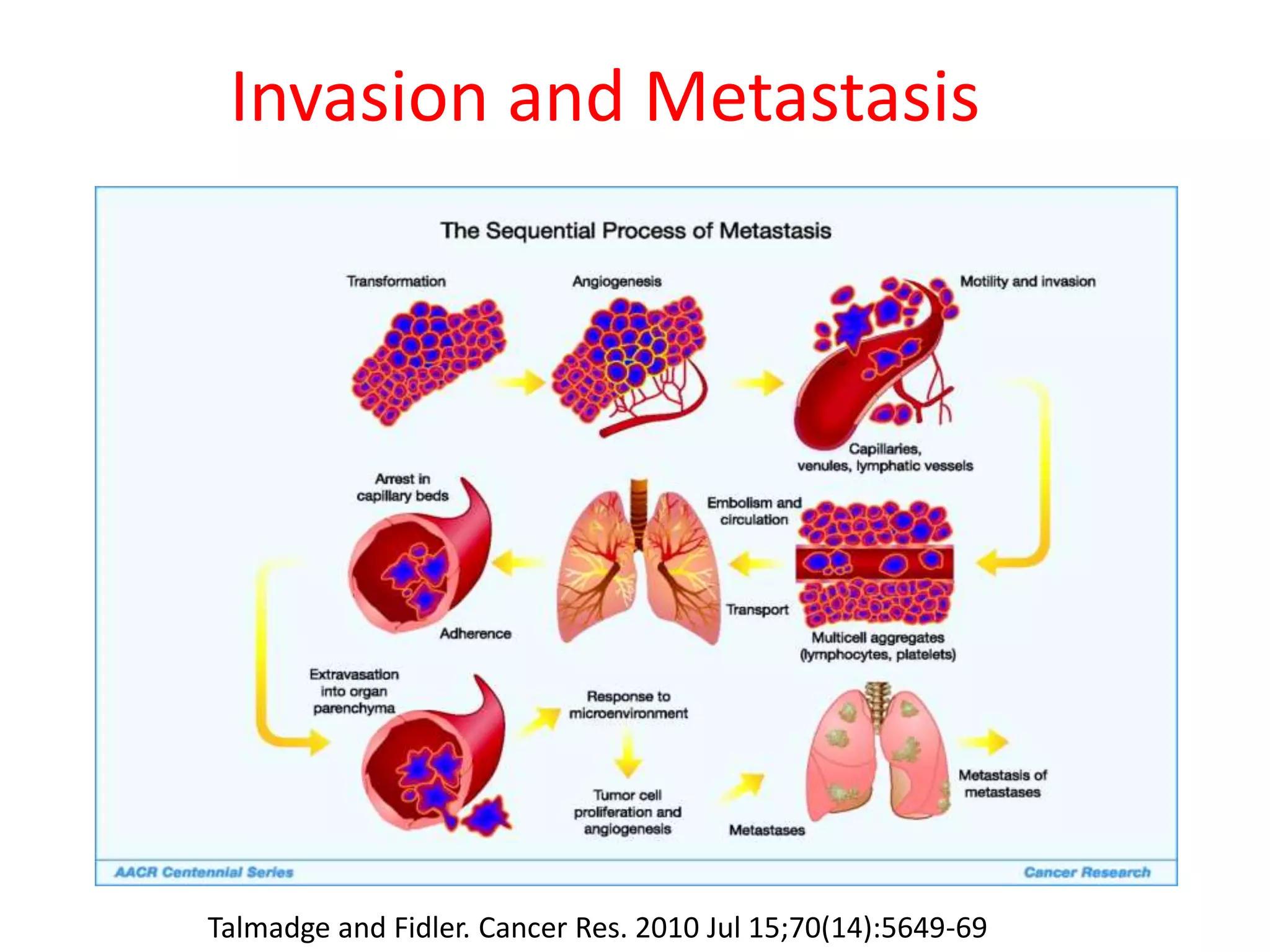
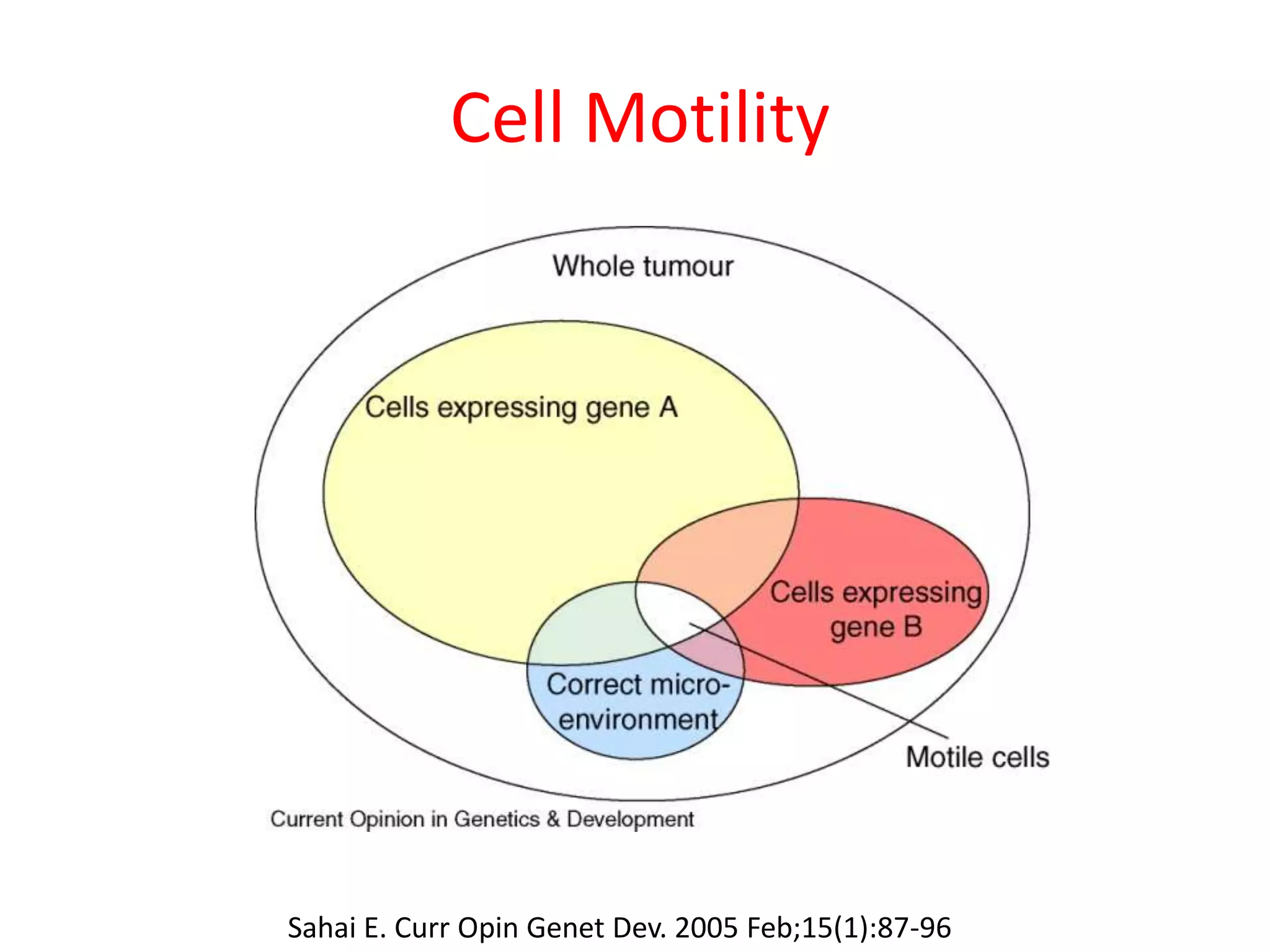
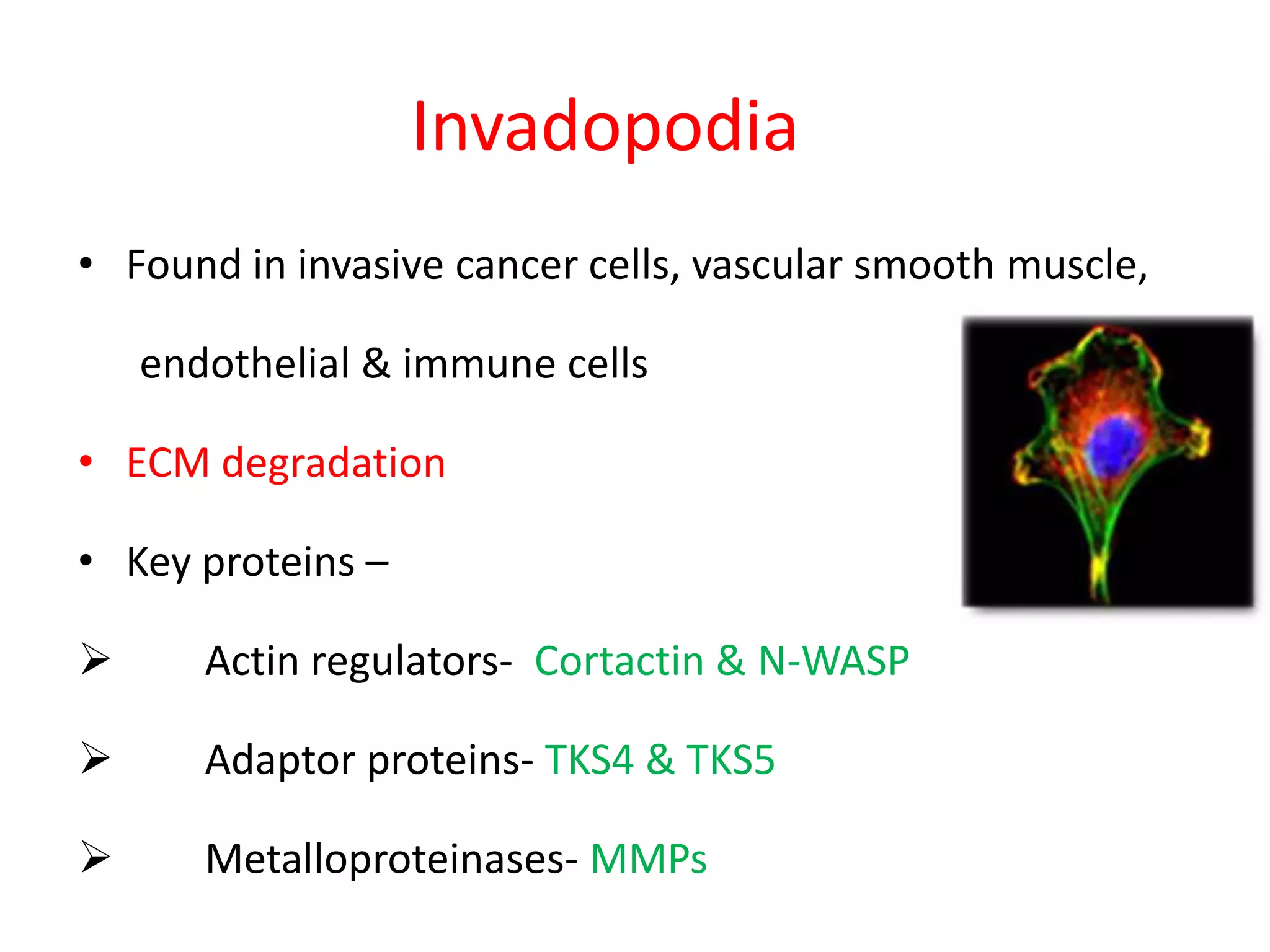
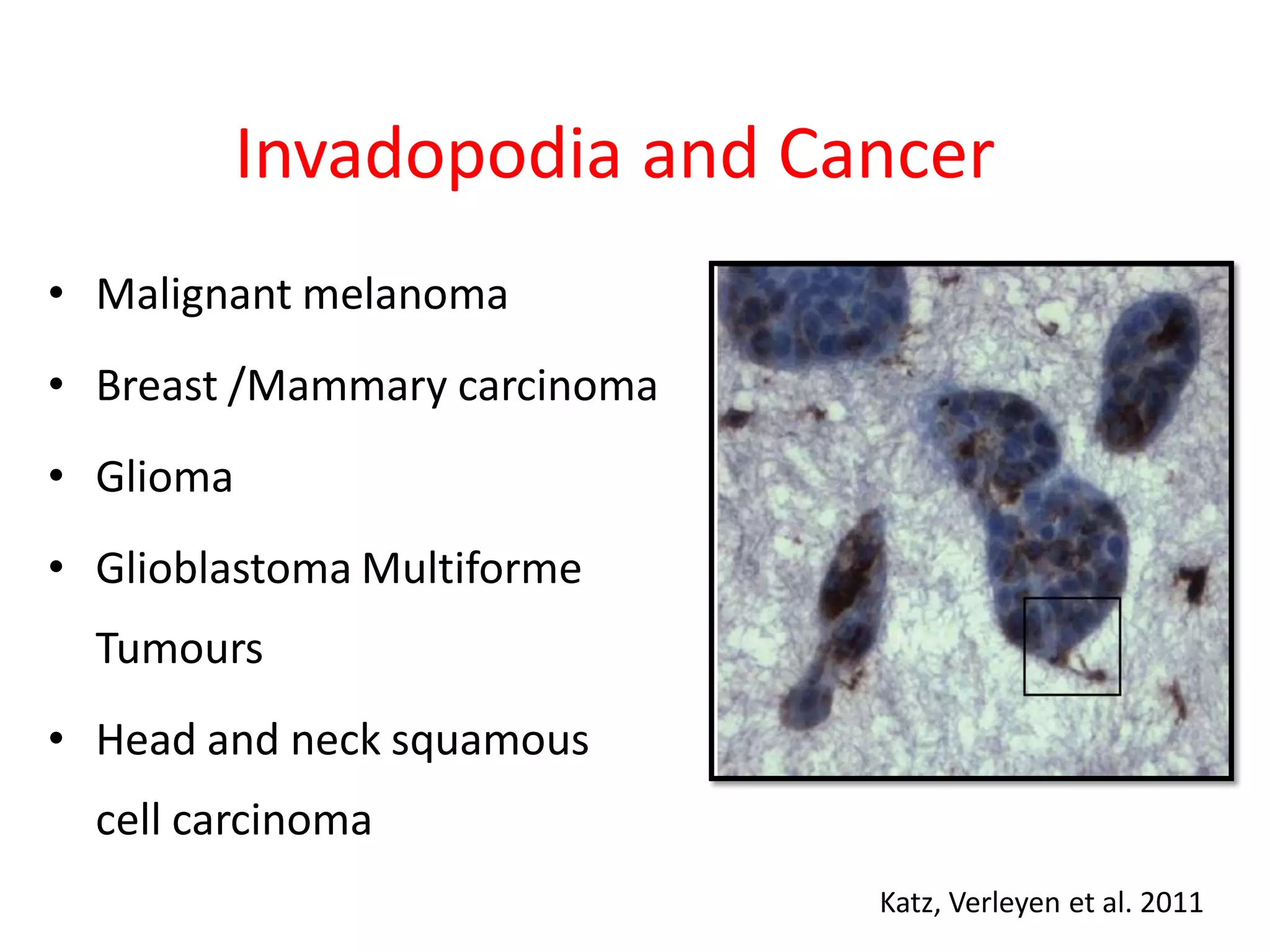
