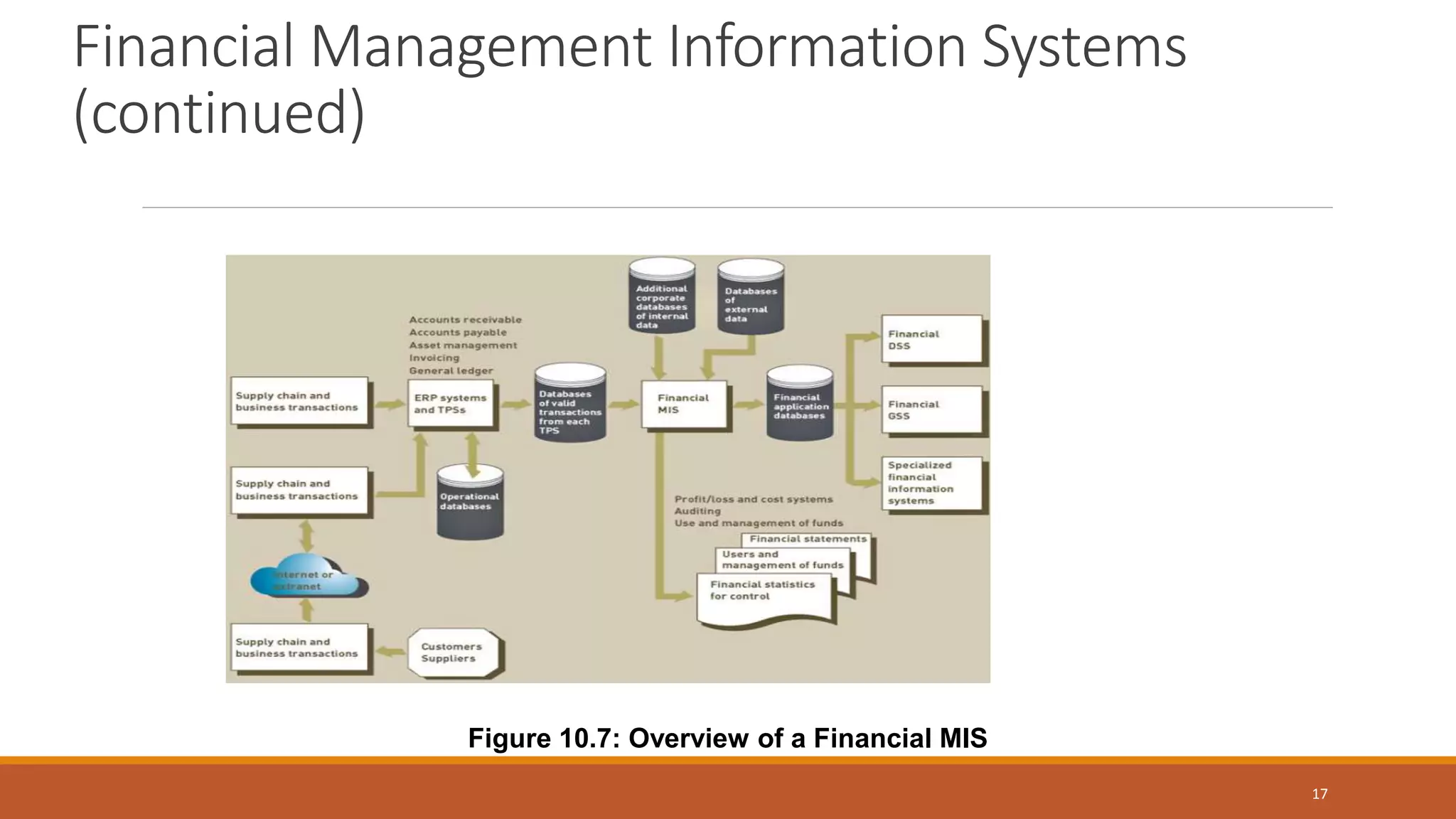
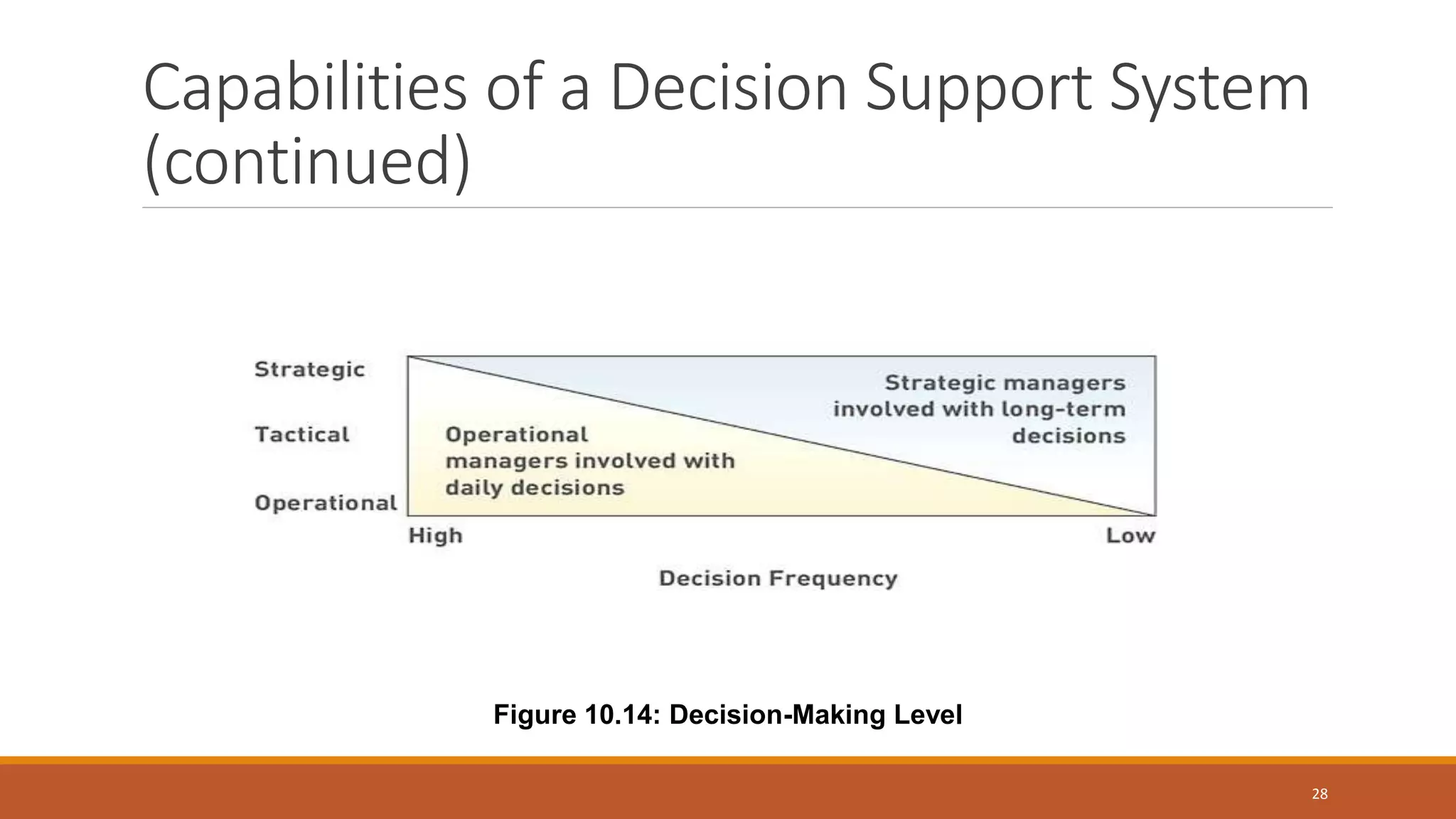
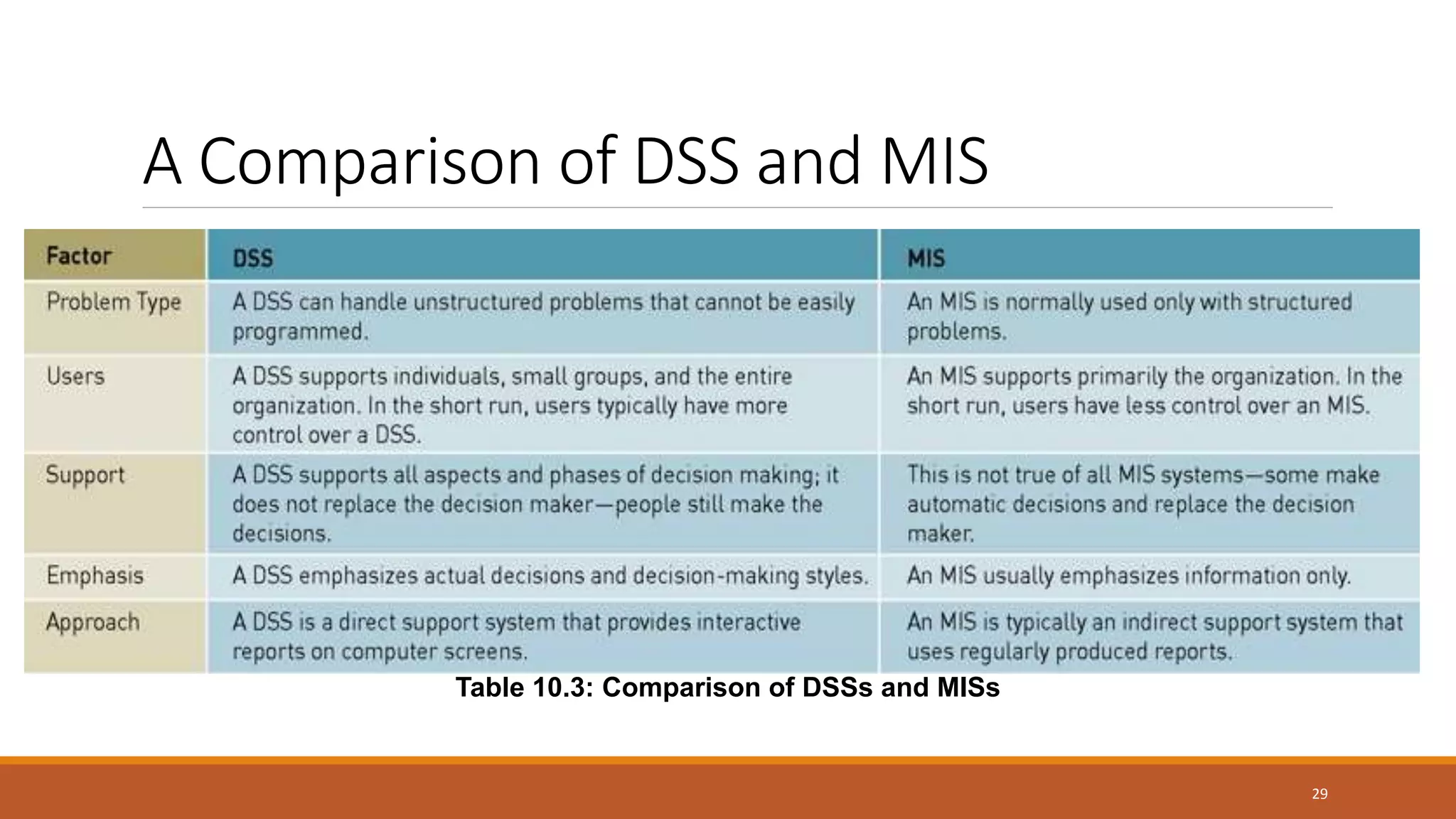
