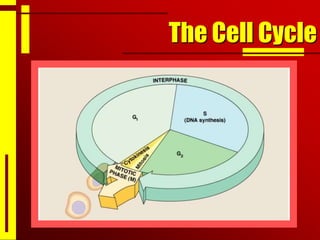
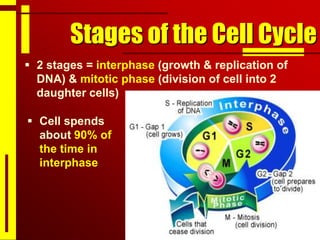
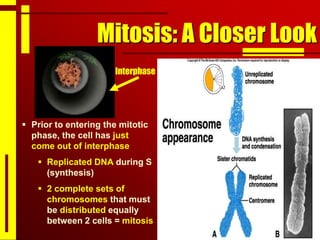
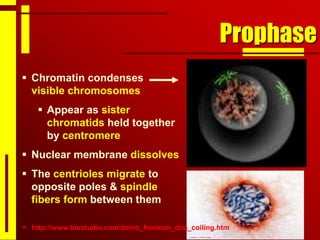
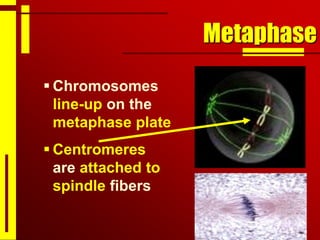
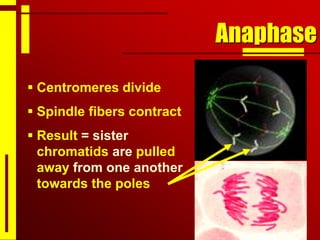
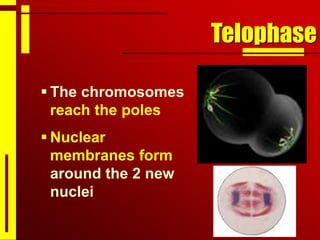
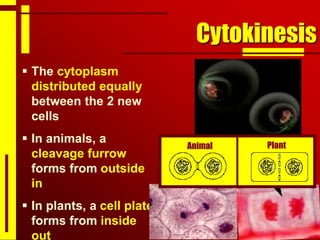
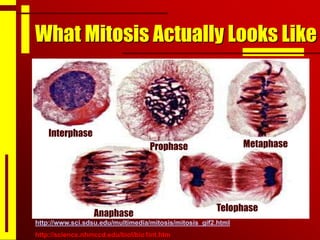
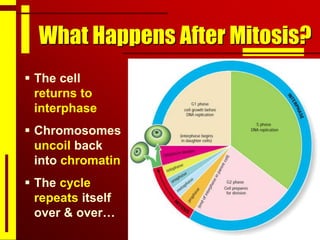
Cells undergo cell division through mitosis in order to distribute replicated DNA equally between two daughter cells. Mitosis consists of four stages - prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase - where the chromosomes condense, align at the center, separate, and reach opposite poles. Cytokinesis then partitions the cytoplasm between the two new cells. The number of times a cell can divide is limited and cell division decreases with age, leading eventually to cell death.