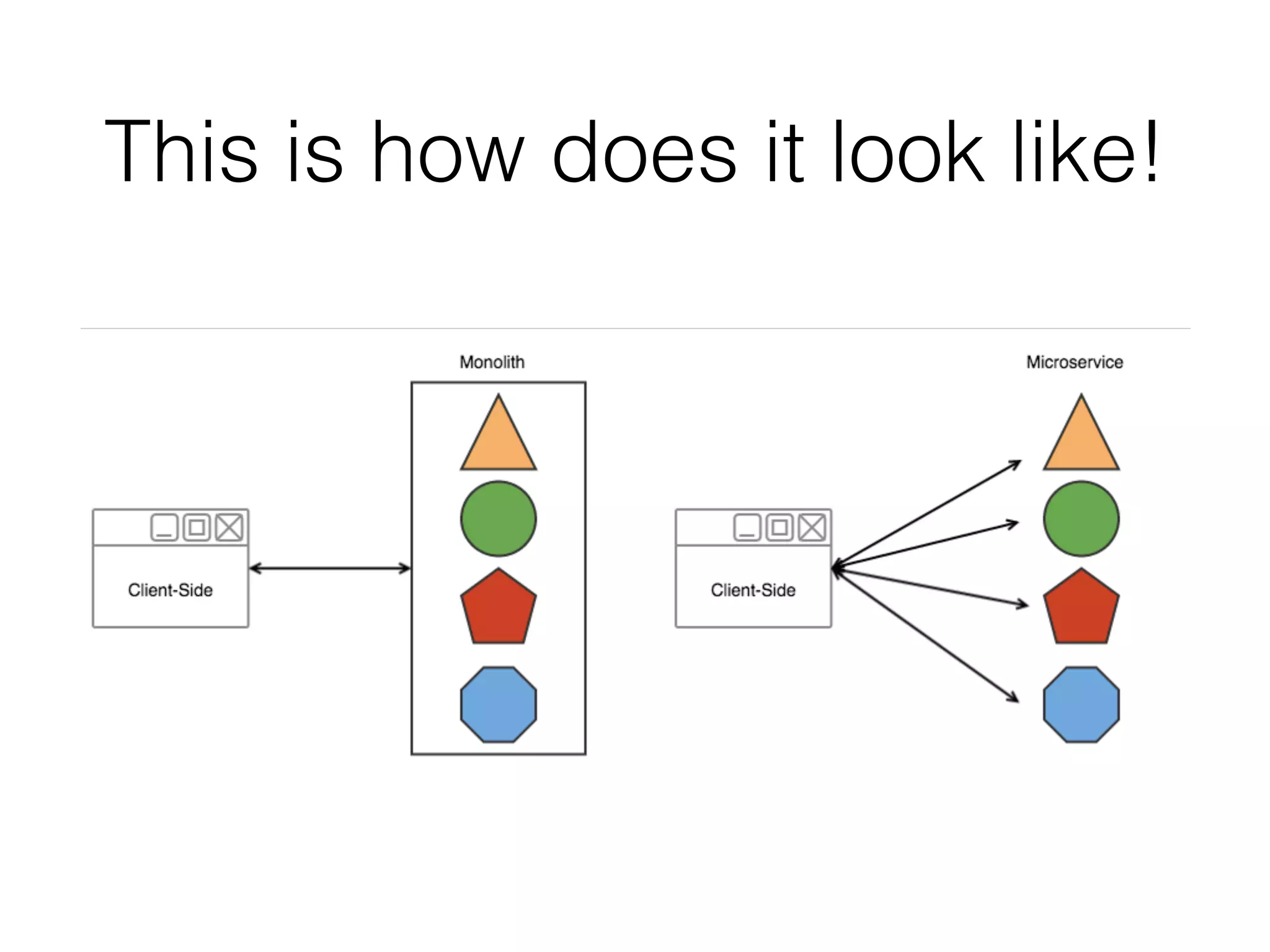
