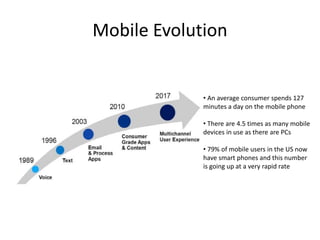
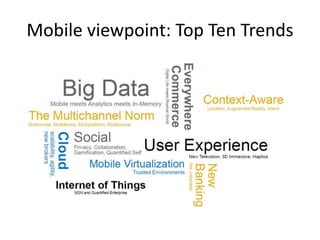
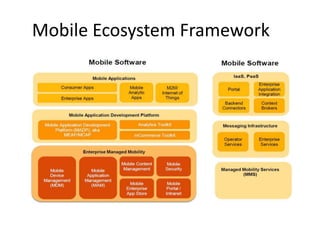
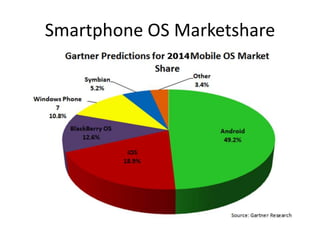
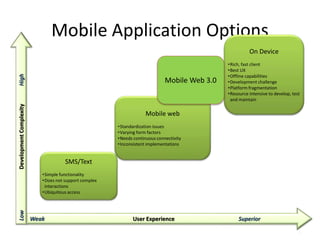
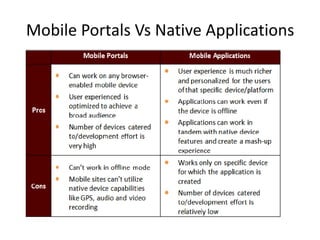
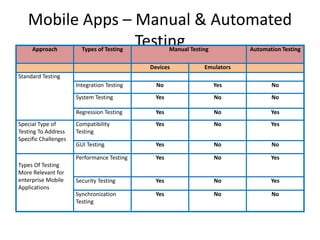
This document discusses mobile application testing. It begins with an introduction to the author's experience in mobile development and quality assurance. It then covers trends in mobile technology and applications. The main sections discuss approaches to testing mobile applications, including requirement analysis, challenges for different mobile platforms, and focus areas for testing like performance, security and compatibility. Automated and manual testing strategies are also outlined.