The document discusses various modes of communication including telephones, ISDN, and CCTV. It provides details on:
- The history and evolution of telephones from Alexander Graham Bell's invention to modern cell phones.
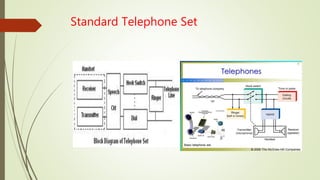
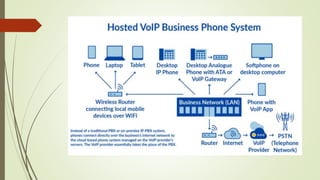
- How telephones work by converting sounds into electronic signals transmitted through cables.
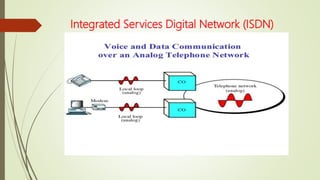
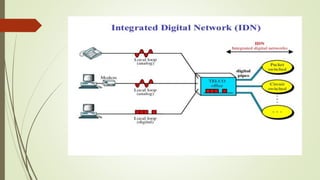
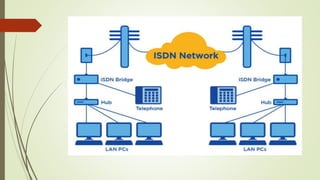
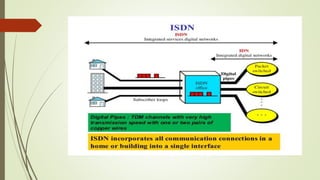
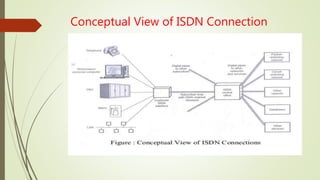
- What ISDN is and how it provides digital transmission of voice, video and data over telephone networks.
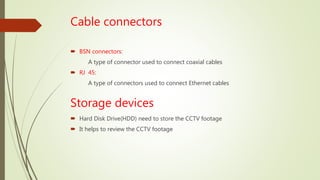
- The basic components and types of CCTV systems used to transmit video signals to monitors for security purposes.