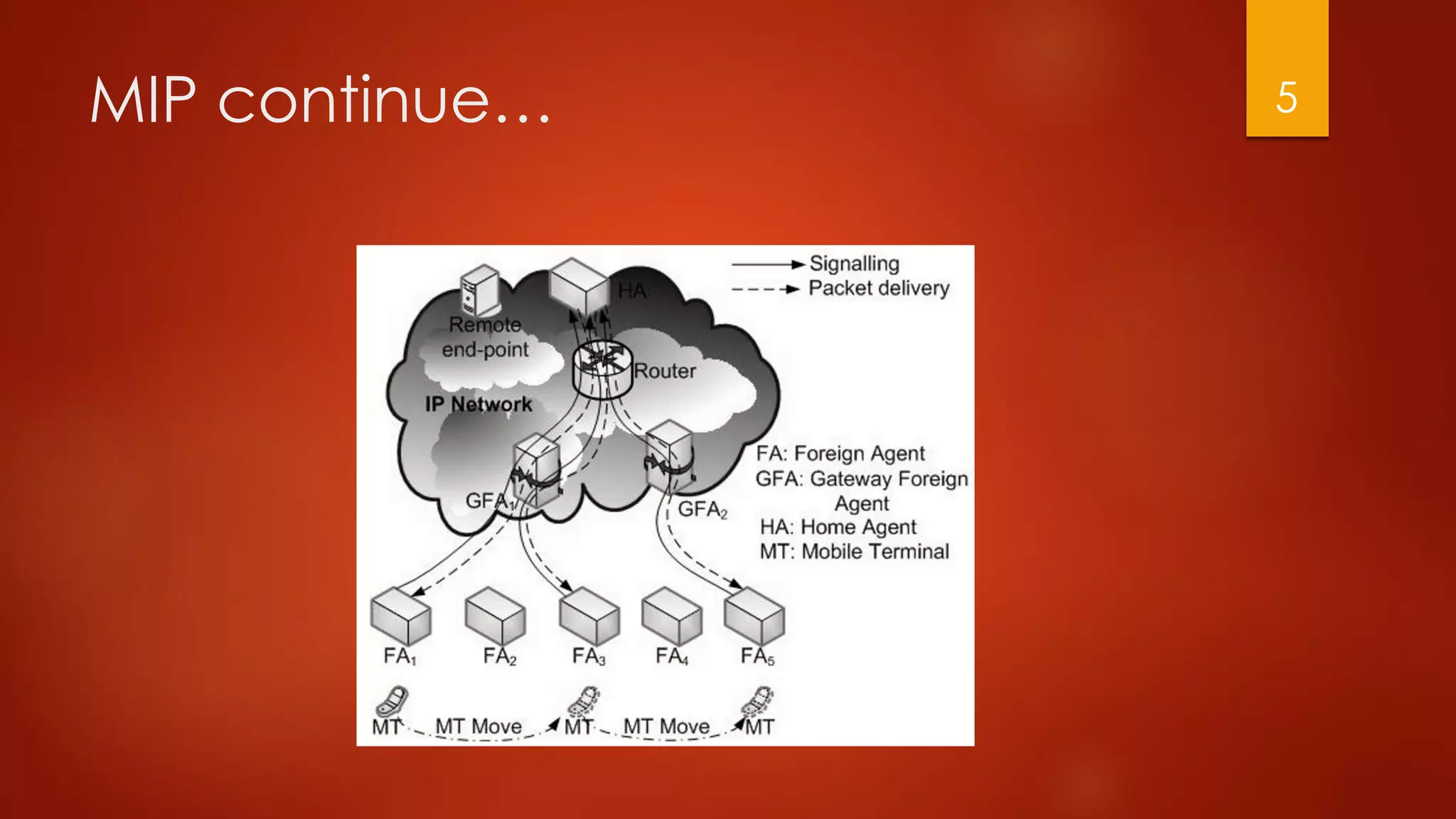
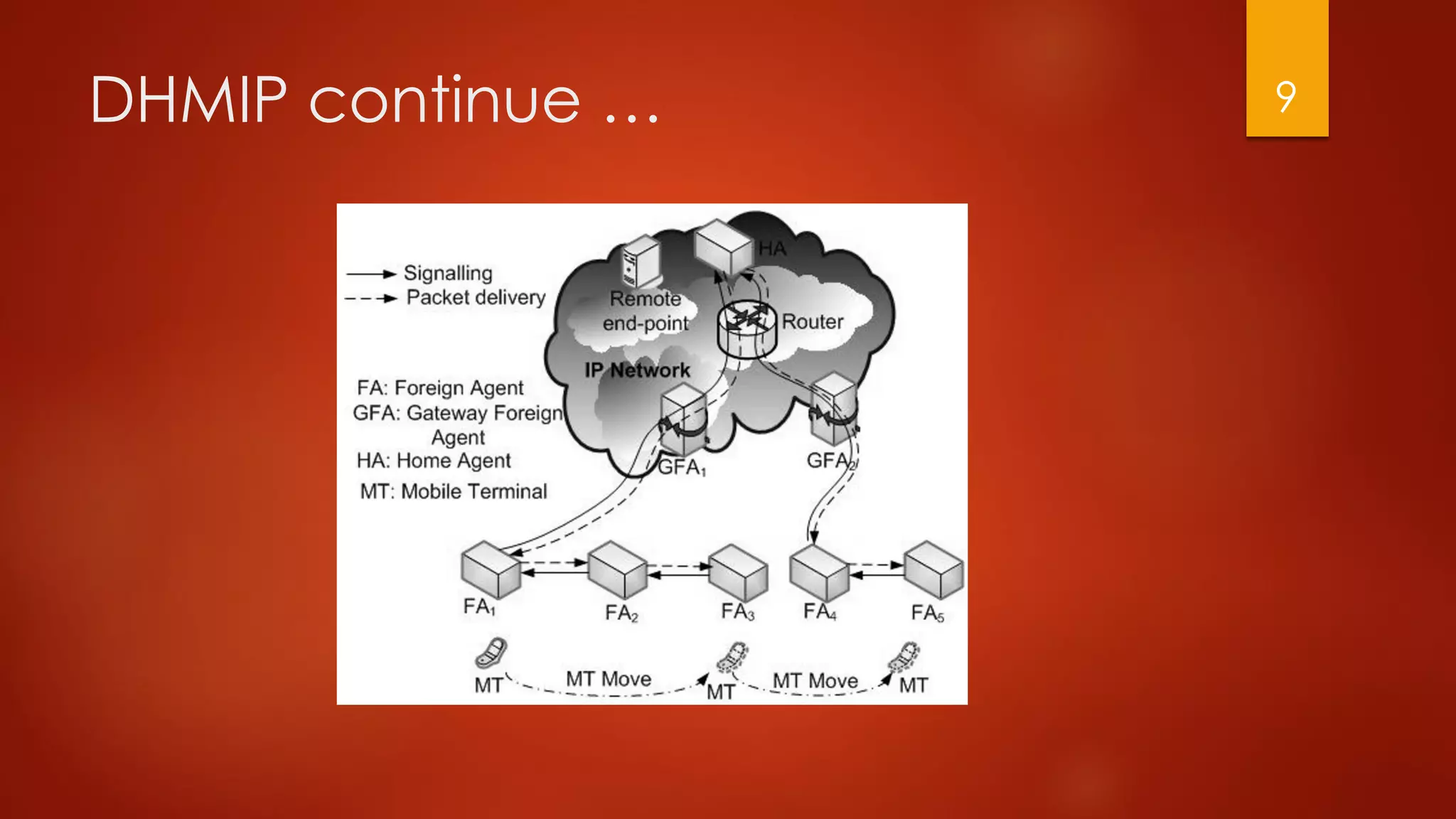
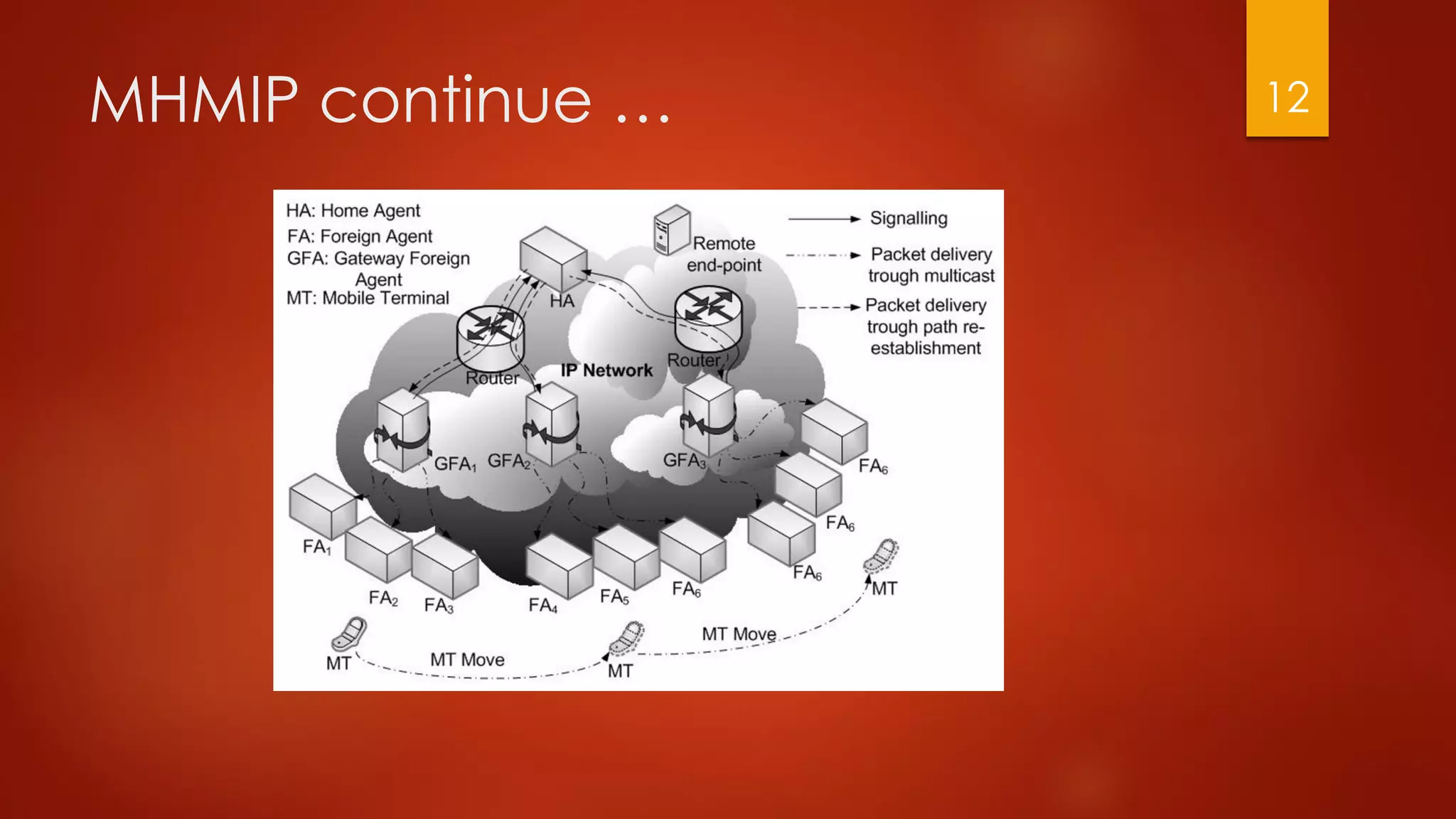
This document compares different approaches for mobile IP networks, including Mobile IP (MIP), Hierarchical Mobile IP (HMIP), Hierarchical Distributed Dynamic Mobile IP (HDDMIP), and Dynamic Hierarchical Mobile IP (DHMIP). It also discusses multicast-based approaches like Multicast Hierarchical Mobile IP (MHMIP). An analysis shows that MHMIP provides the best performance for mean handoff delay and mean bandwidth per call for high mobility terminals. It is recommended to use MHMIP for most cases, but to use DHMIP if inter-gateway foreign agent handoffs are frequent or the number of links in the MHMIP path is high.