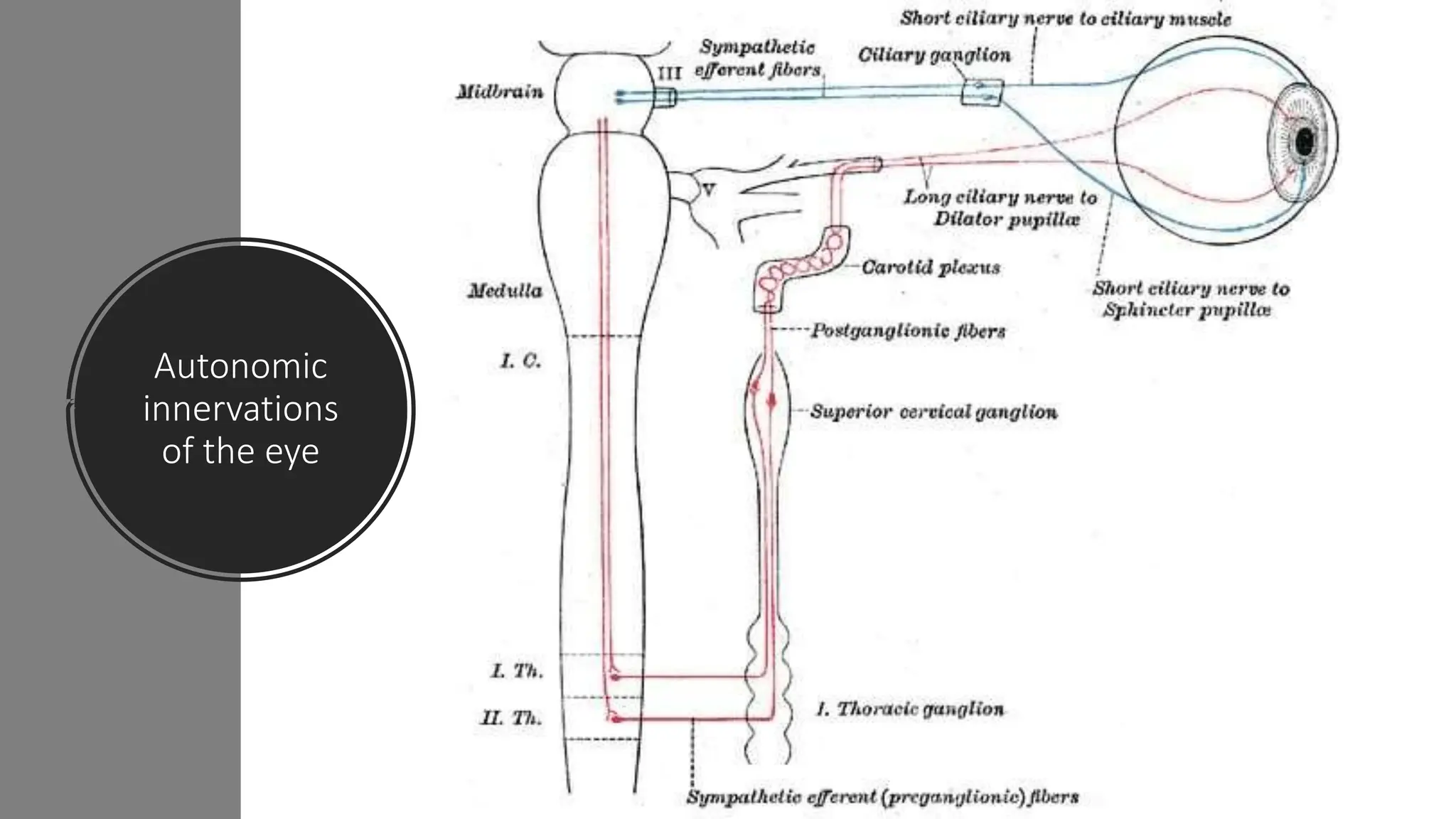
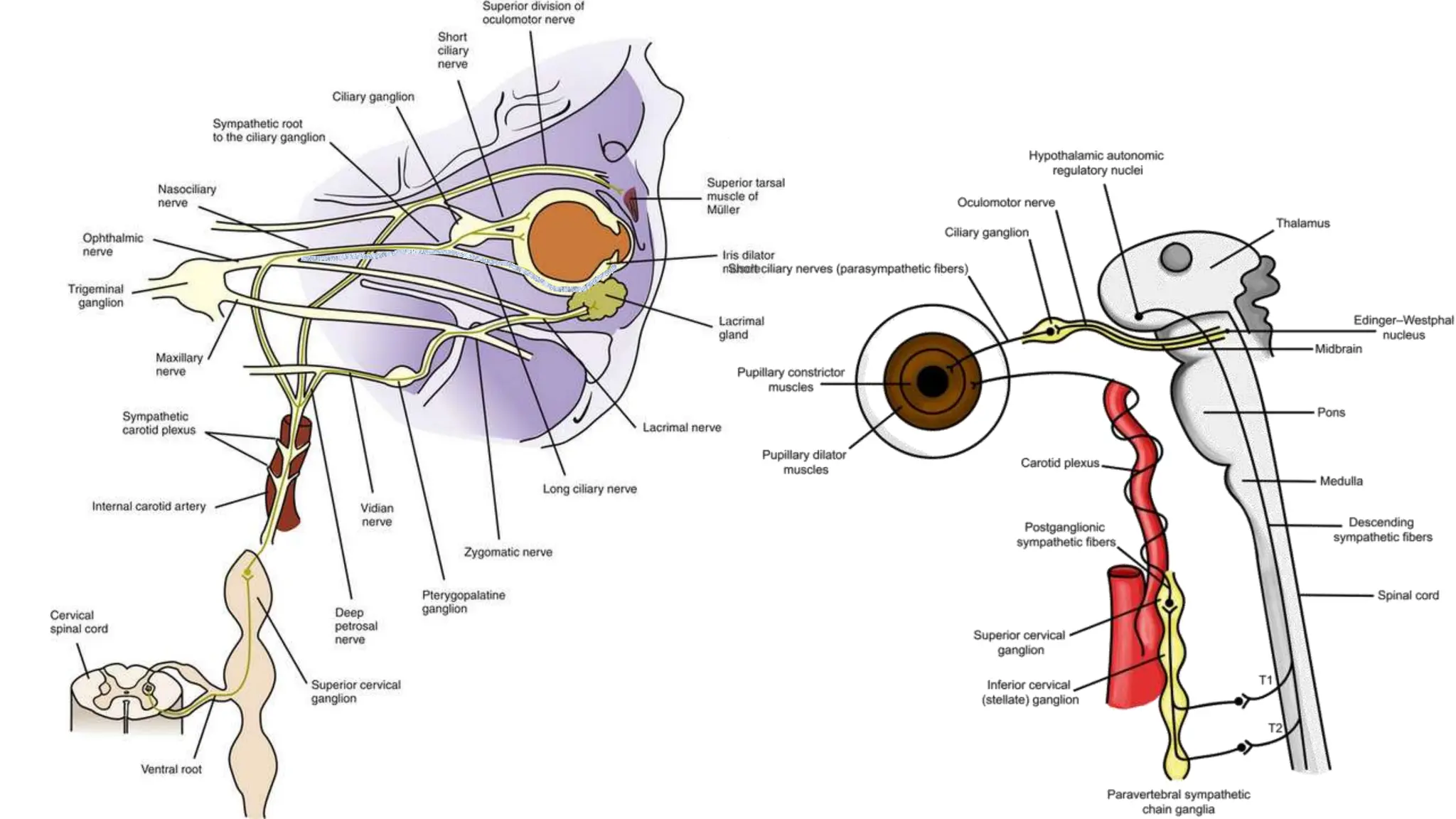
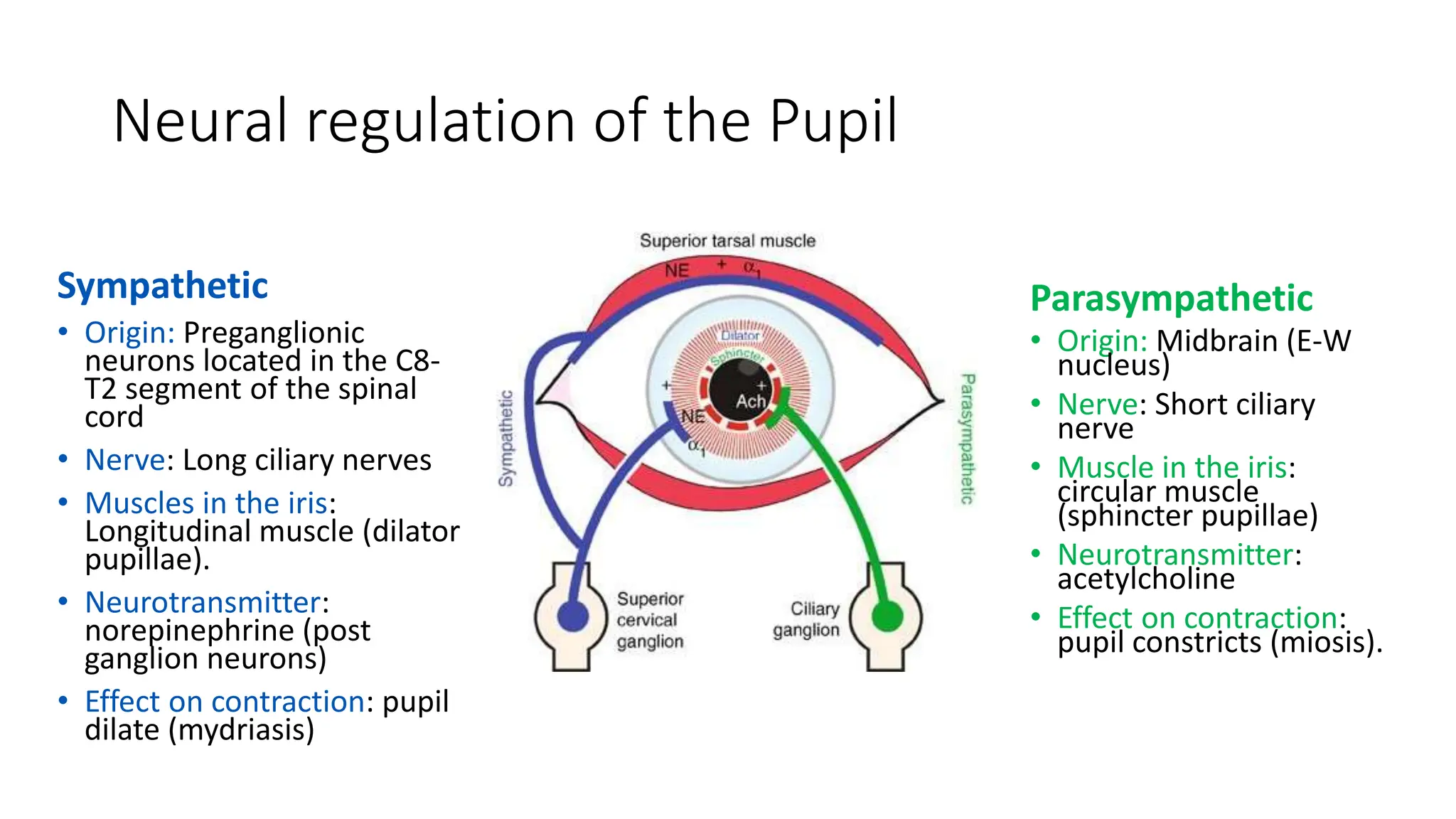