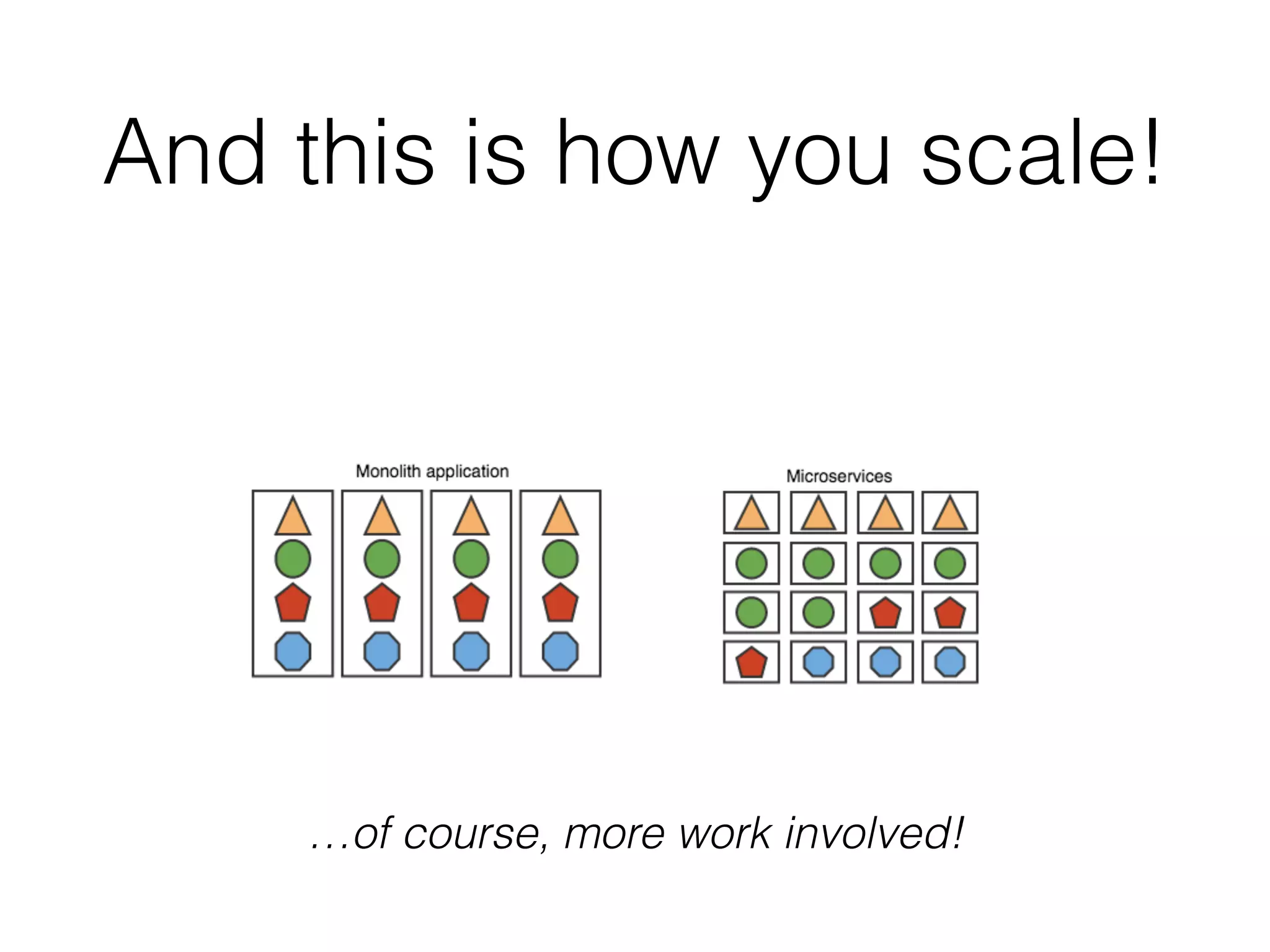
