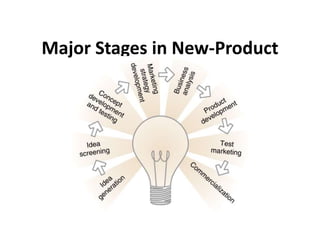
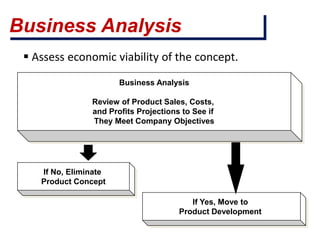
This document outlines the key stages in the new product development (NPD) process. It begins with generating ideas for new products, which can come from internal or external sources. Ideas are then screened according to criteria like market size and development costs. Successful concepts are developed and test marketed to customers. If testing goes well, the product proceeds to commercialization with a full market launch. The NPD process helps companies focus their resources on projects most likely to be rewarding and brings products to market more quickly. It describes common challenges in NPD like defining specifications and managing resources and timelines, and how to overcome them through practices like prioritizing projects and involving all company functions early.