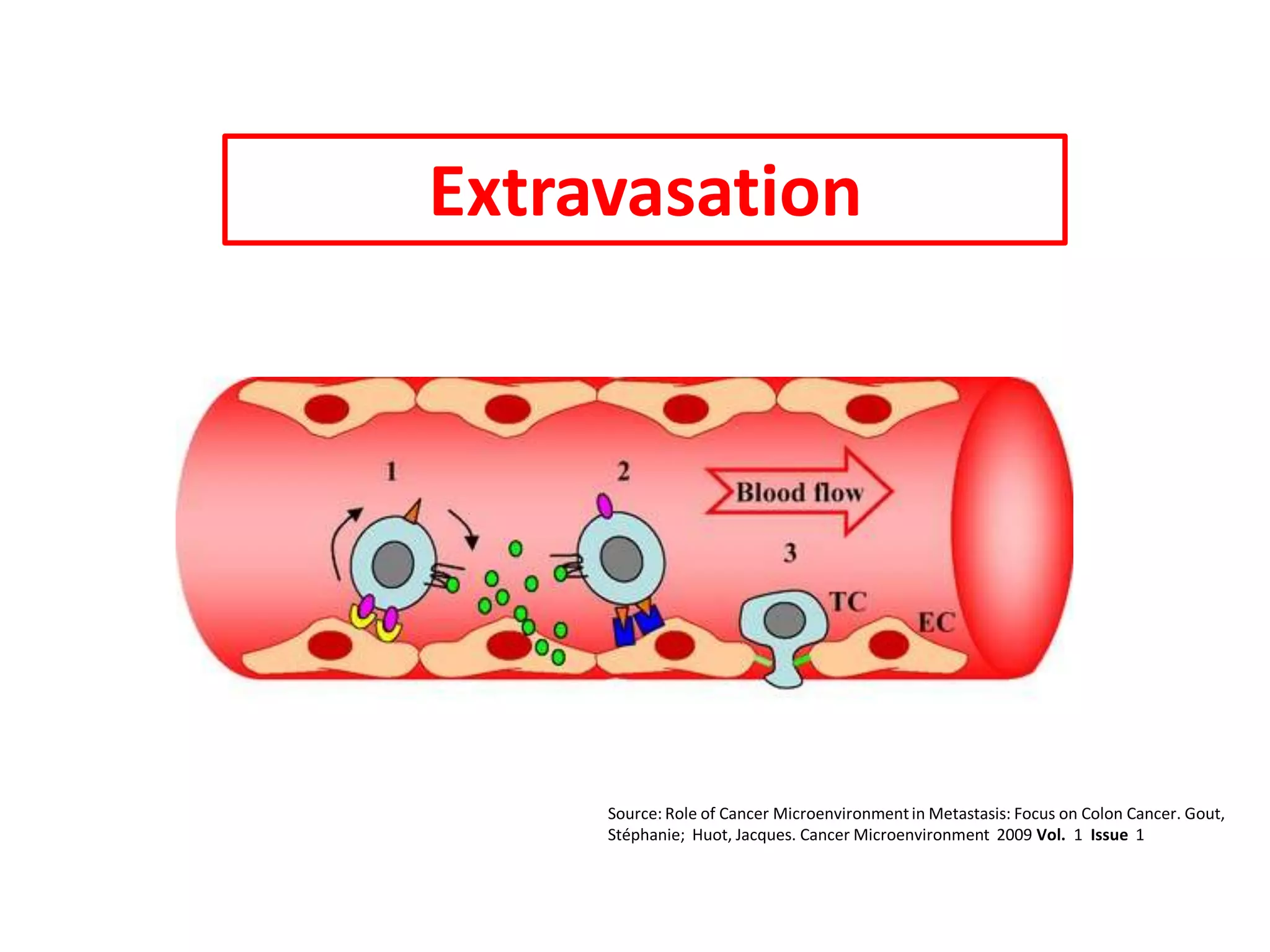
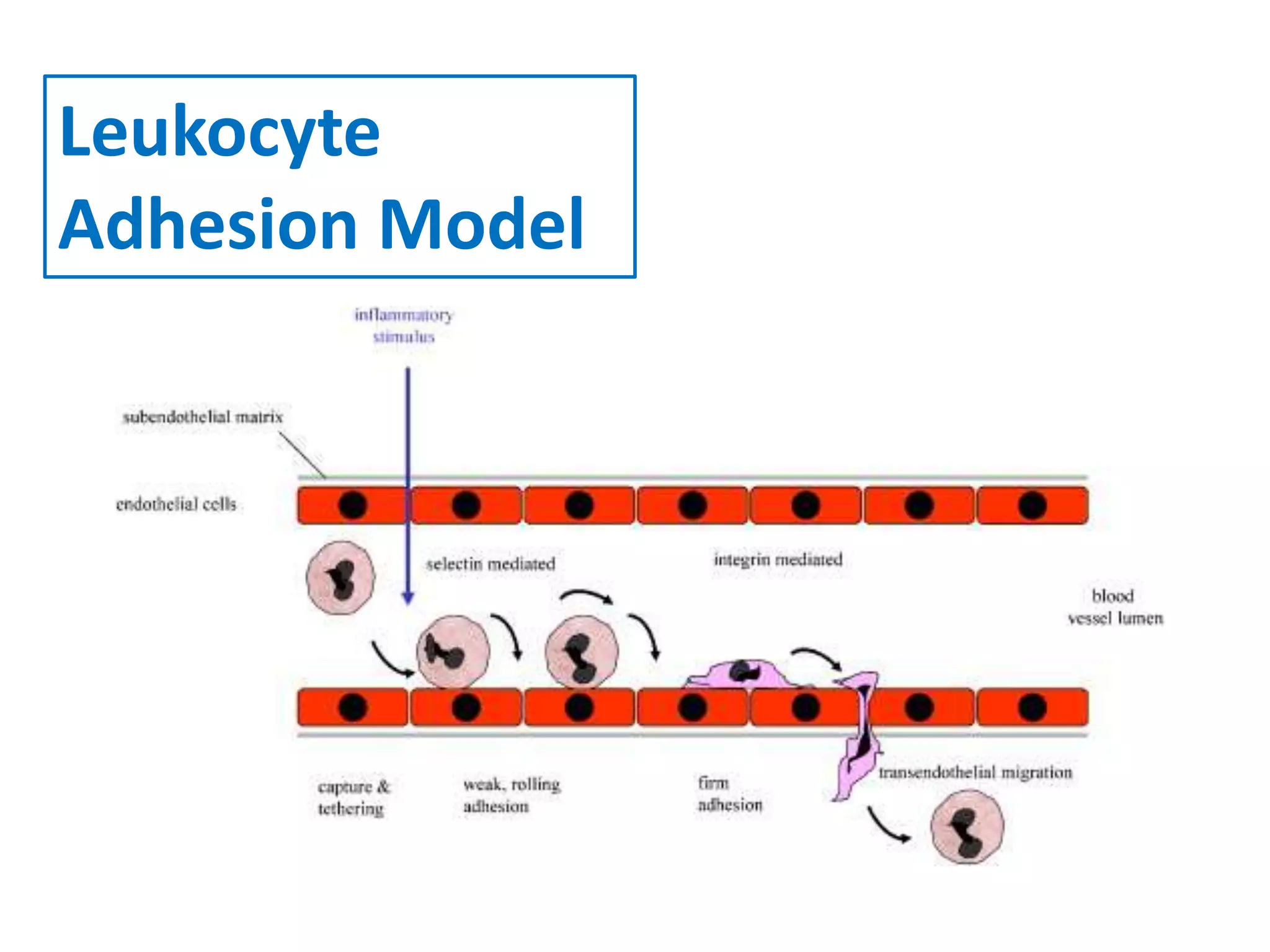
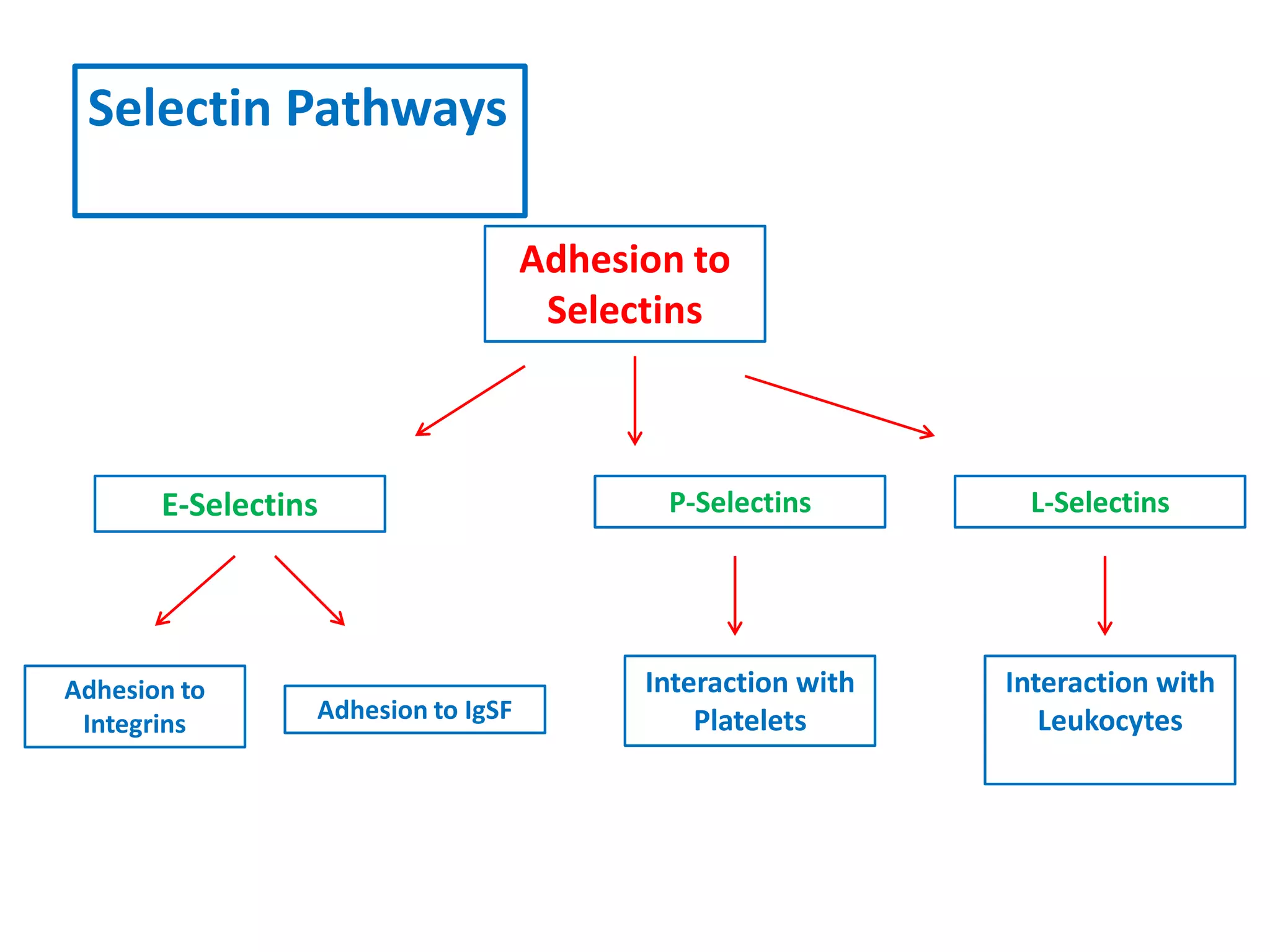
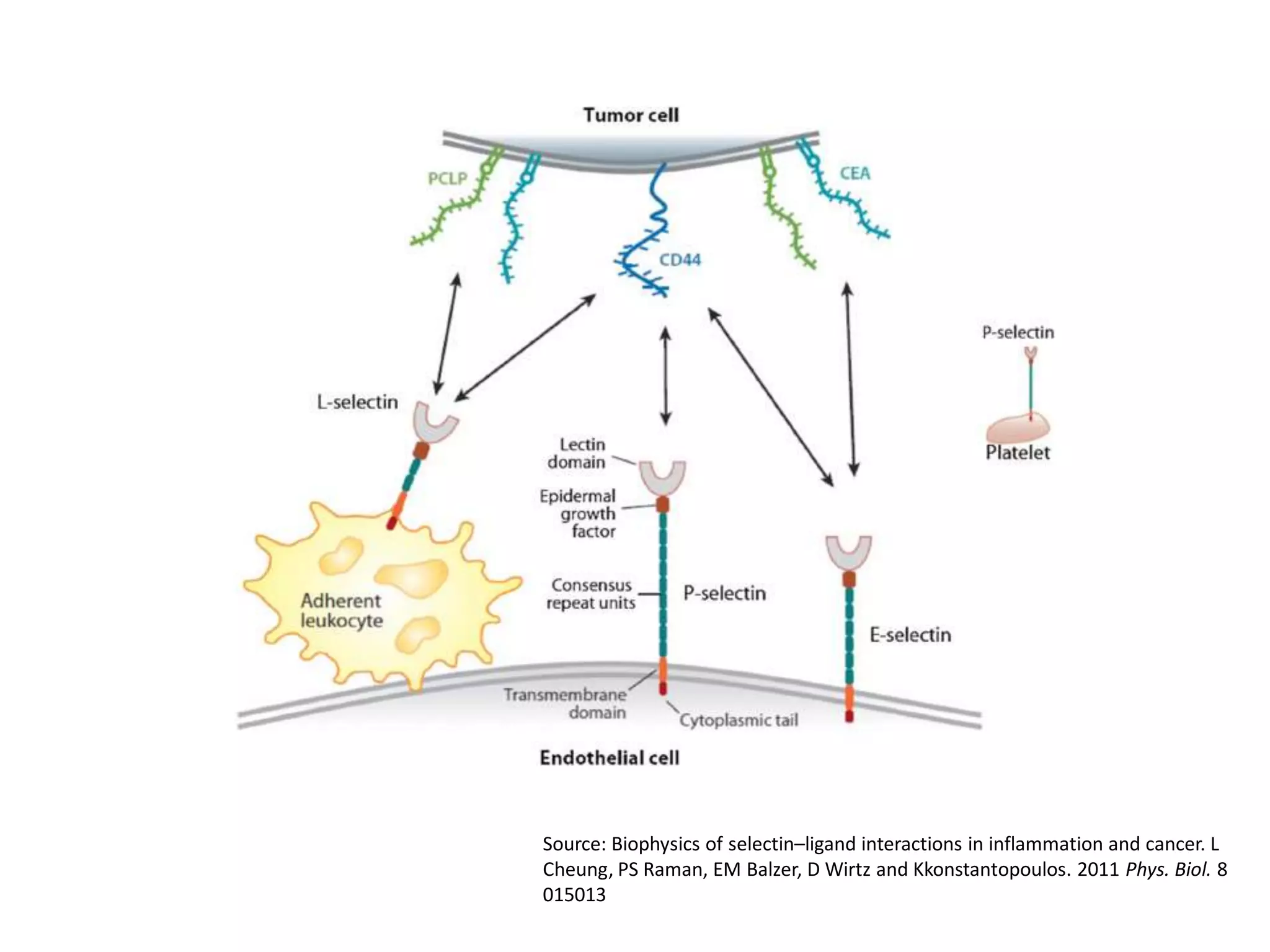
