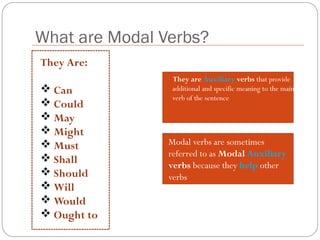
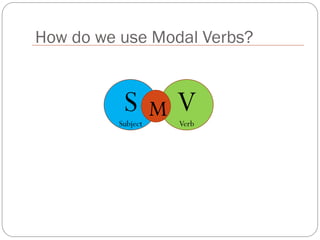
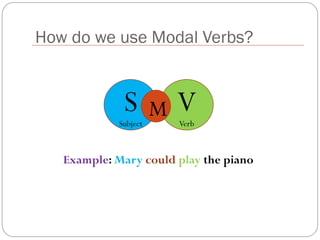
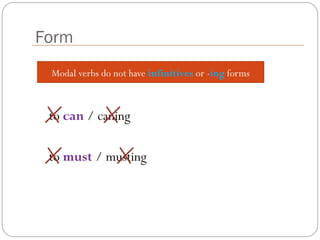
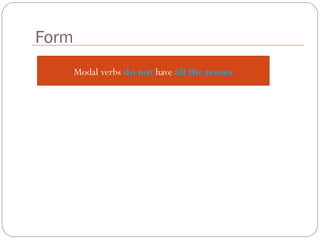
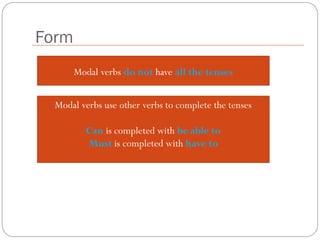
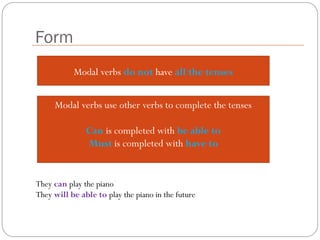
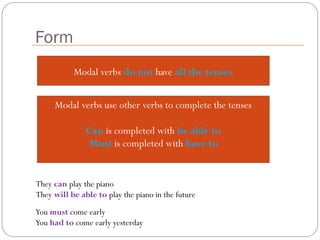
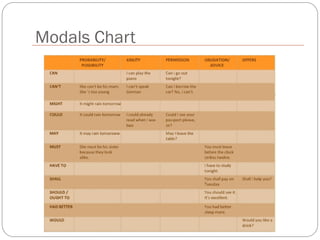
The document defines and explains modal verbs. It states that modal verbs are auxiliary verbs that provide additional meaning to the main verb of a sentence. Some common modal verbs are can, could, may, might, must, shall, should, will, would, and ought to. The document then discusses how modal verbs are used, including that they do not conjugate or use other auxiliary verbs. It also notes that modal verbs do not have infinitives, -ing forms, or all tenses. Modal verbs use other verbs like be able to or have to to complete their tenses. Finally, the document provides examples of modal verb usage.