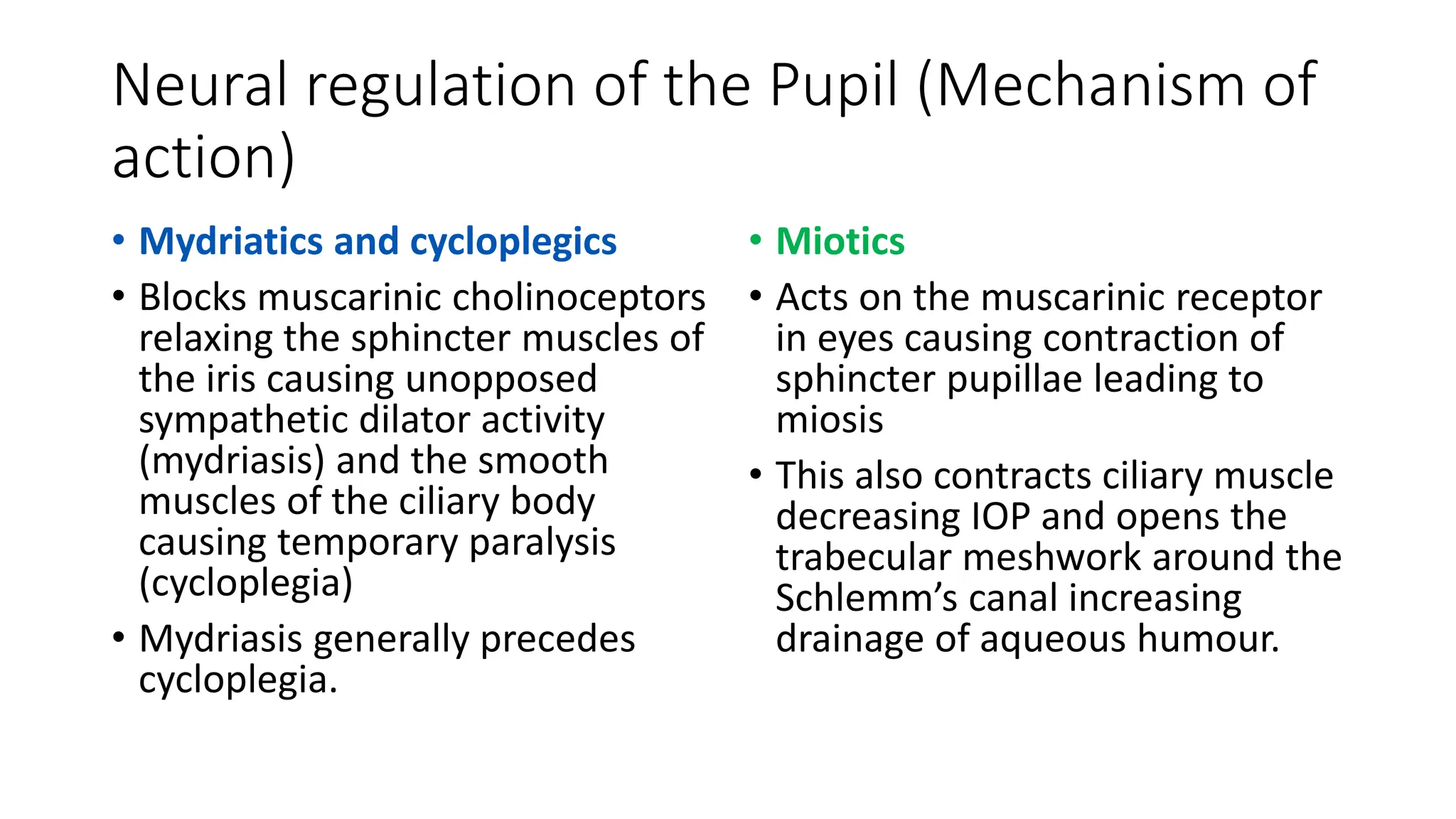
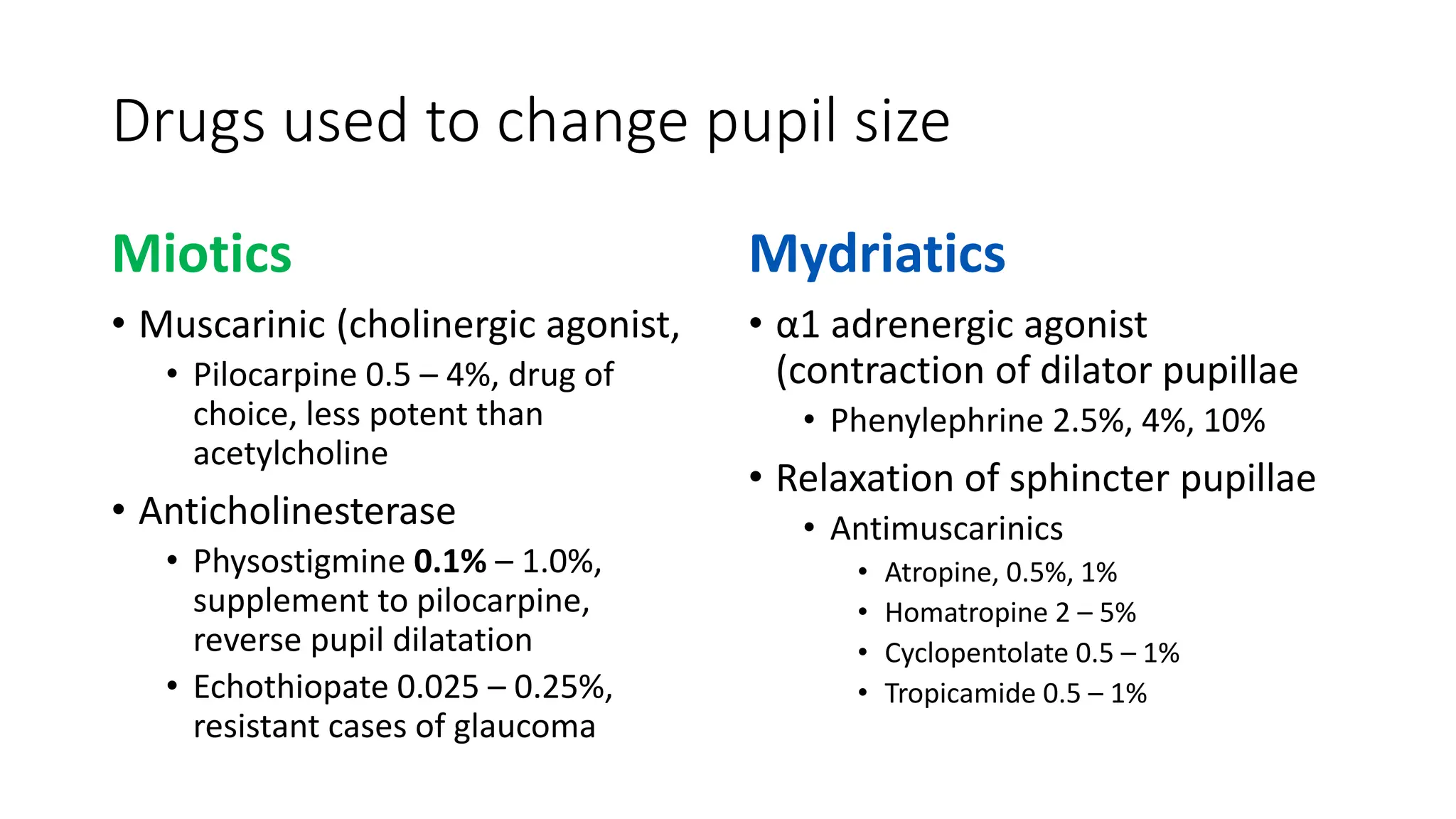
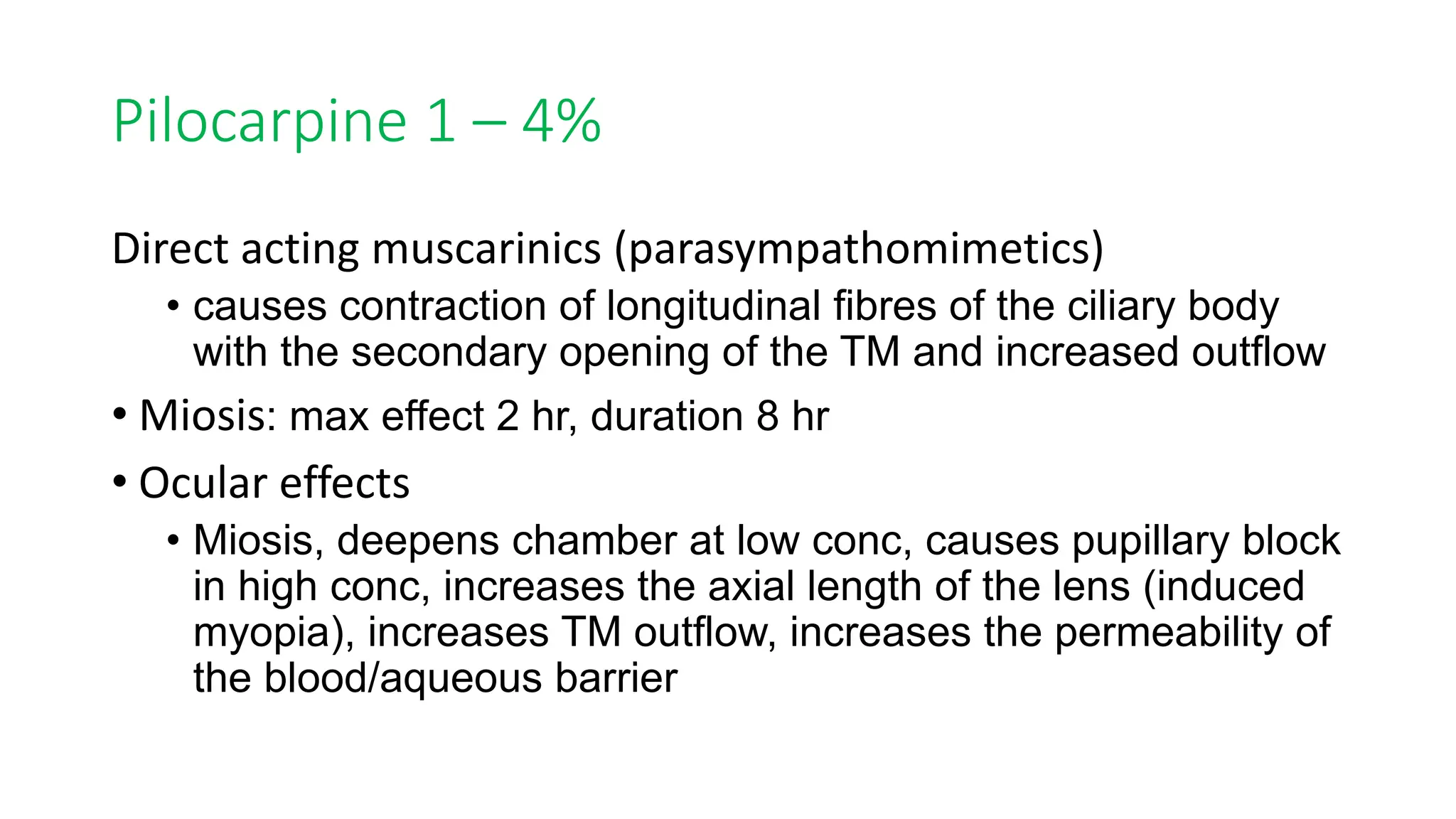
