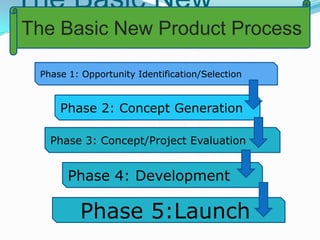
The document discusses new product development (NPD) processes and challenges. It describes the typical 5 phase NPD process: 1) opportunity identification, 2) concept generation, 3) concept evaluation, 4) development, and 5) launch. It also discusses concurrent engineering across functions, ensuring products contribute to business goals, and managing multiple projects. Common reasons for new product failure include small markets, poor fit with company strengths, lack of benefits, and inadequate support. Not all new products come from planned processes, as some result from accidental discoveries later recognized as opportunities.