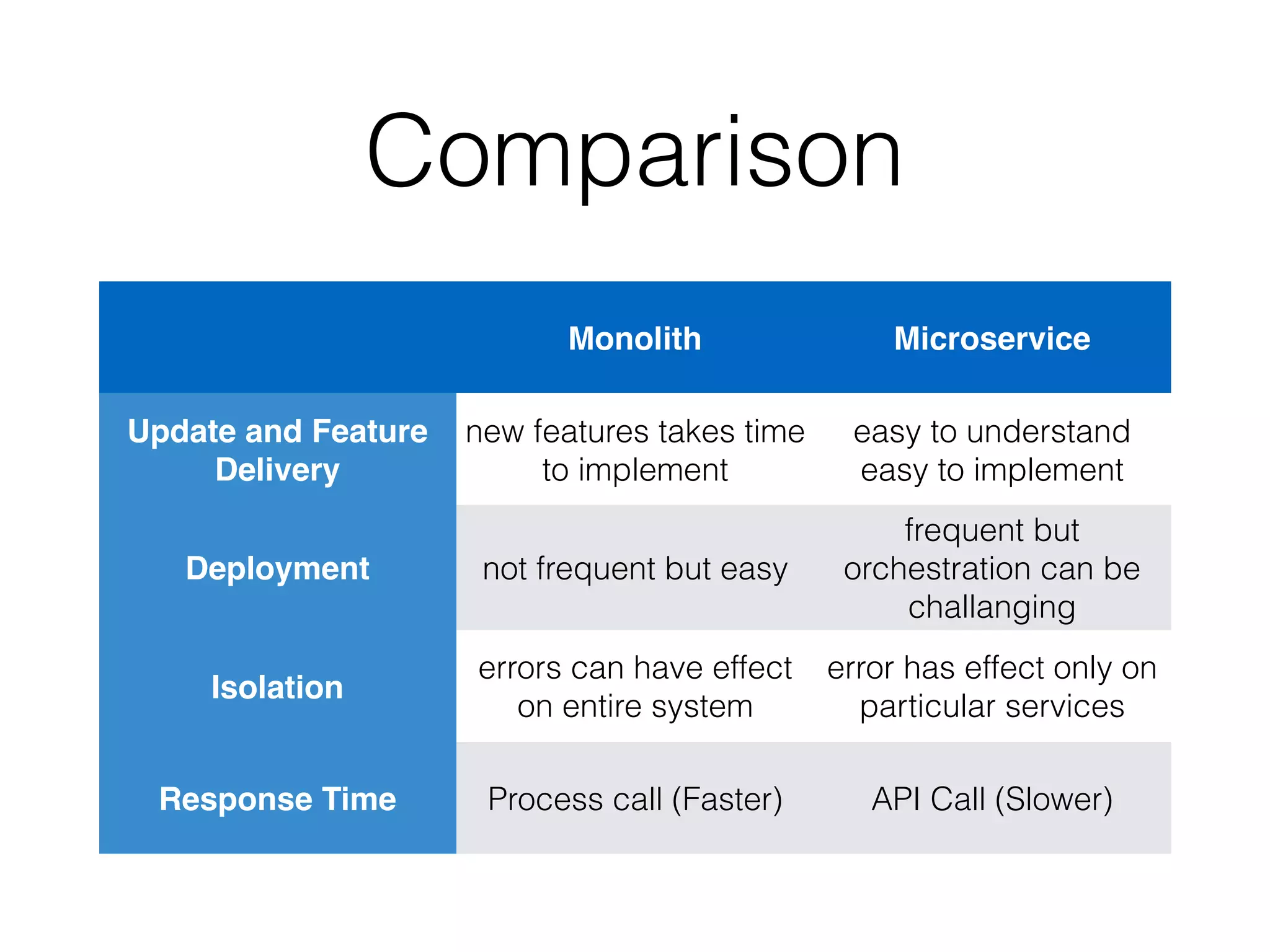
