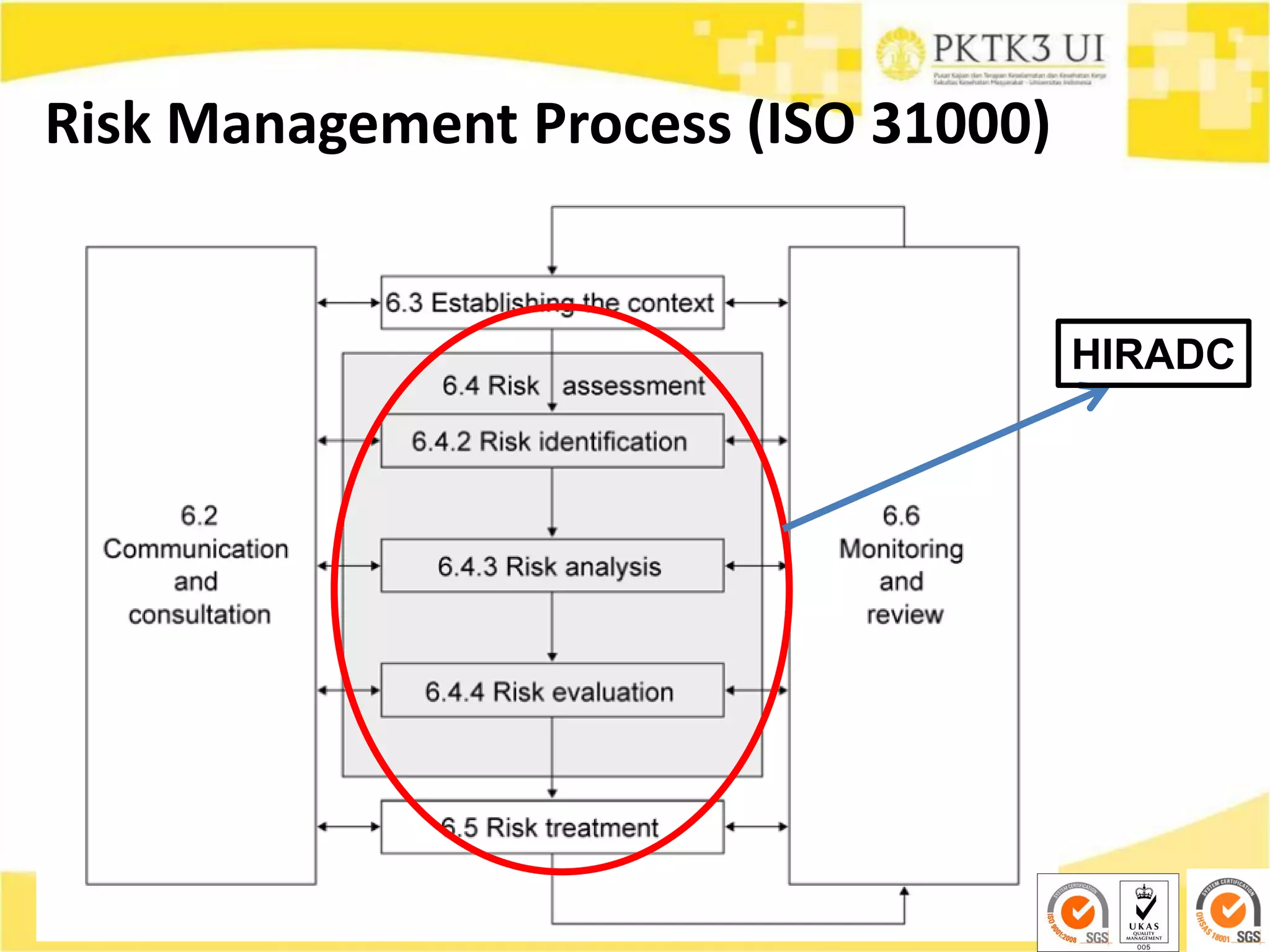
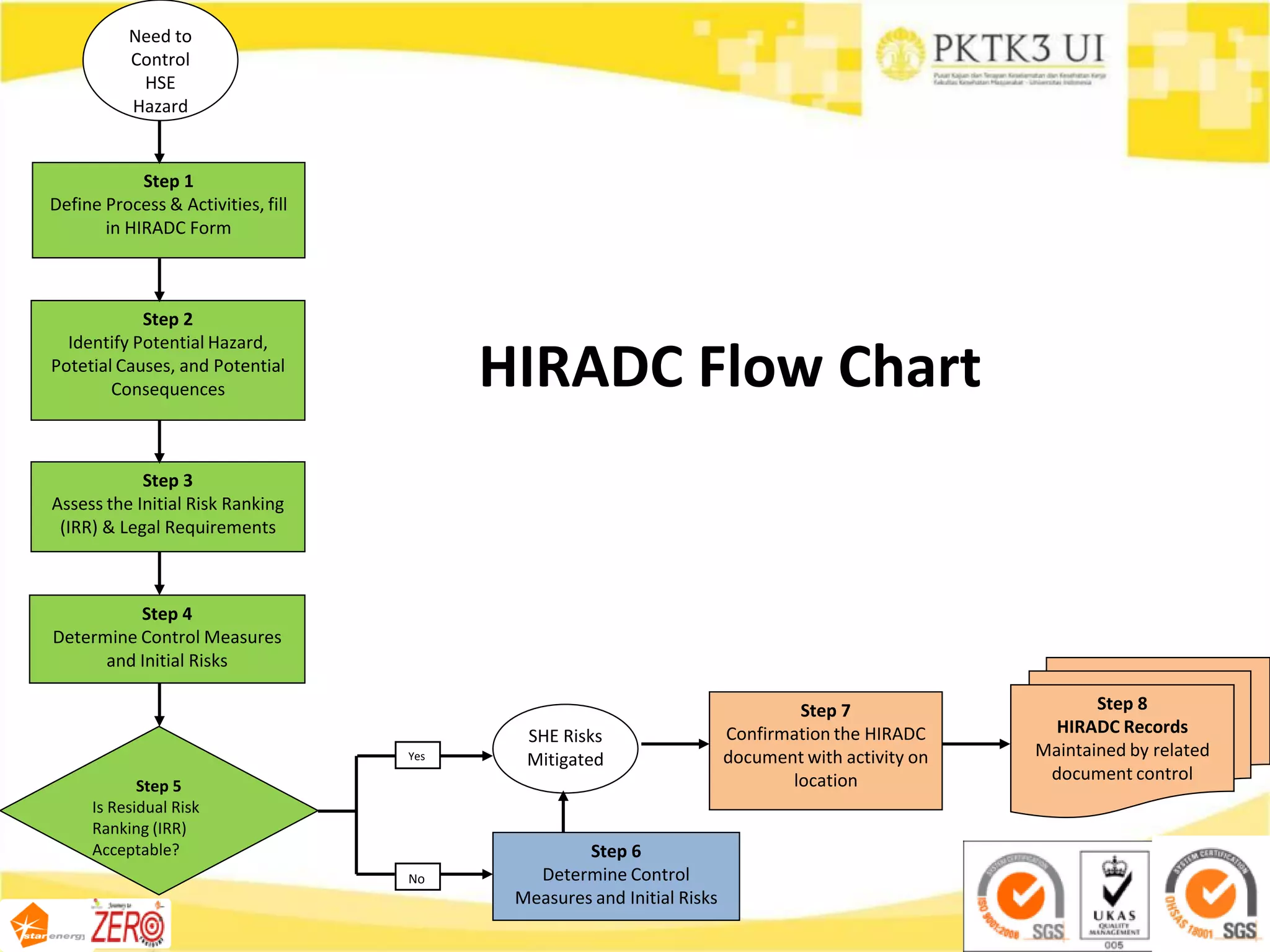
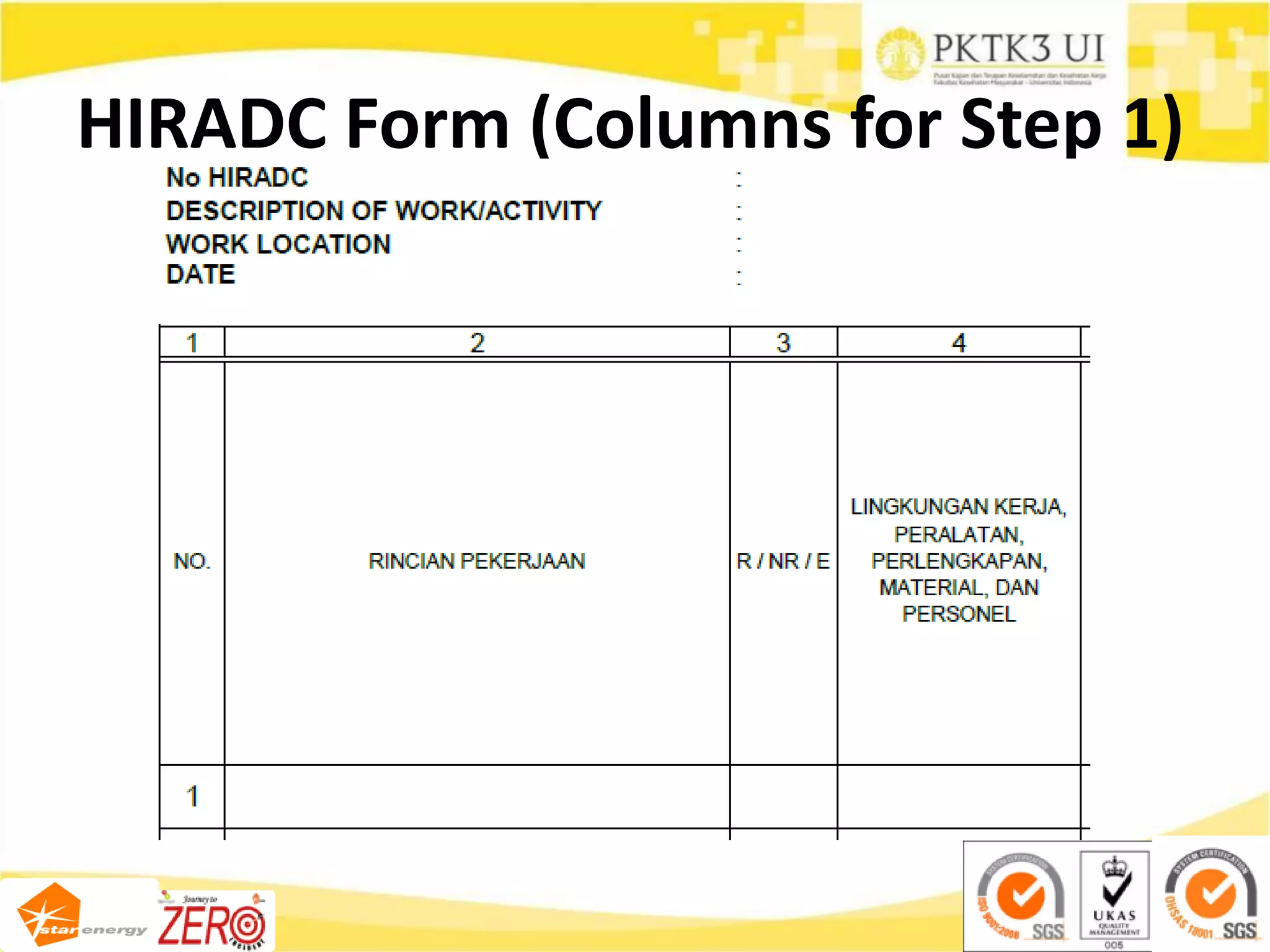
