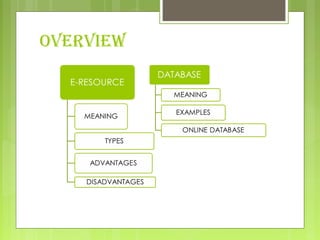
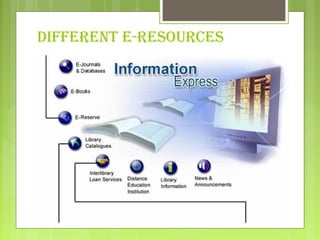
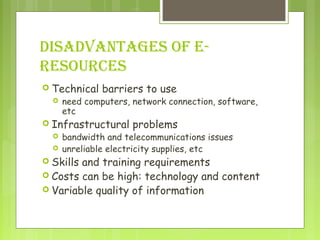
This document discusses different types of e-resources available through libraries. It defines e-resources as electronic data, programs, or combinations that can include various media types. Some key e-resources mentioned include research guides, electronic books and texts, electronic journals, library catalogs, reference sources, and image databases. Advantages of e-resources are the huge amount of timely and up-to-date information available, while disadvantages include technical barriers, infrastructure problems, skills requirements, and variable quality. Databases and online databases are also discussed, with examples provided.