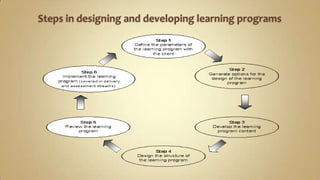
The document provides guidance on designing modular or part-time learning programs. It outlines steps to:
1) Analyze learner needs and program parameters by defining purpose, outcomes, target group characteristics and benchmark standards.
2) Generate content and structure options using learning principles and styles.
3) Develop the program content, structure, resources, timeframes and costs.
4) Review and finalize the program for approval and implementation.