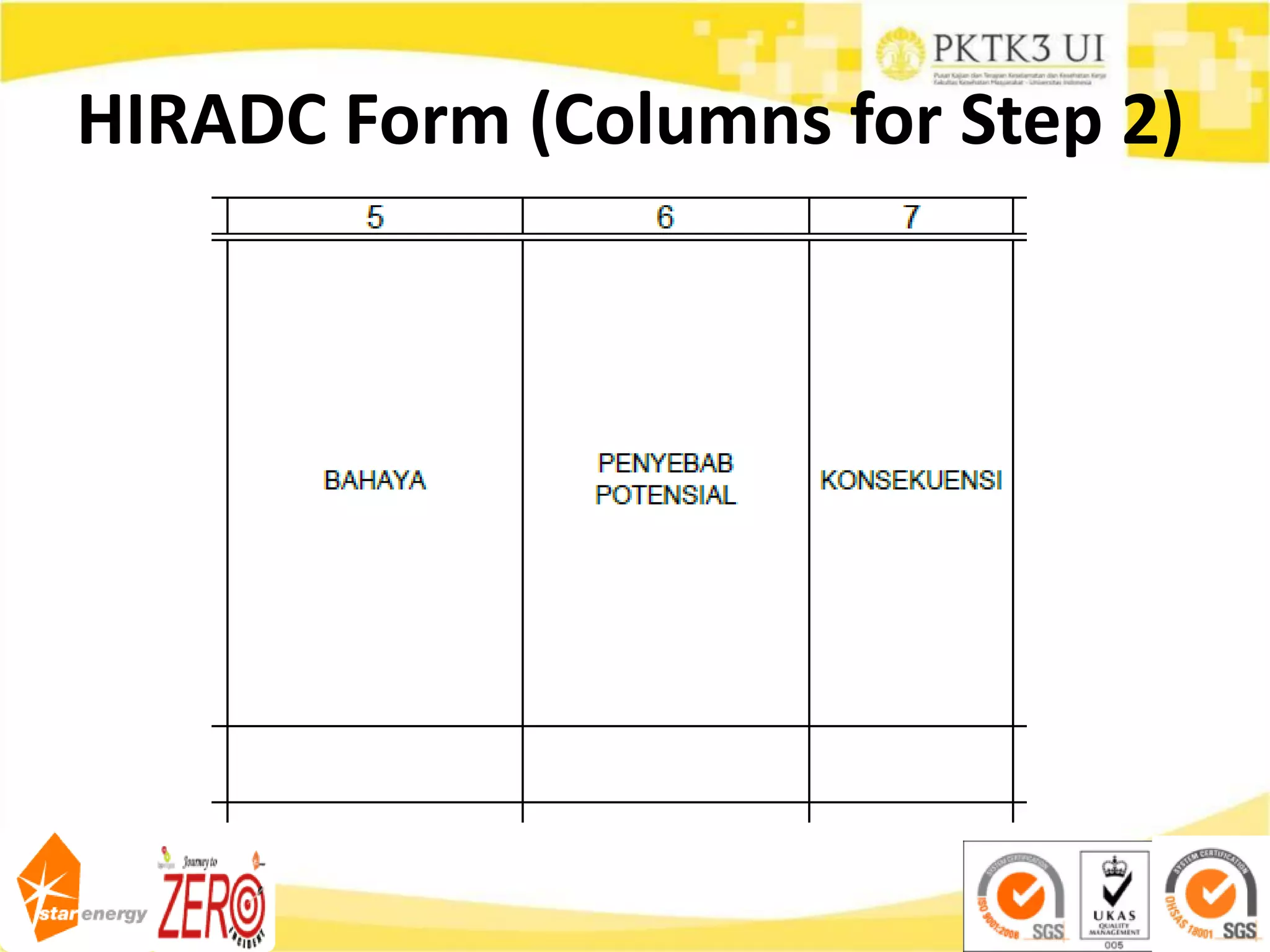
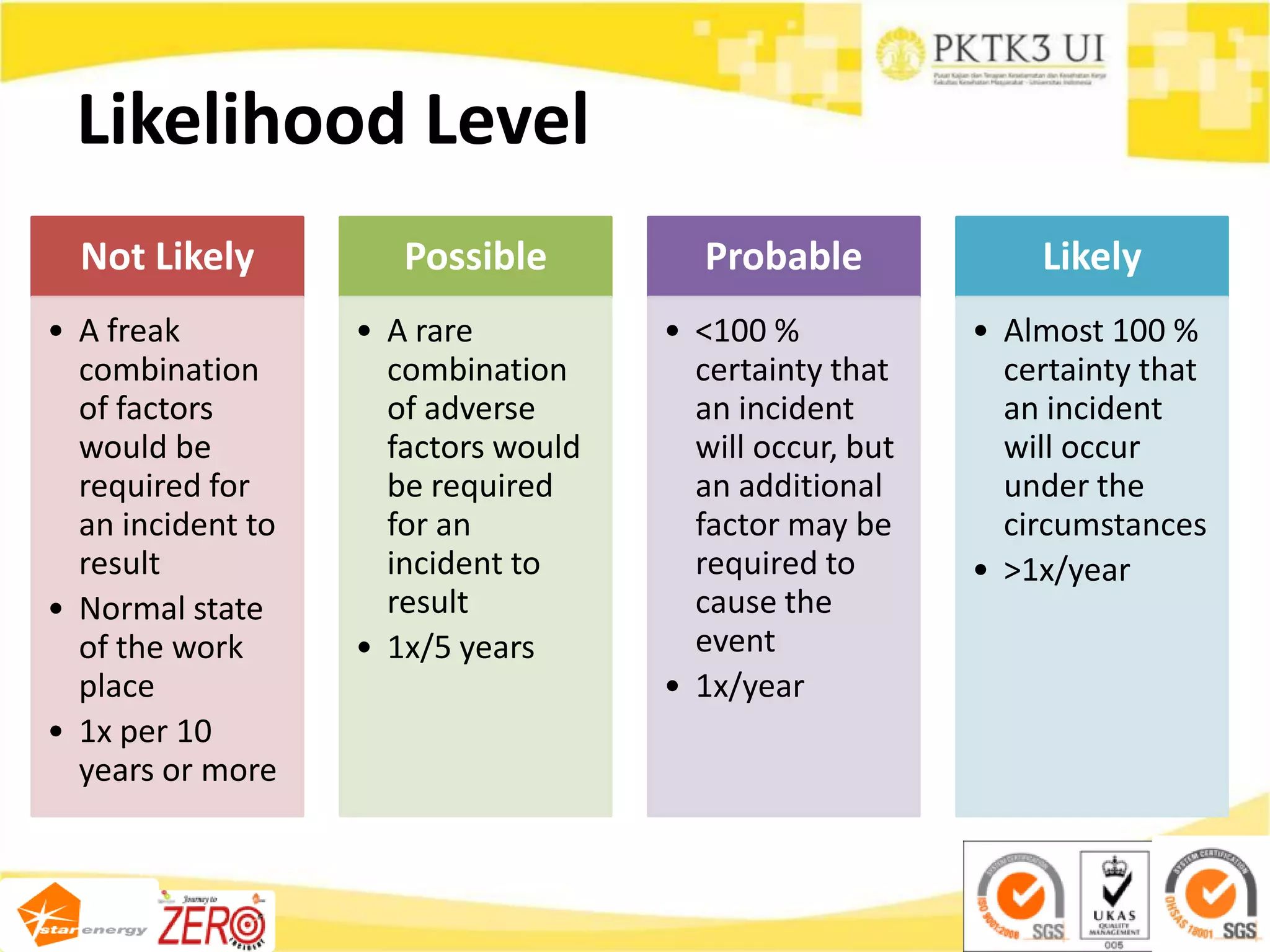
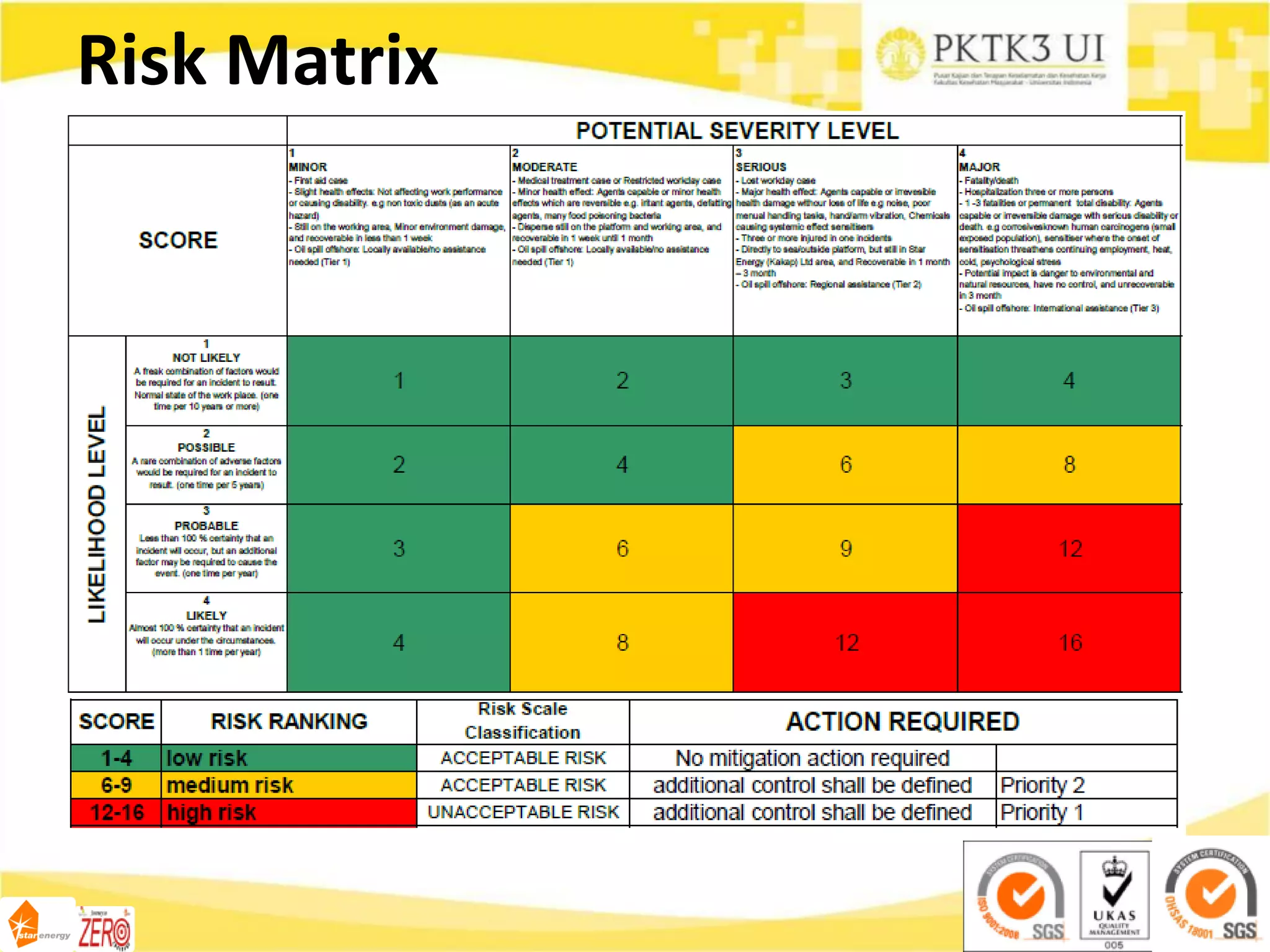