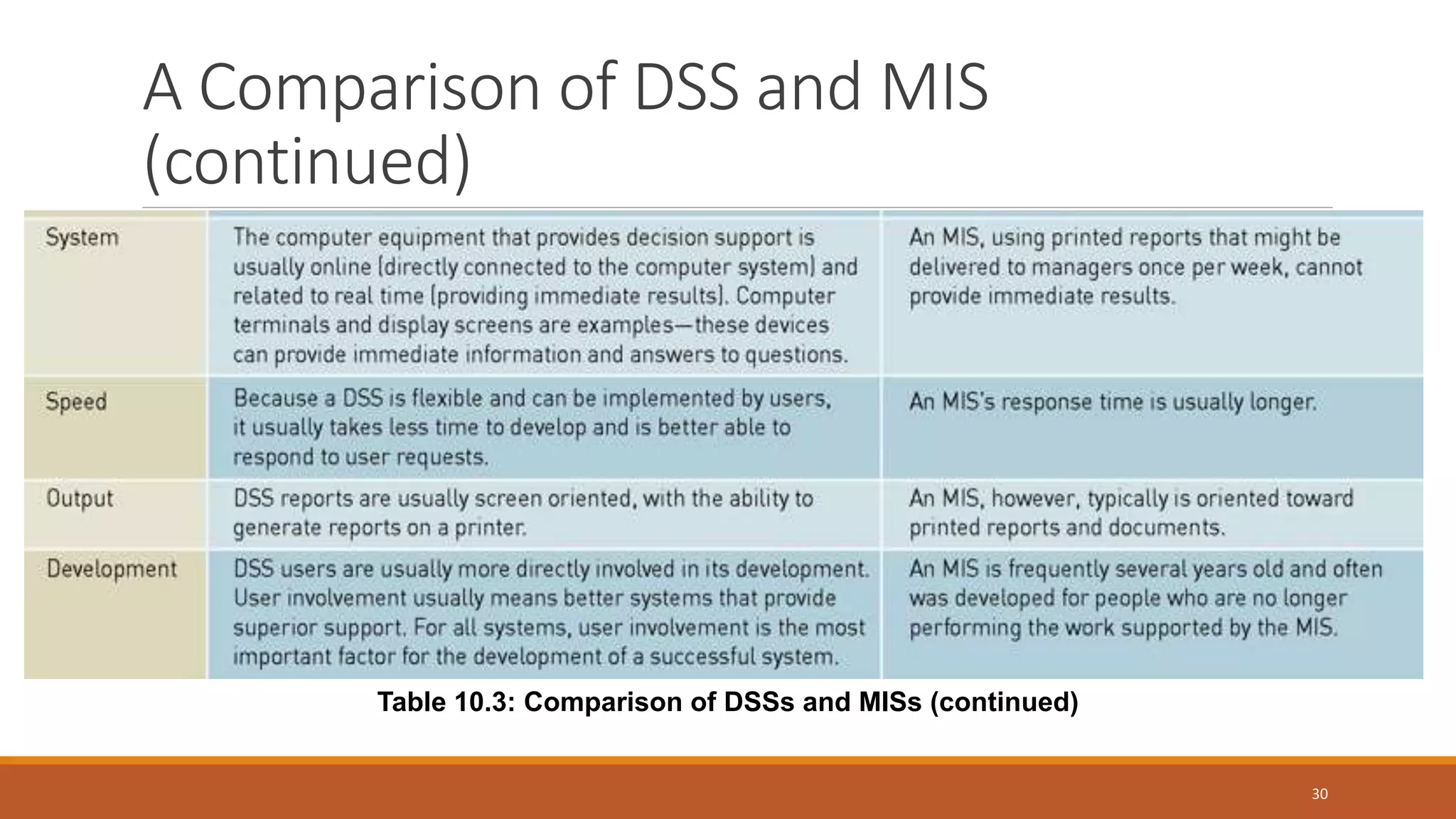
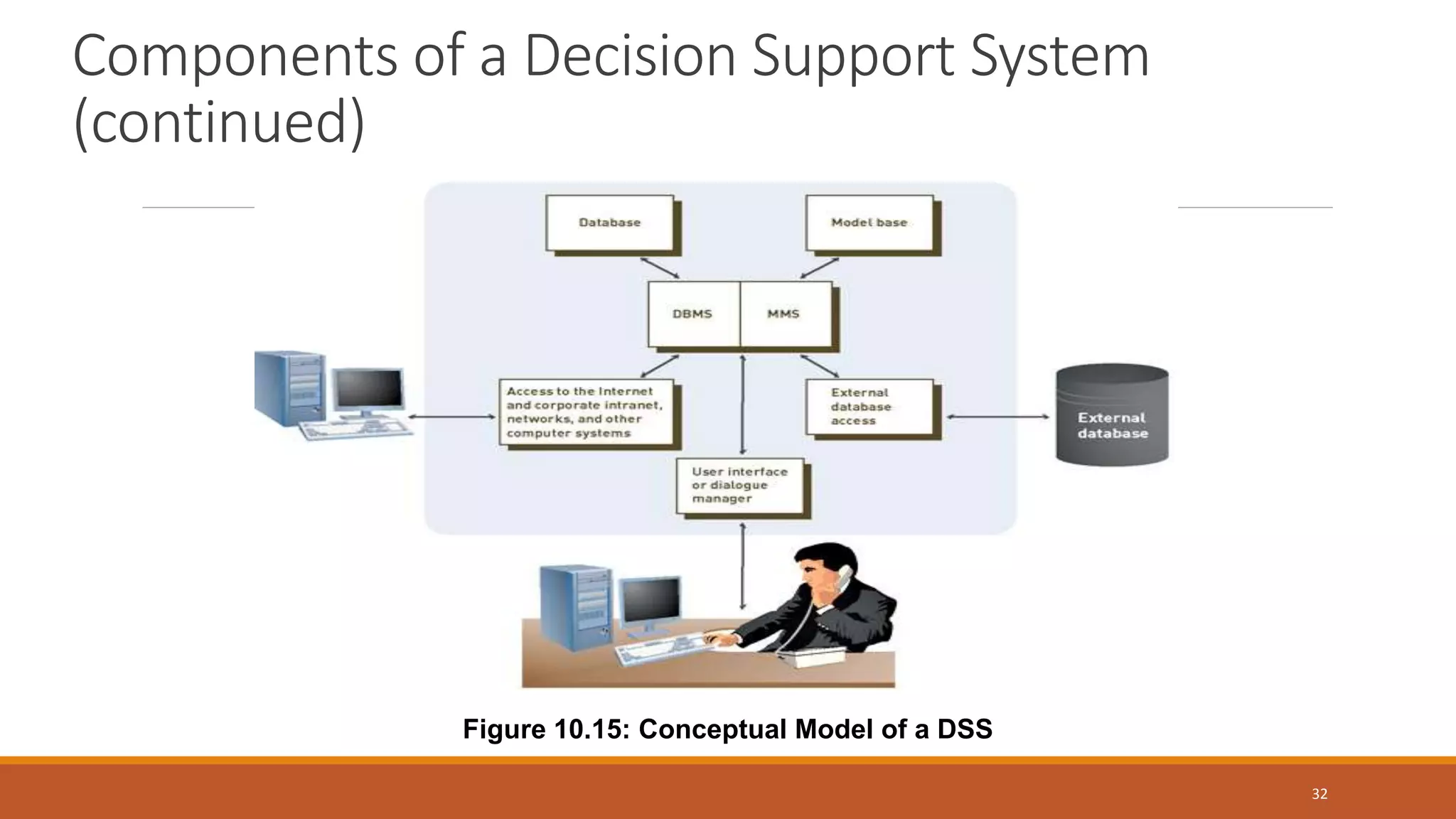
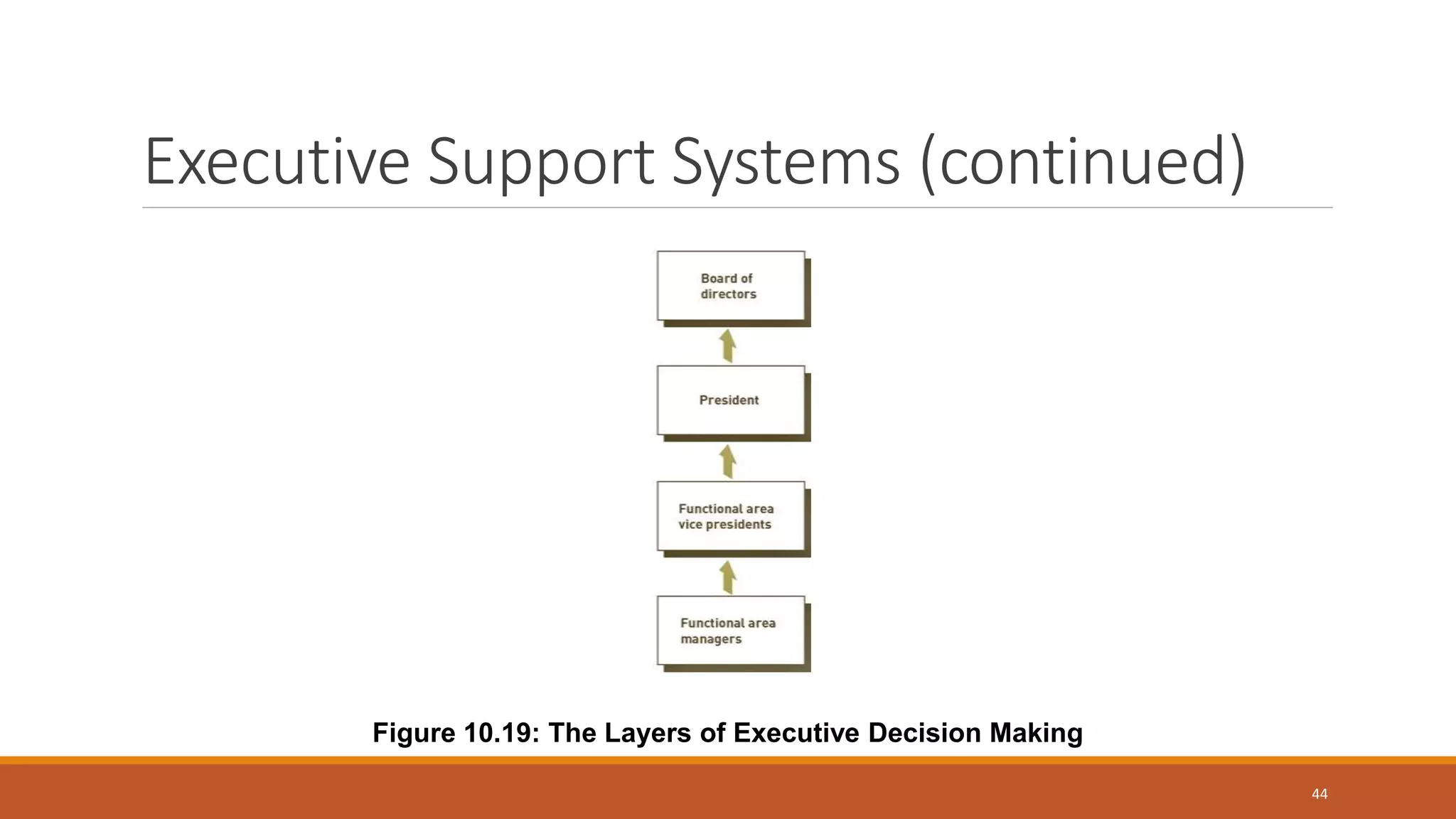
A Decision Support System (DSS) is a computer-based information system that aids organizational decision-making by integrating software applications and hardware. It consists of various components, including databases and model bases, and facilitates structured and unstructured decision-making processes while distinguishing between programmed and non-programmed decisions. DSS provides benefits such as improved decision accuracy and timeliness while also facing challenges like information overload and potential costs.