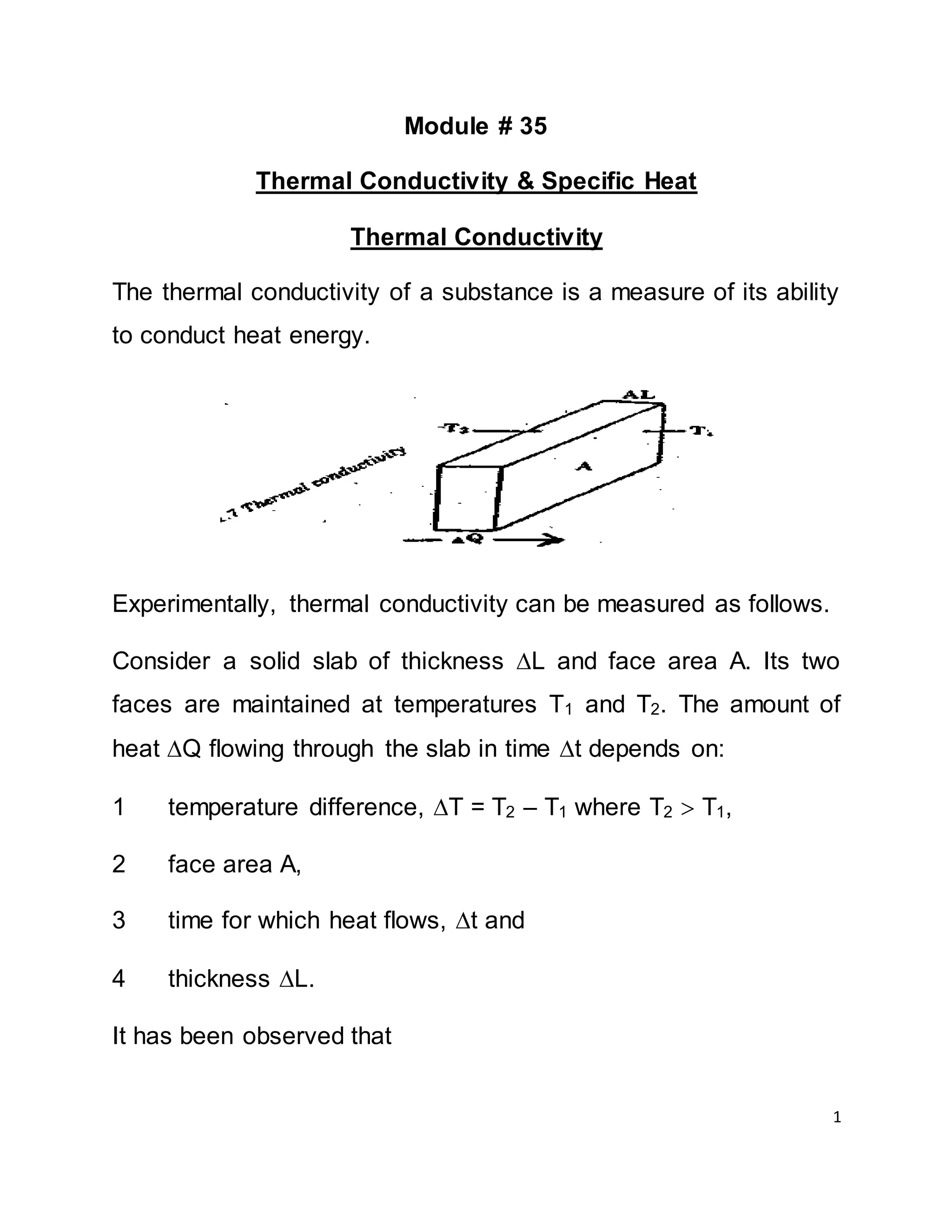
1. Thermal conductivity is a measure of a material's ability to conduct heat. It is defined as the amount of heat conducted through a 1 m^2 area with a 1°C temperature difference over 1 second.
2. Specific heat is the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 kg of a substance by 1°C. Latent heat is the heat absorbed or released during a phase change without changing temperature.
3. Rumford rejected the caloric theory of heat, concluding that heat is a form of energy produced by friction or mechanical work, not a fluid. The mechanical equivalent of heat is the amount of work required to produce 1 calorie of heat.
![2
Q A,
Q T,
Q t and
Q 1/L
A x T x t A x T x t
Q ---------------- OR Q = K ----------------- [1]
L L
Where, K is a constant of proportionality called thermal
conductivity. Its value depends on the material of the slab and is a
measure of the thermal conductivity of the material.
If
A = 1m2
L = 1m
T = 1°C
and
t = 1 Sec
then, by putting these values in Eq. [1]
we get,](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/moduleno-200324170600/85/Module-No-35-2-320.jpg)