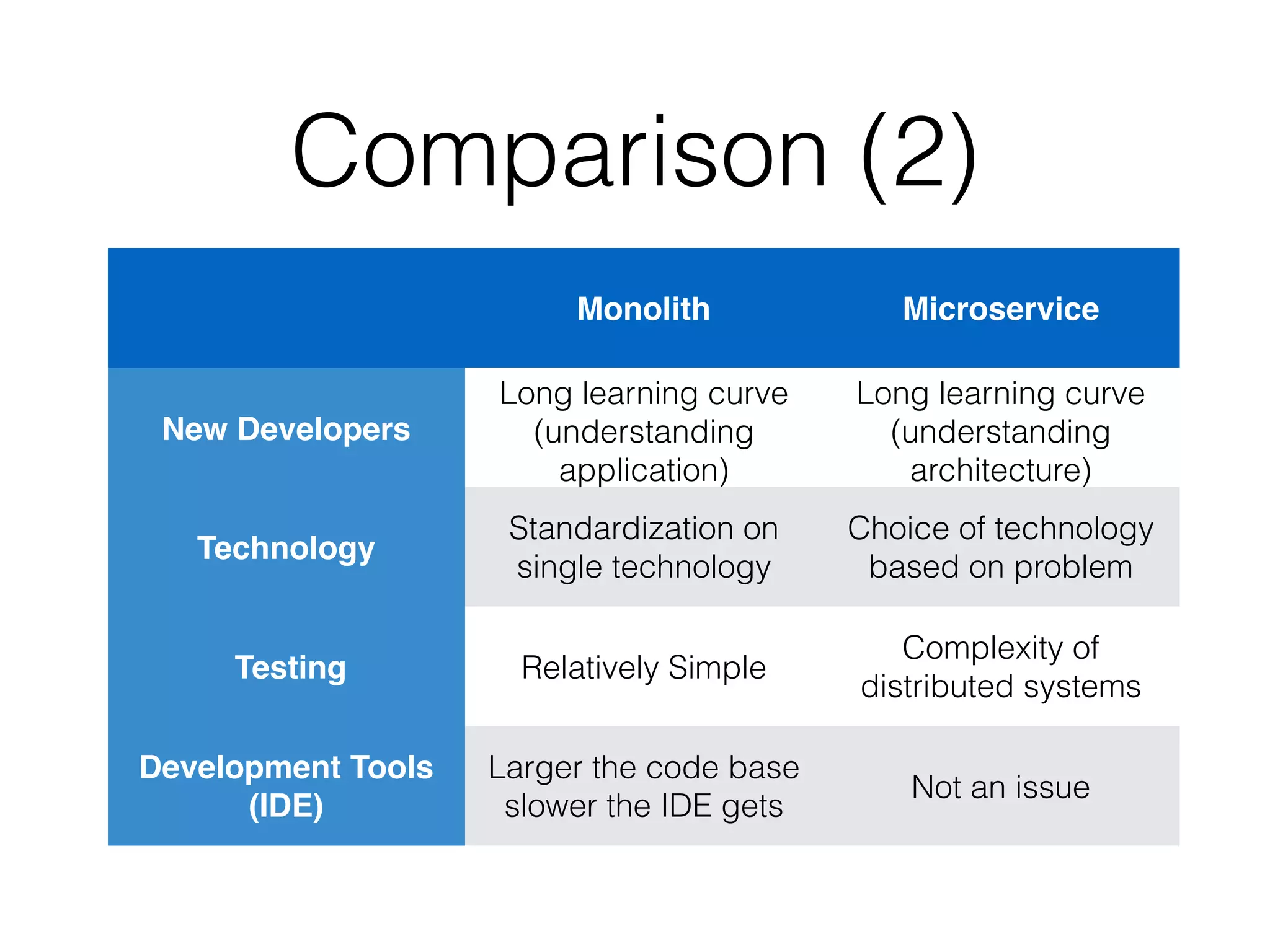