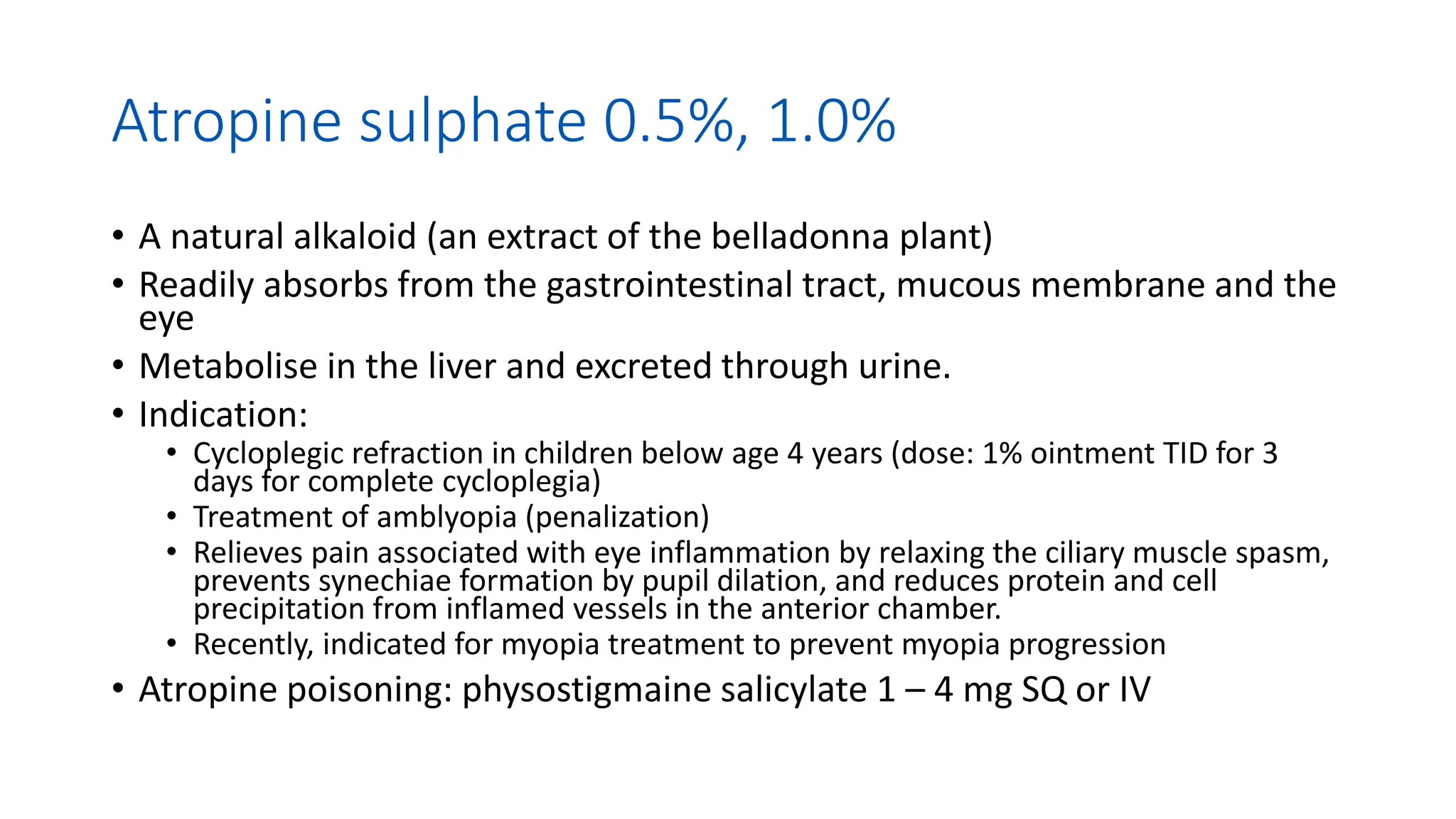
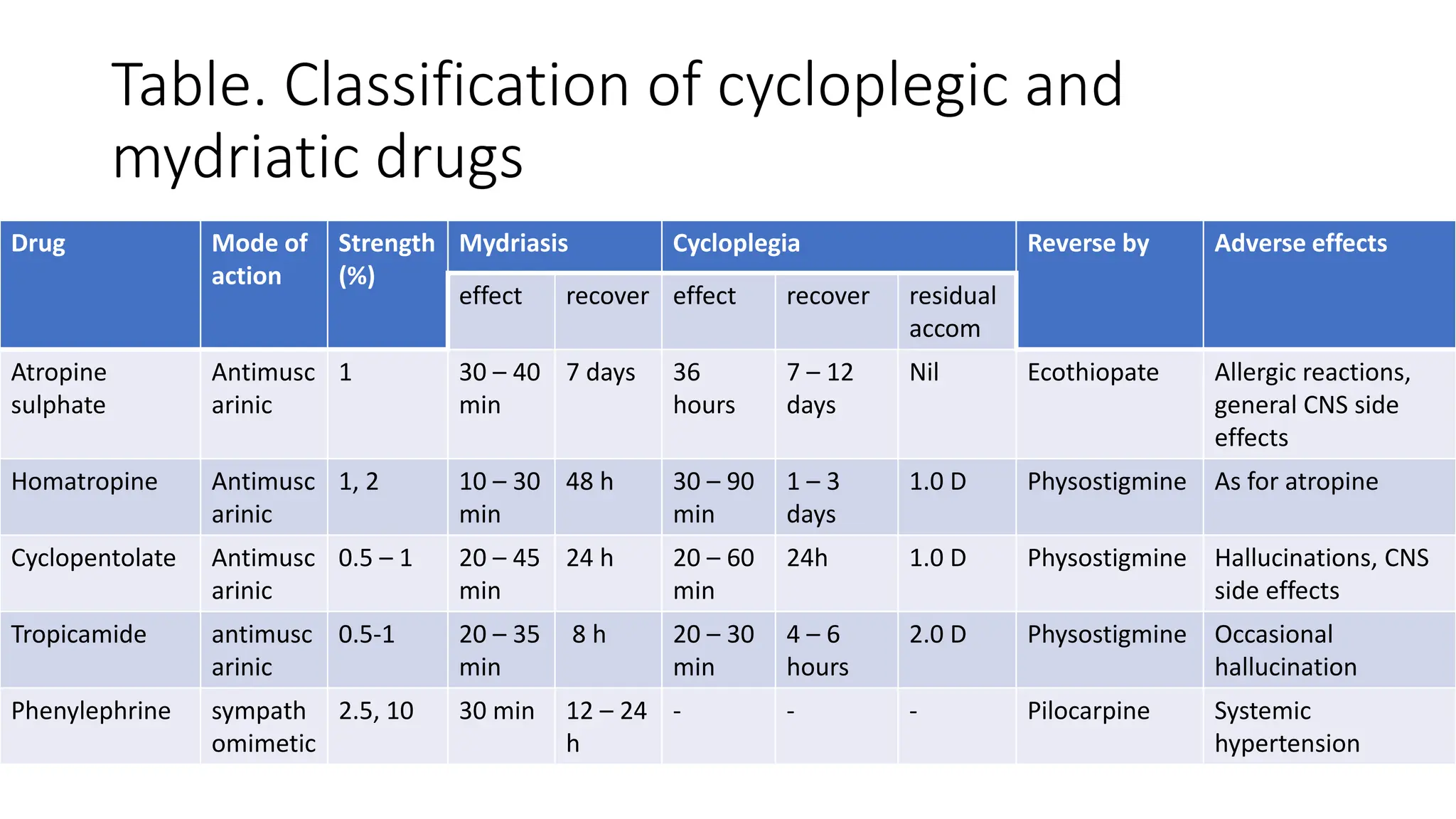
This document discusses drugs that are used to change the size of the pupil, including miotics, mydriatics, and cycloplegics. It explains the neural pathways that control pupil size and the mechanisms of action of different drug classes. Miotics like pilocarpine constrict the pupil by activating muscarinic receptors. Mydriatics like phenylephrine and atropine dilate the pupil by blocking muscarinic receptors or activating alpha receptors. Cycloplegics like atropine, cyclopentolate, and homatropine temporarily paralyze the ciliary muscles in addition to dilating the pupil. The document provides details on the indications, contraindications, dosages, durations of action and