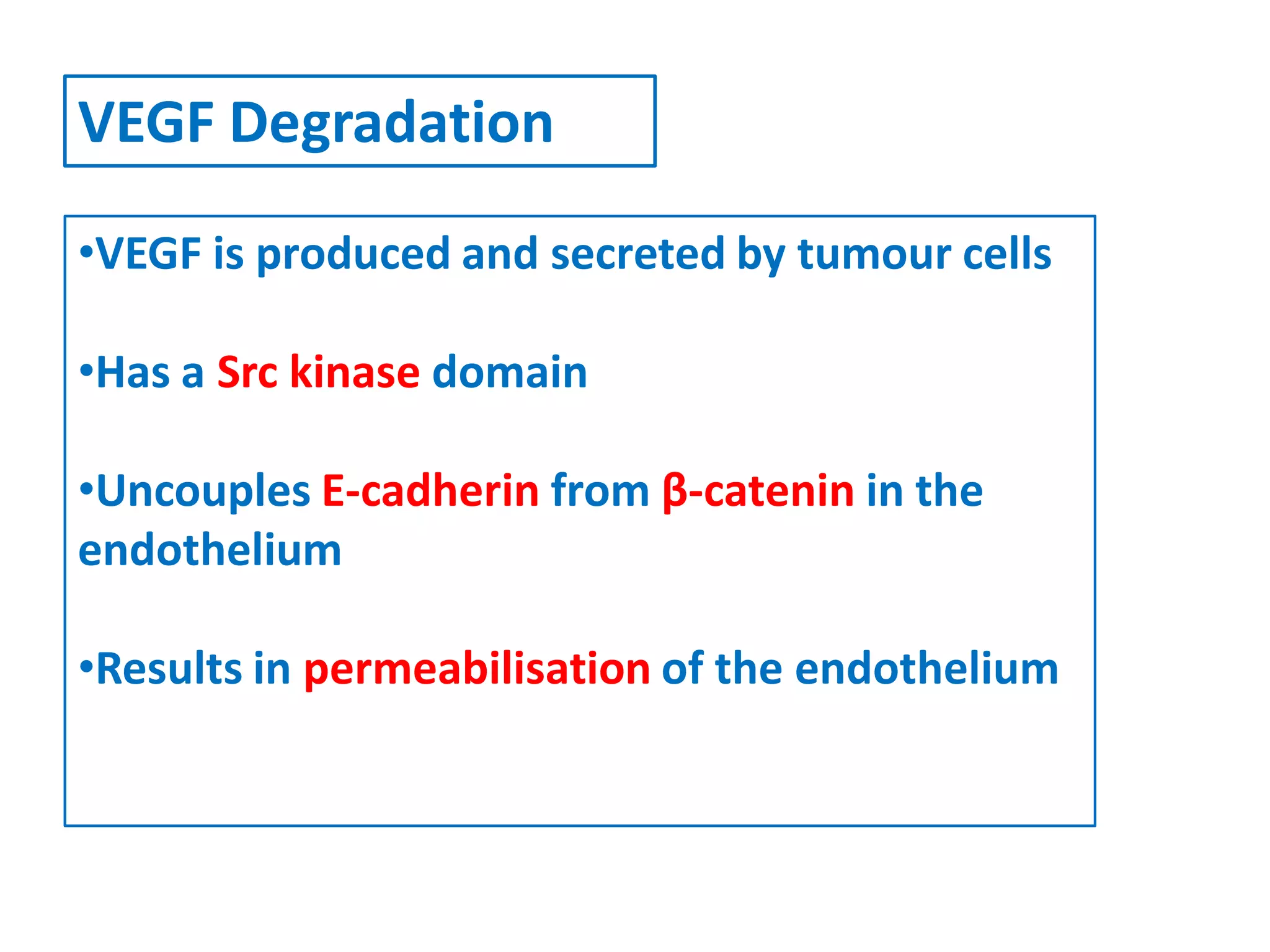
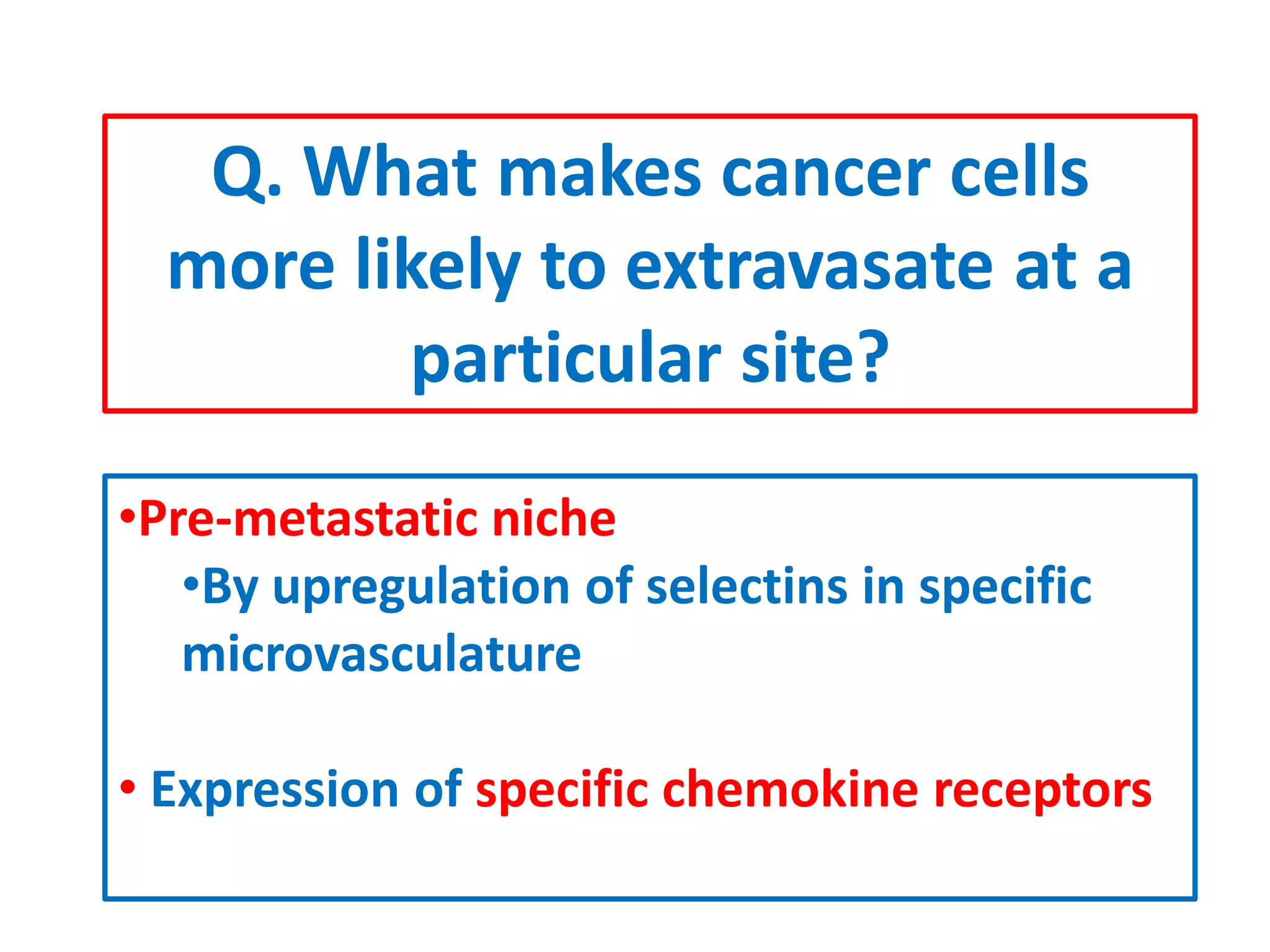
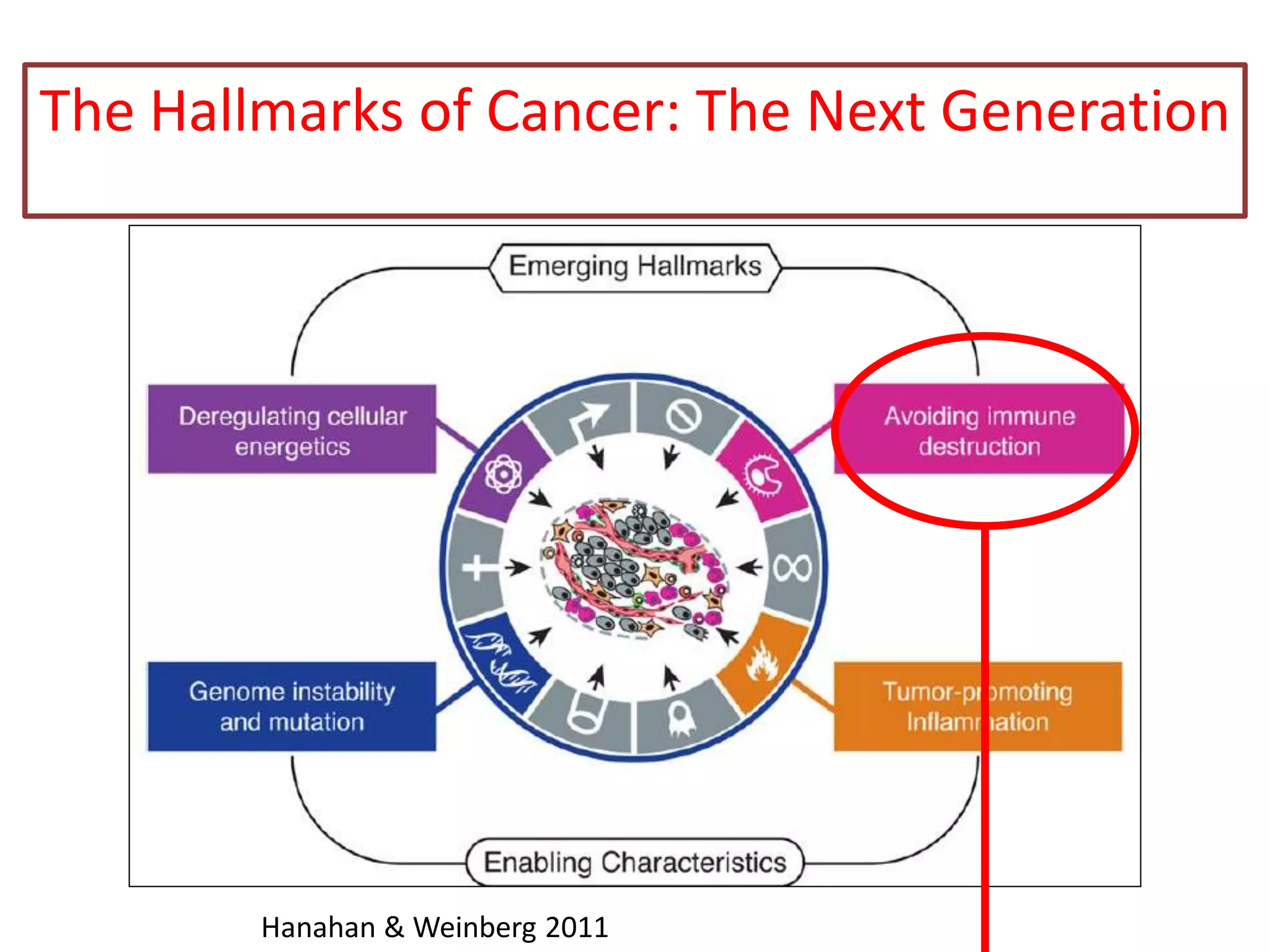
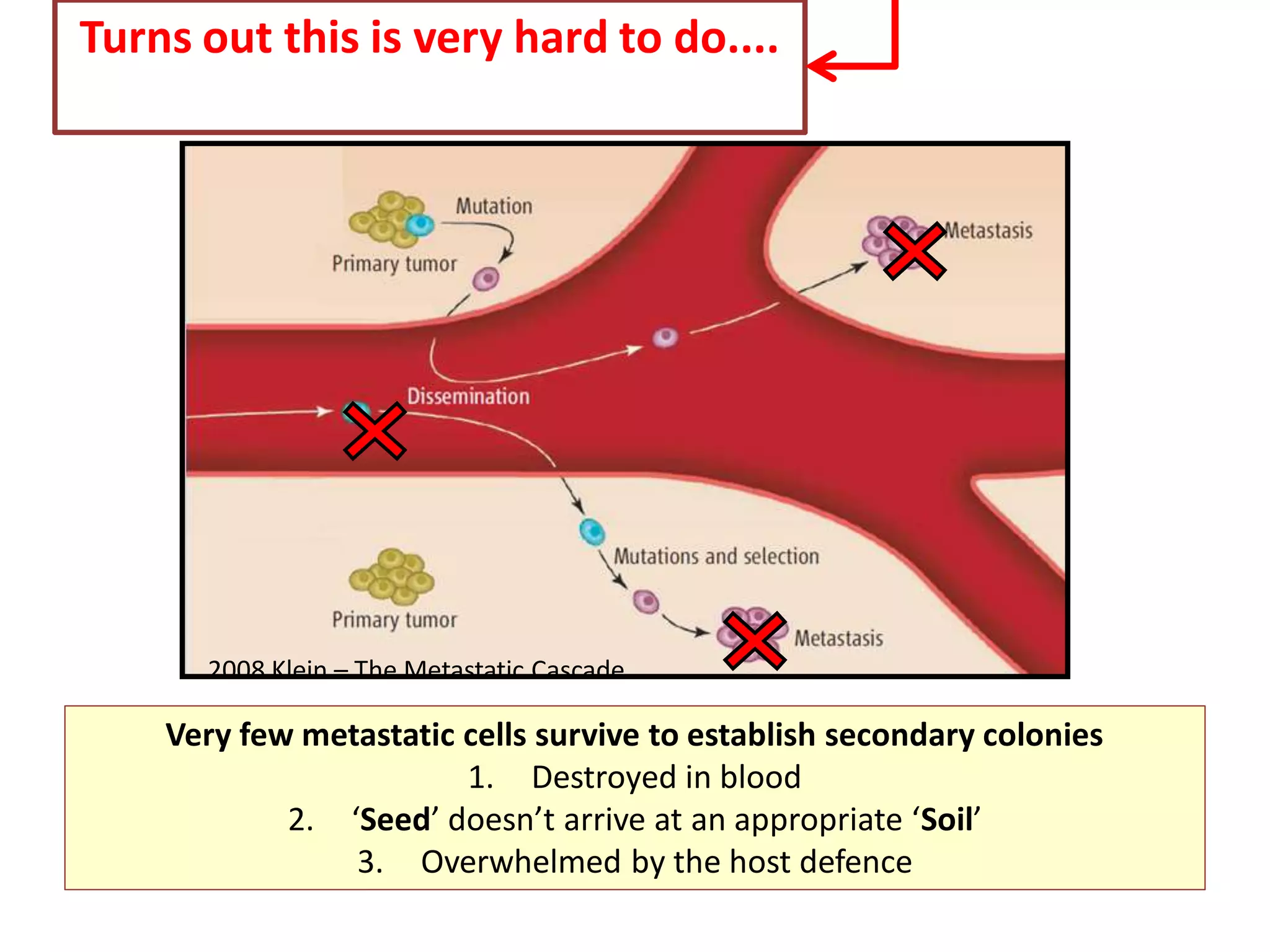
