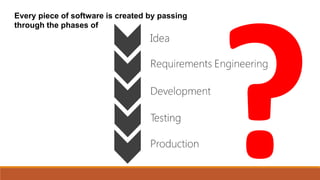
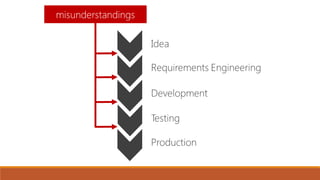
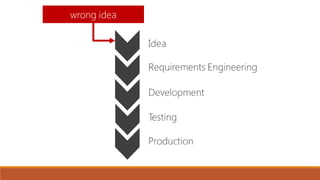
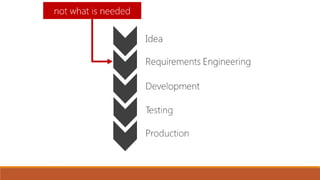
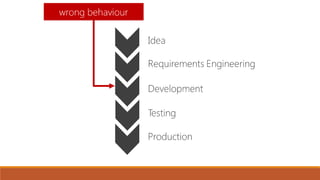
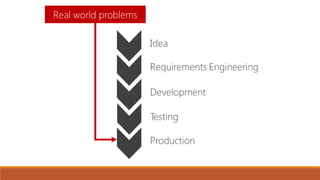
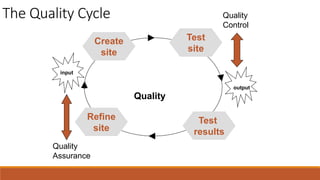
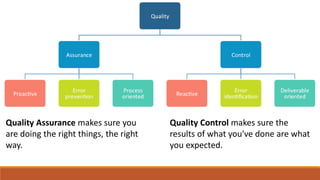
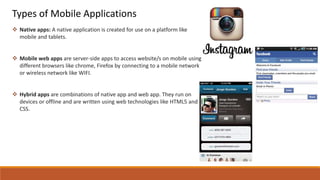
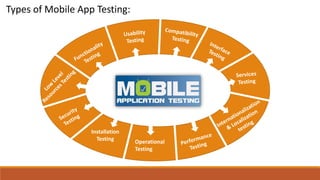
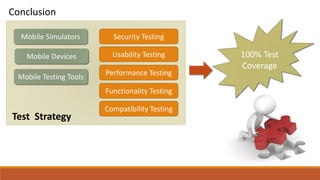
The document discusses the importance of quality assurance (QA) and quality control (QC) in mobile application development, emphasizing that QA ensures products meet user satisfaction while QC focuses on testing and validating the product's quality. It highlights various types of mobile testing, including hardware and software tests, as well as the different categories of mobile applications such as native, mobile web, and hybrid applications. The document also outlines mobile application testing strategies, challenges, and considerations for testing on various devices and networks.