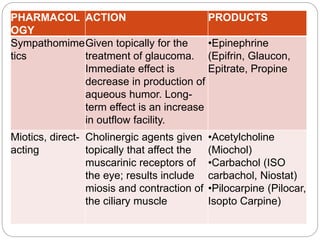
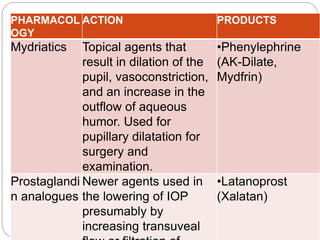
This document summarizes various drugs used to treat common eye disorders, organized by drug class. It lists the pharmacology, action, and example products for each class. The main classes covered are: sympathomimetics, miotics, beta-adrenergic blockers, carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, osmotic diuretics, mydriatics, prostaglandin analogues, local anesthetics, cycloplegic mydriatics, ophthalmic anti-infectives, NSAIDs, ophthalmic steroid anti-inflammatories, vasoconstrictors, and antiallergy medications. For each class it provides a brief 1-2 sentence description of the pharmacological action and lists 1




![PHARMAC
OLOGY
ACTION PRODUCTS
Ophthalmic
anti-infectives
Topical agents used for
treatment of ophthalmic
infections. Commercial
products are intended for
treatment of superficial
ocular problems, such as
conjunctivitis and
blepharitis.
Extemporaneous
(compounded) drops are
used for more serious
topical infections (ie,
corneal ulcer,
endophthalmitis [intraocular
infection]).
•Antibiotics Bacitracin (AK-
Tracin)
•Chloramphenicol (Chloroptic)
•Ciprofloxacin (Ciloxan)
•Erythromycin (Ilosone)
•Gentamycin (Garamycin,
Genoptic)
•Levofloxacin (Quixin)
•Moxifloxacin (Vigamox)
•Neomycin/polymyxin/bacitraci
n (Neosporin)
•Norfloxacin (Chibroxin)
•Sulfacetamide (Sulamyd,
Bleph-10)
•Tobramycin (Tobramycin,
Tobrex)
•Antifungal Amphotericin B
(Fungizone)
•Fluconazole](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/drugsusedincommoneyedisorders-200602165120/85/Drugs-used-in-common-eye-disorders-7-320.jpg)