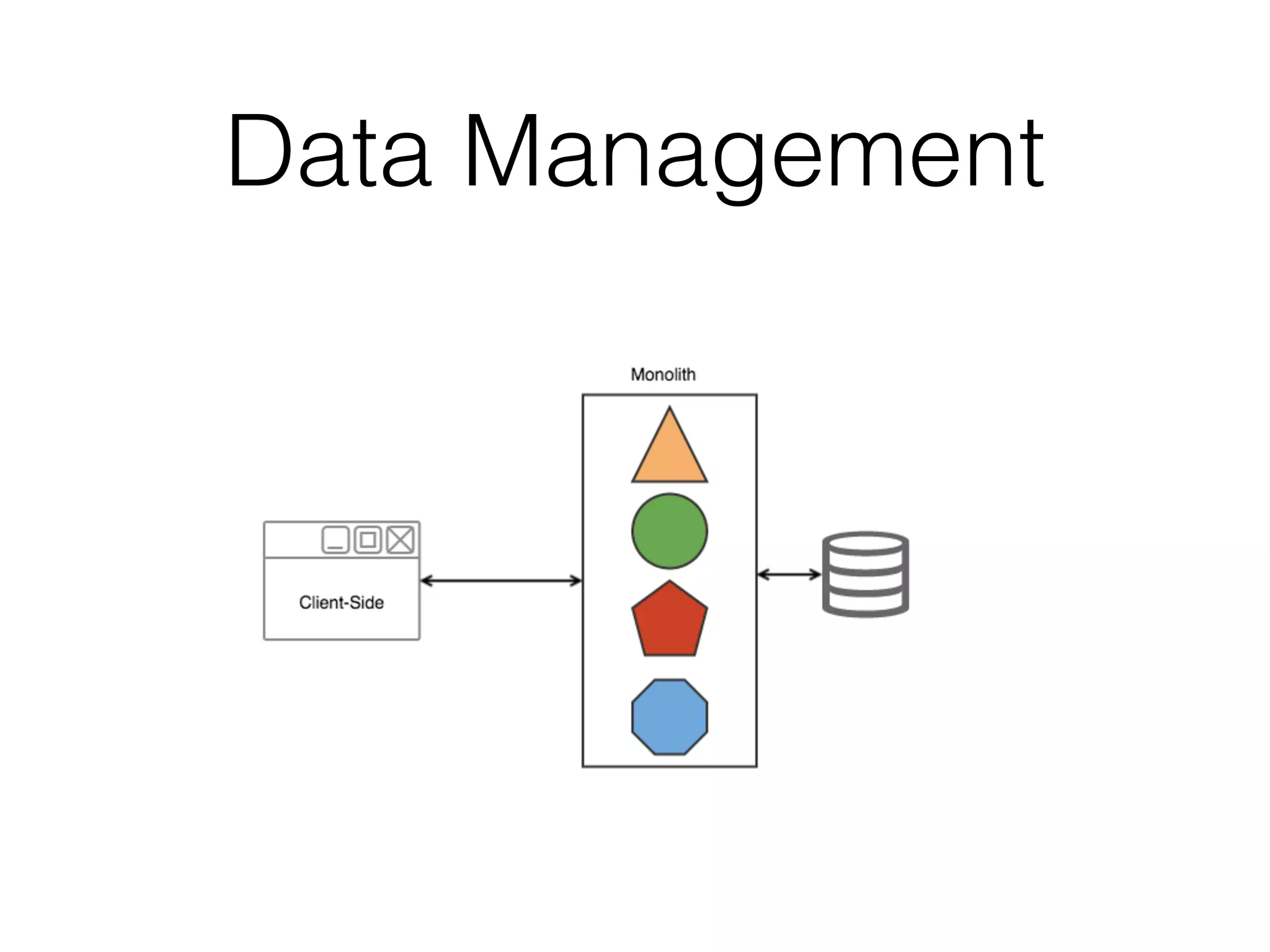
