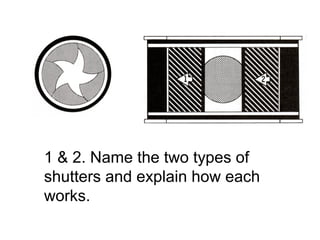
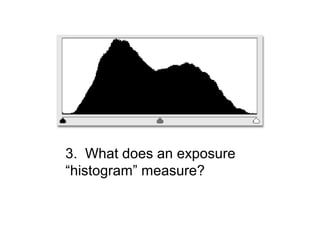
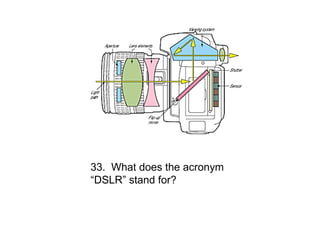
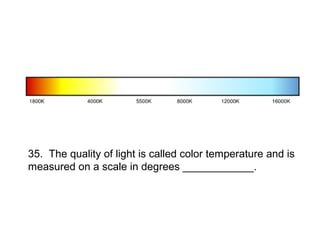
The document is a mid-term exam for a digital photography course consisting of 50 multiple choice questions testing students' knowledge of various photography concepts and techniques. The questions cover topics like camera shutter types, histograms, metering, aperture, focal length, depth of field, white balance, and more. Students are asked to identify exposures, lenses, and techniques used to take various example photos.