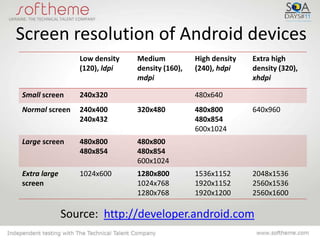
The document discusses the transition from web testing to mobile application testing, highlighting the growth of mobile platforms and the need for compatibility checks across various devices and screen resolutions. It outlines objectives for testing, methods for evaluating both mobile websites and applications, and the pros and cons of different testing approaches, including the use of real devices, emulators, and remote access services. The conclusion states that mobile application testing is easy to perform and plan but comes with challenges due to the variety of models and operating systems.