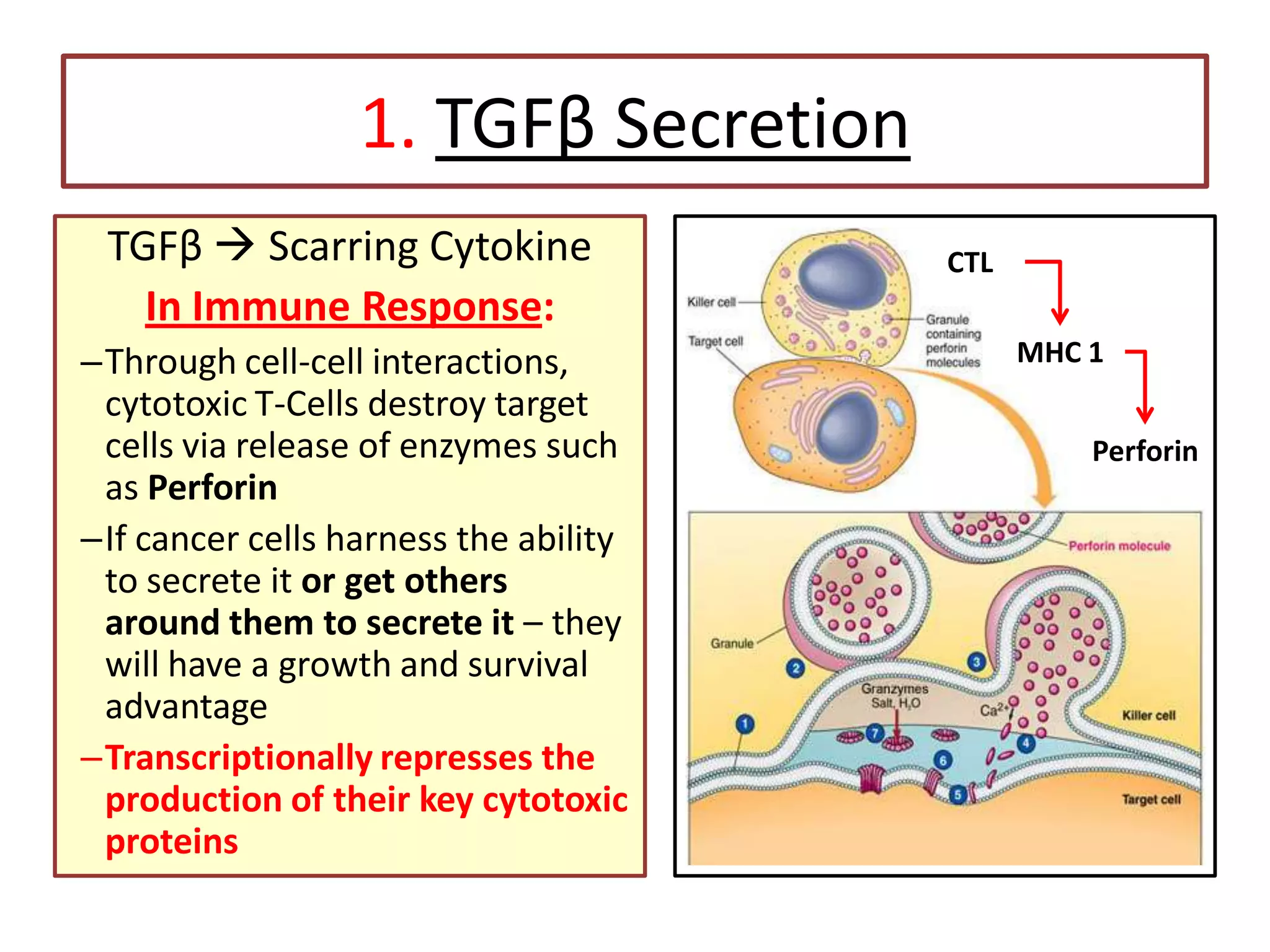
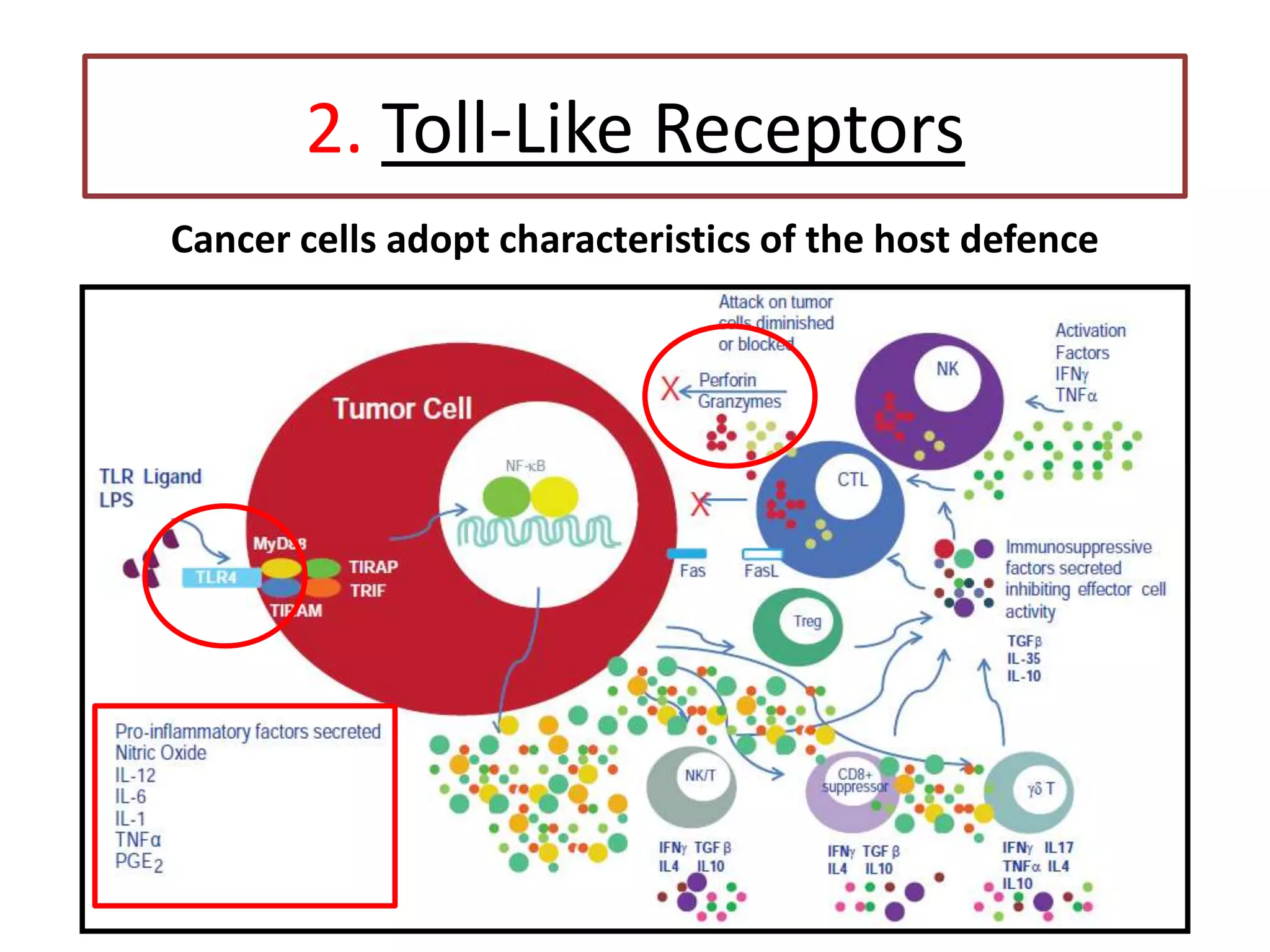
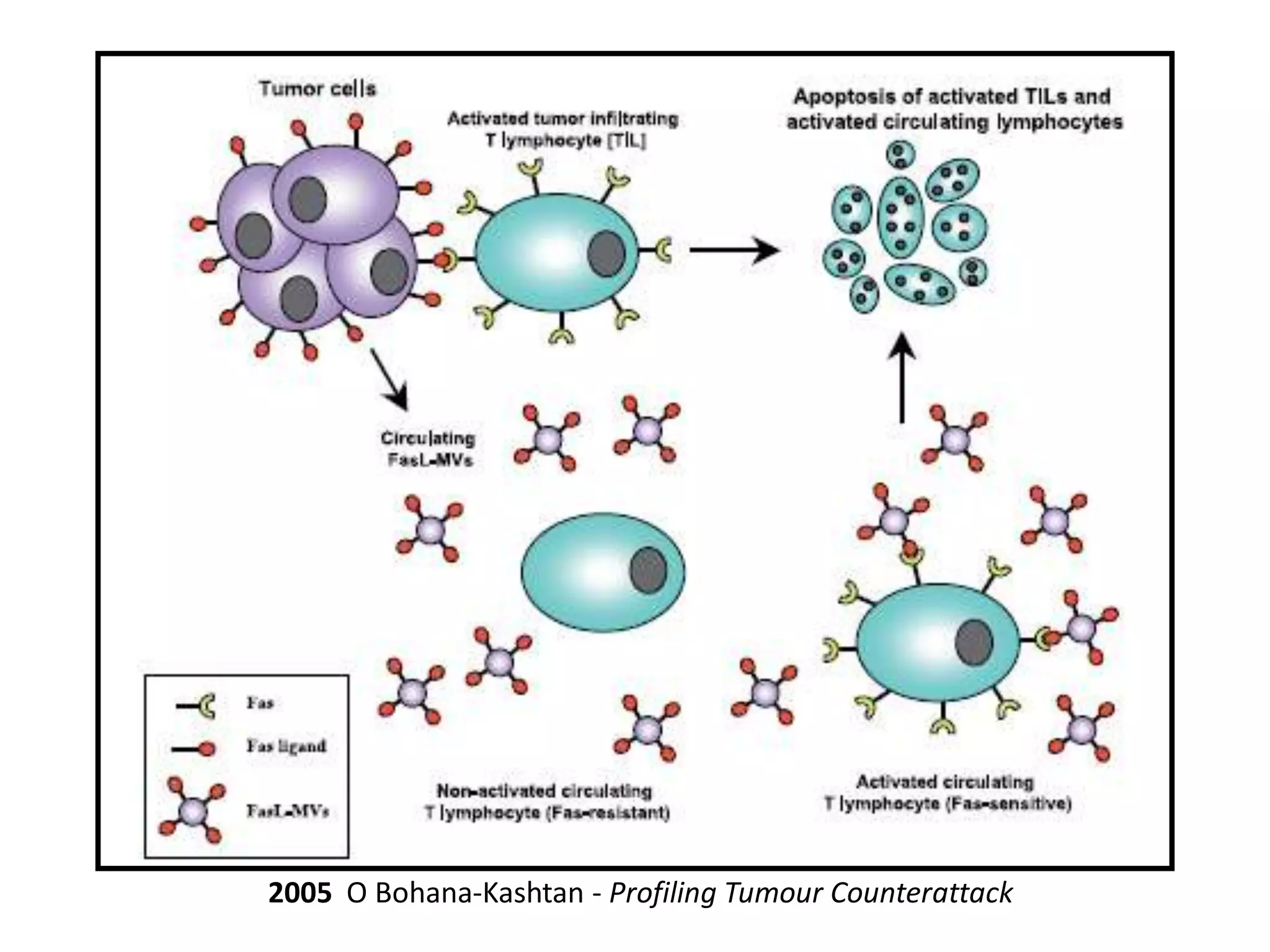
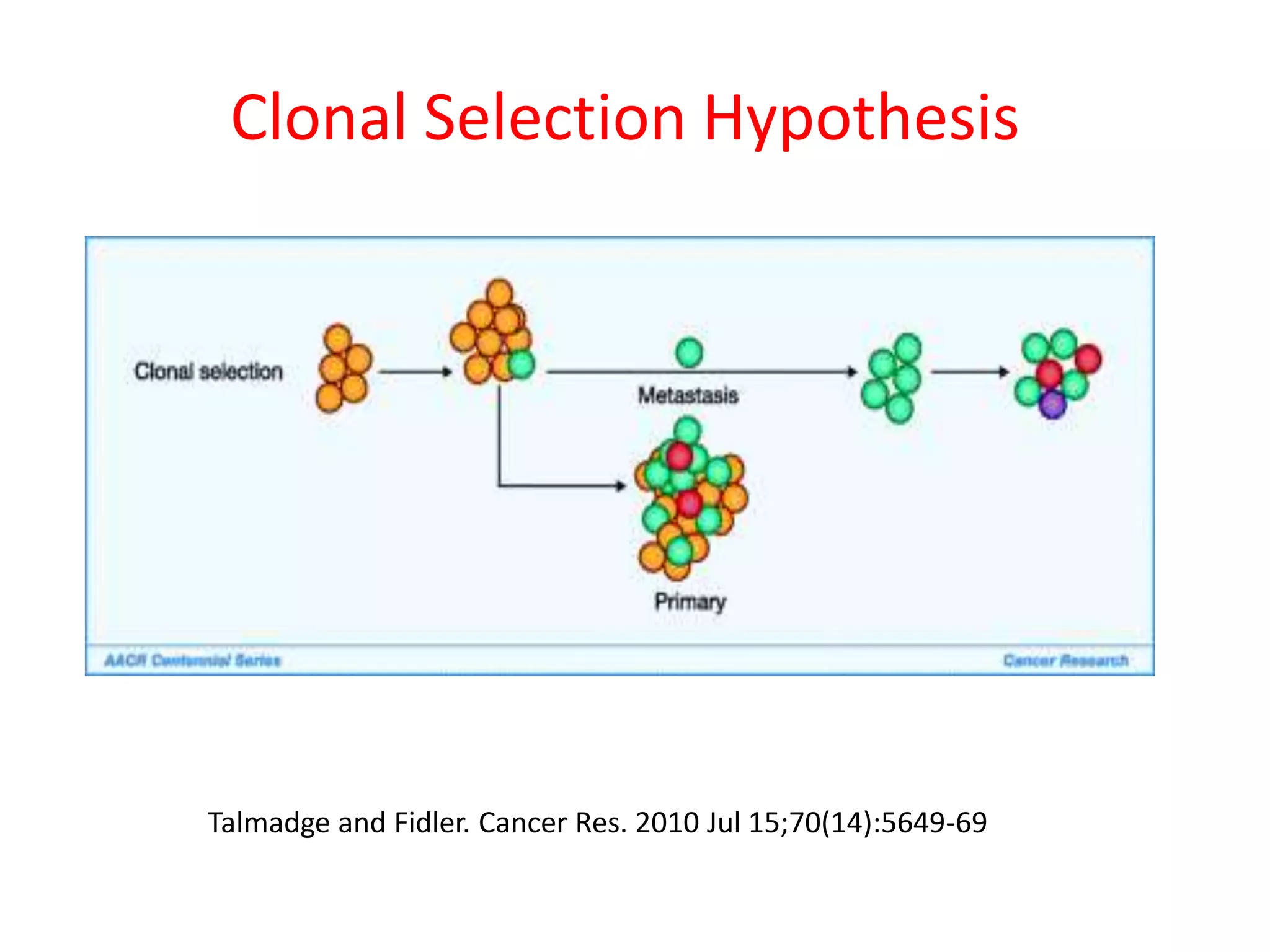
Invadopodia play an important role in cancer cell invasion and metastasis. Key proteins involved in invadopodia include actin regulators like cortactin and N-WASP, and adaptor proteins like TKS4 and TKS5. Invadopodia allow cancer cells to degrade the extracellular matrix through metalloproteinases. Cancer cells employ various mechanisms to evade the host immune response after extravasation, including secreting TGFβ and expressing toll-like receptors and tumor counterattack proteins that can kill lymphocytes. Successful metastasis requires cancer cells to survive in the bloodstream, home to appropriate tissues, and overcome host defenses at the secondary site.