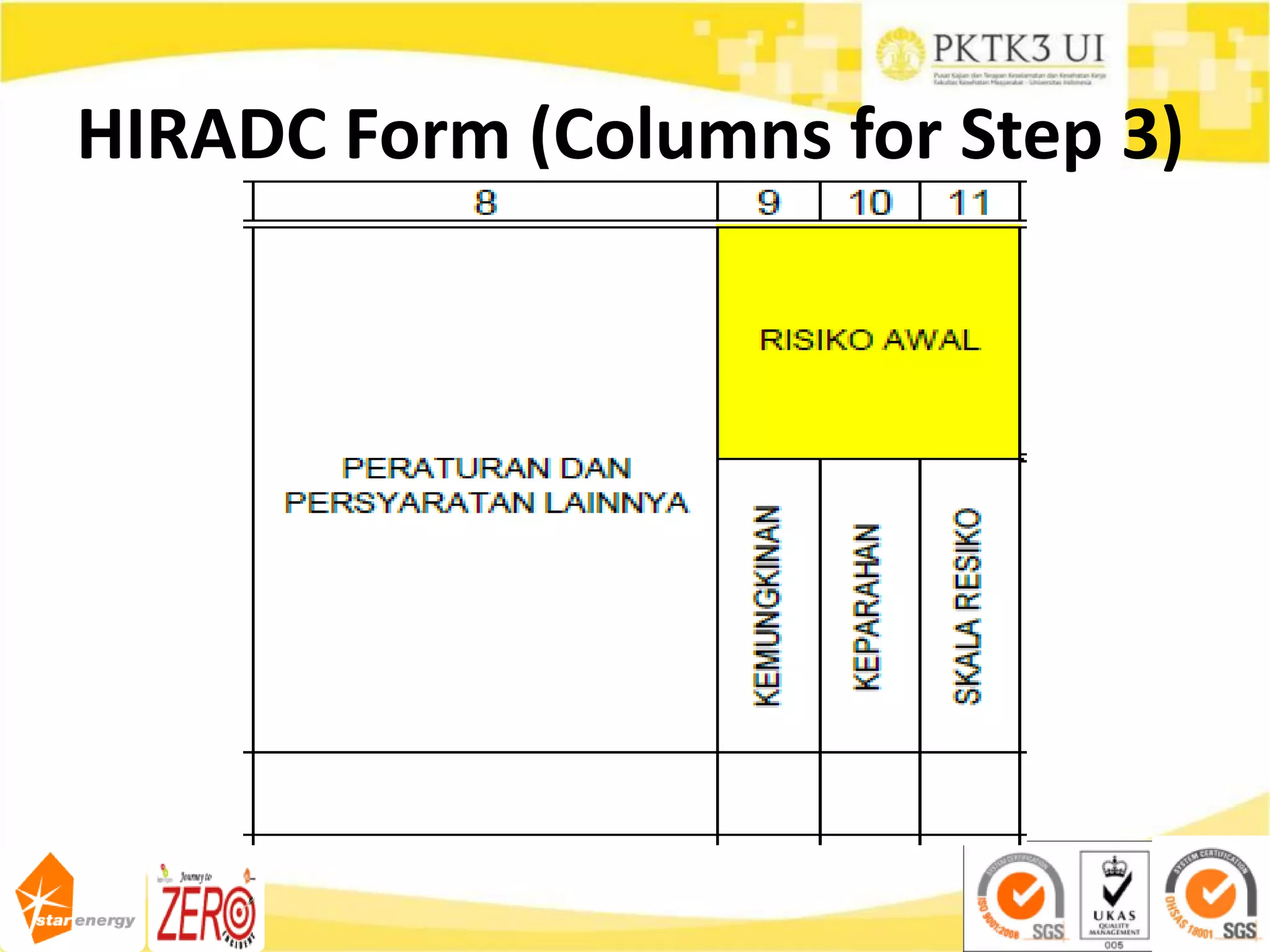
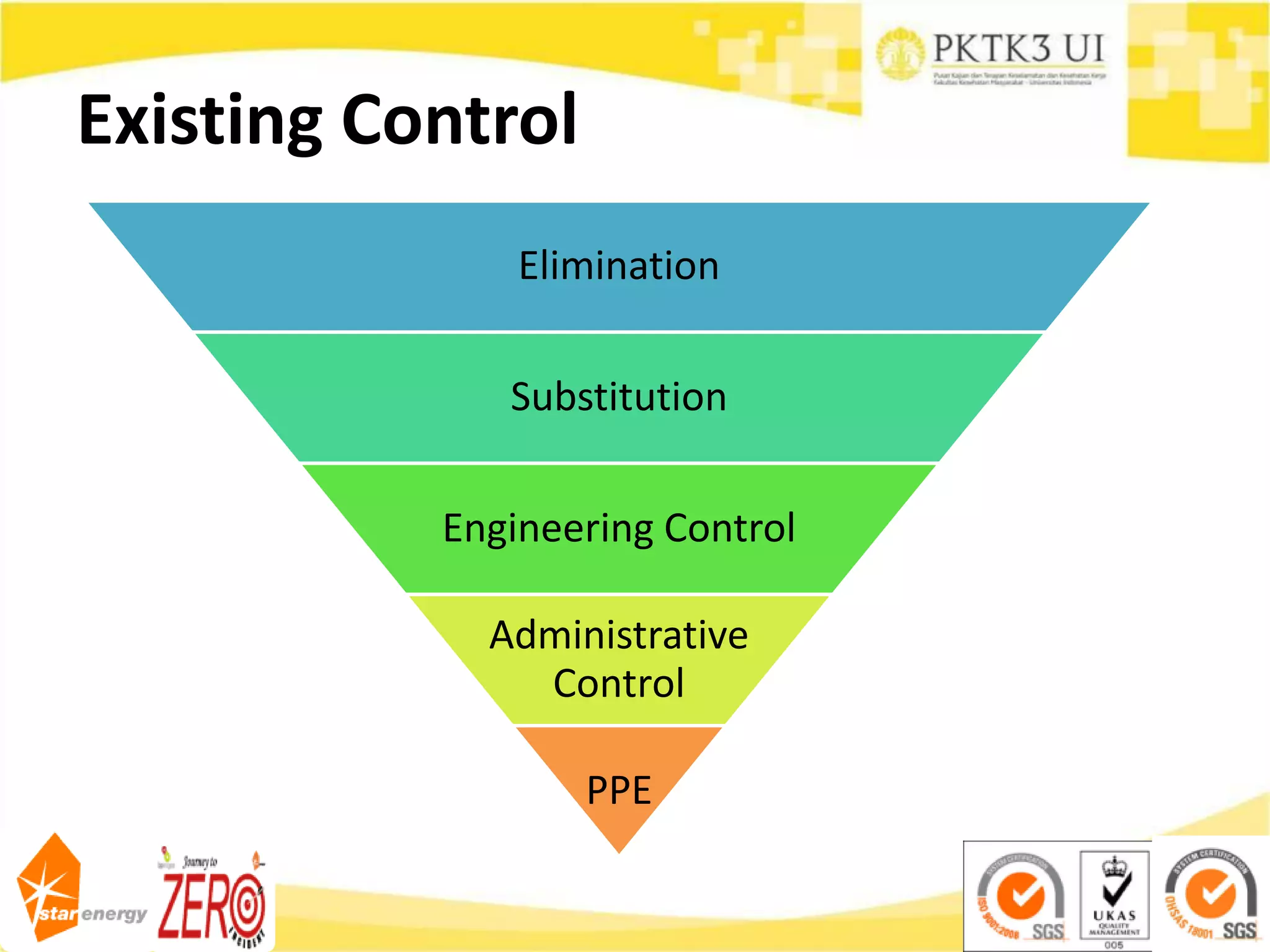
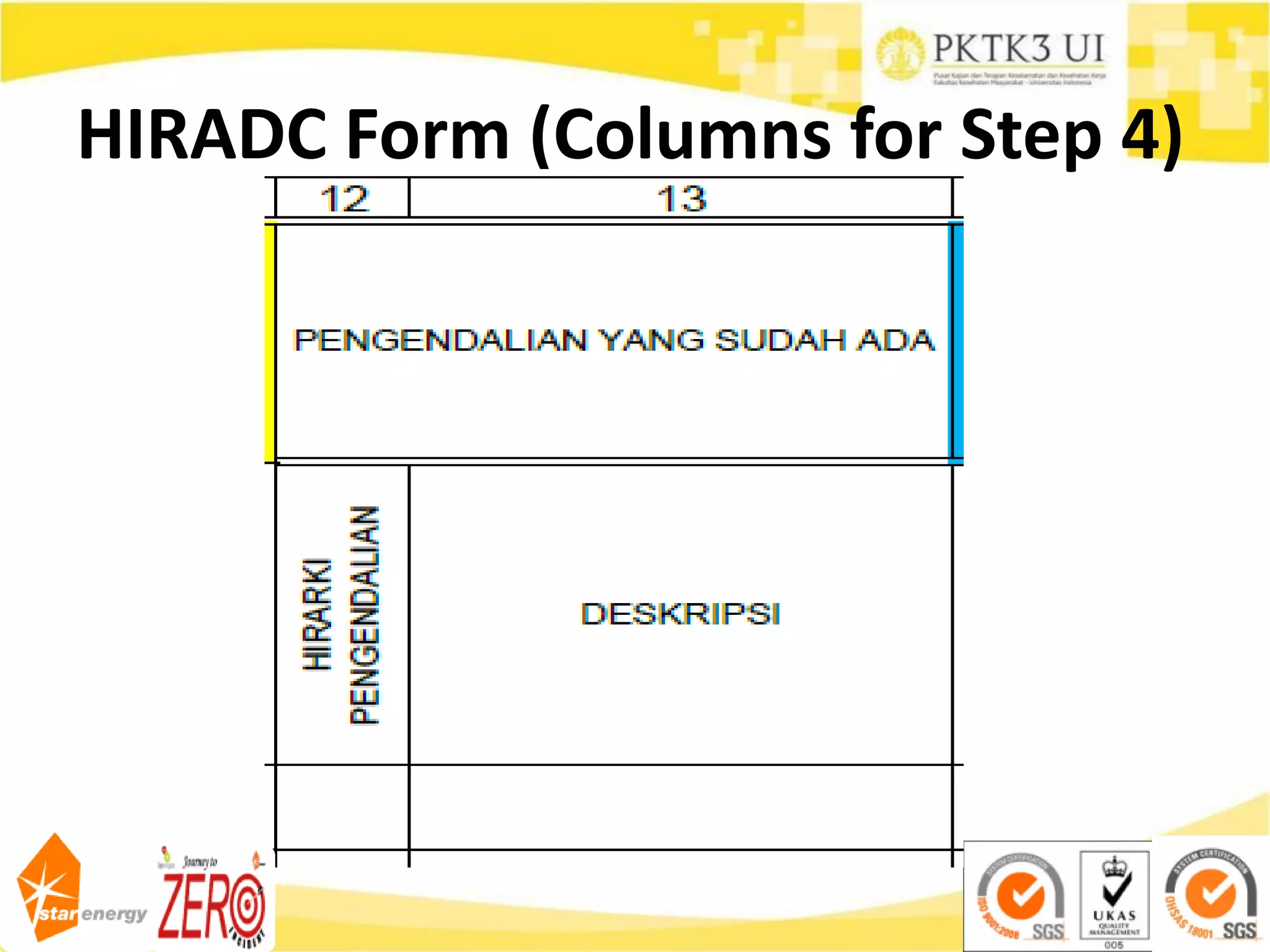
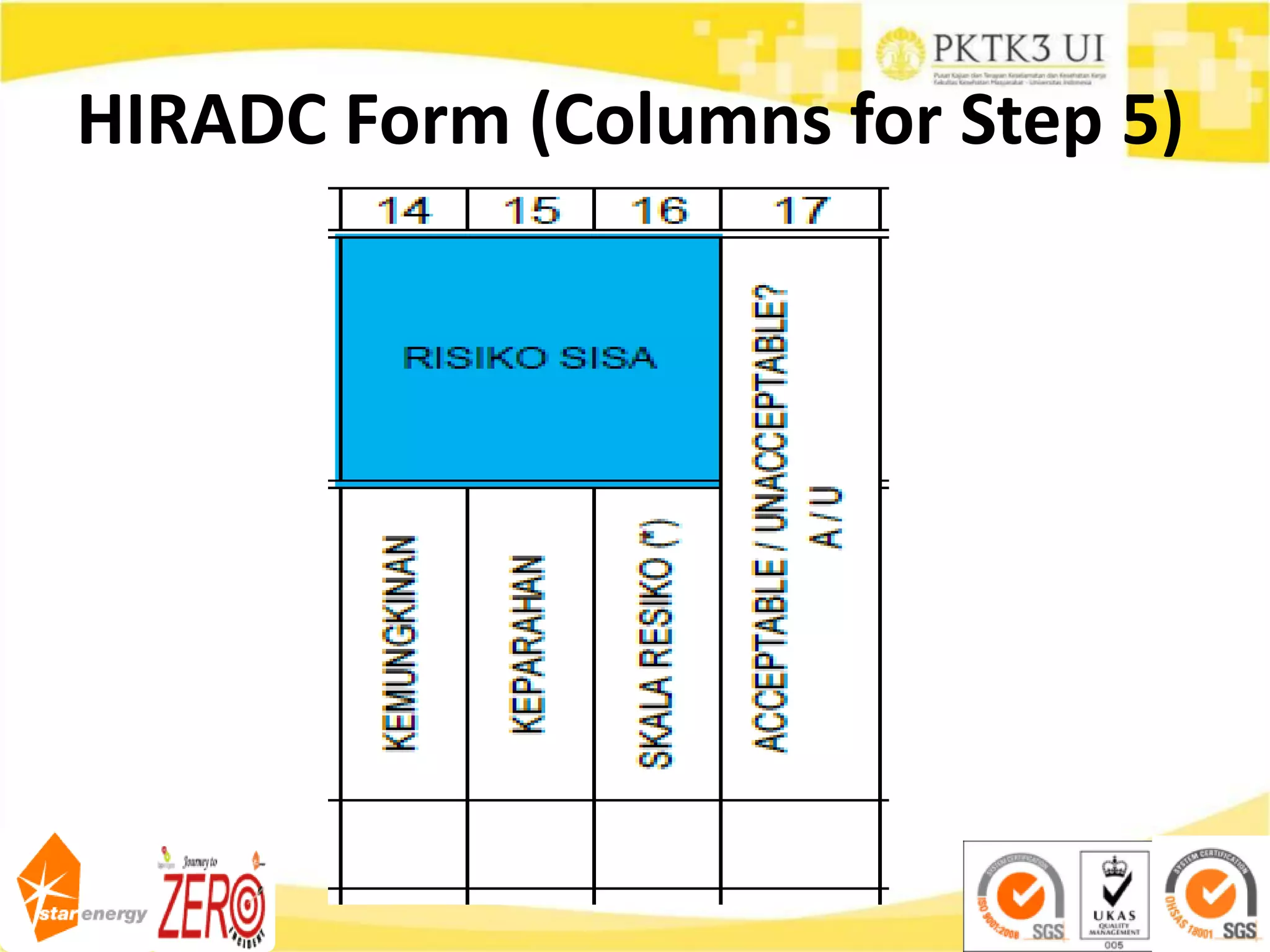
