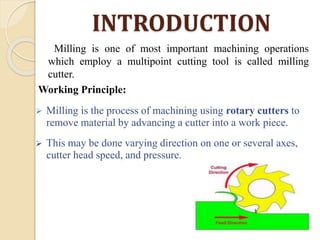
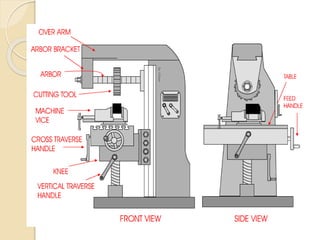
The document discusses different types of milling machines. It describes milling as a machining process that uses a rotating cutting tool to remove material from a workpiece. There are various types of milling machines classified by their construction and motion capabilities, including horizontal, vertical, and universal milling machines. Horizontal milling machines have a spindle parallel to the workpiece, while vertical milling machines have a vertically oriented spindle. The document provides details on key parts and operation of horizontal milling machines.