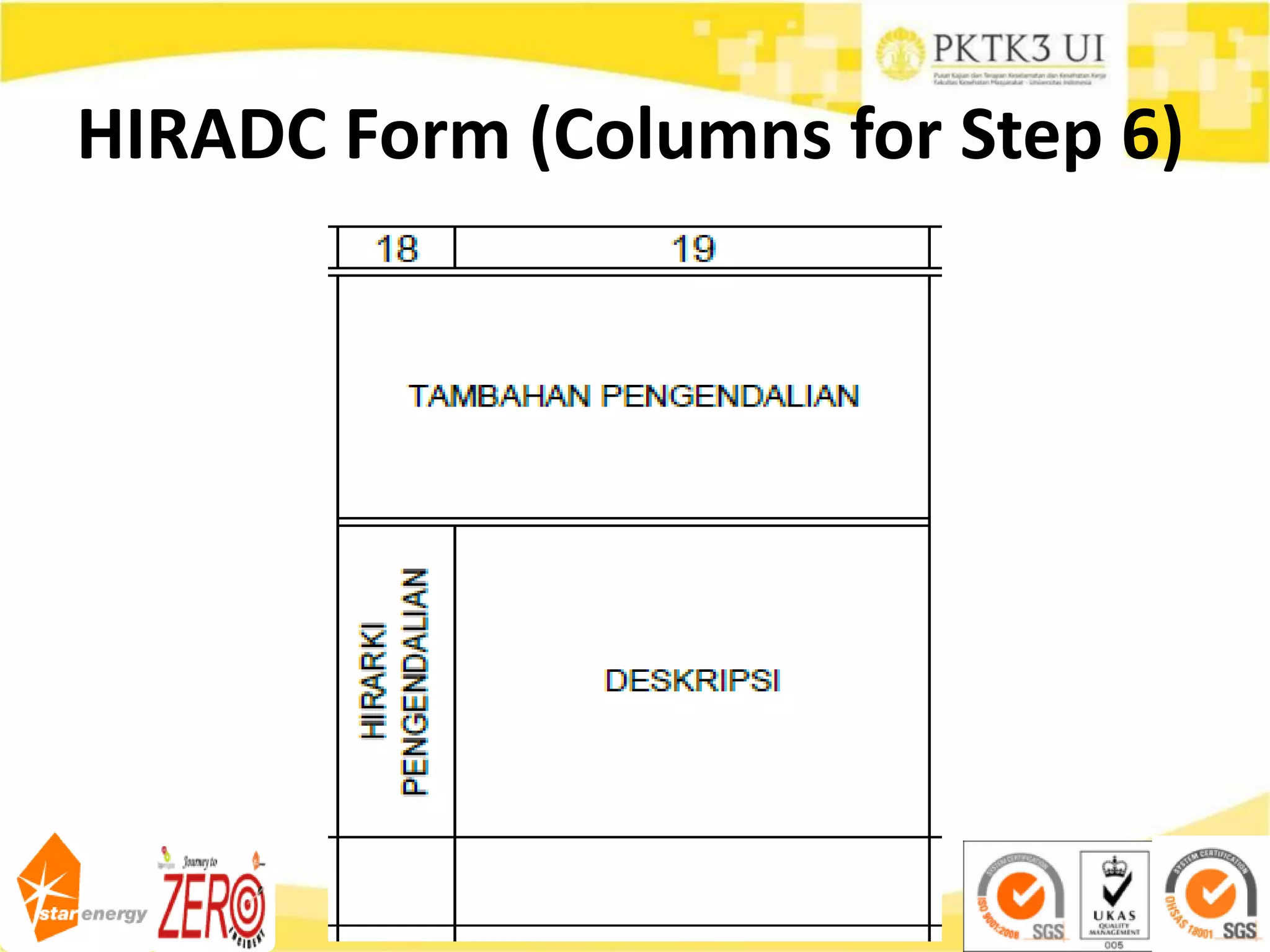
This document provides an overview of hazard identification, risk assessment, and determining risk controls (HIRADC) training. It outlines the 8-step HIRADC process, which includes defining activities, identifying hazards and risks, assessing initial risk ranking, determining control measures, evaluating residual risk, documenting the assessment, reviewing and confirming the assessment in the field, and maintaining HIRADC records. The goal of the process is to proactively identify and control risks to reduce them to acceptable levels in accordance with OHSAS 18001 and ISO 31000 standards.