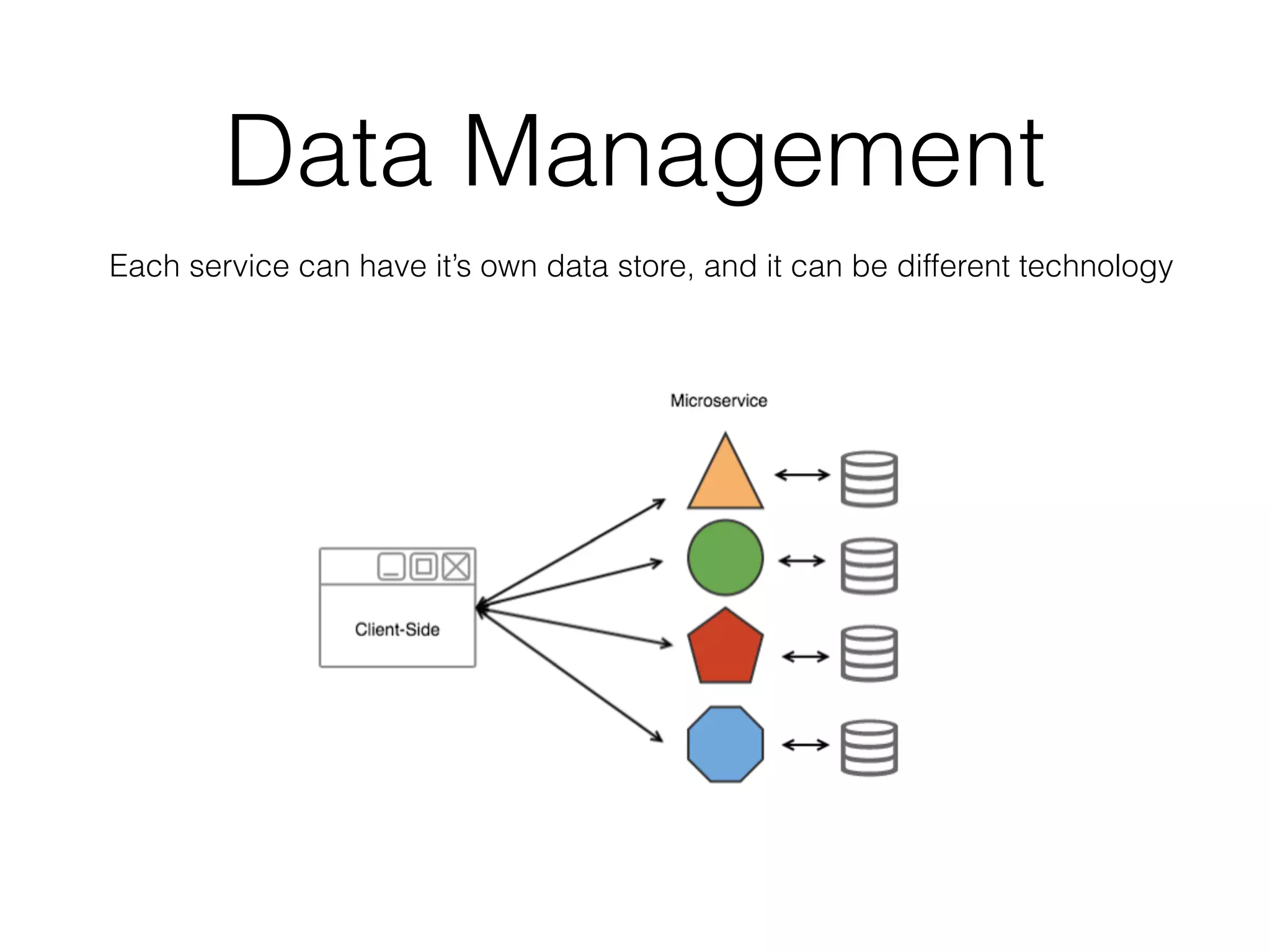
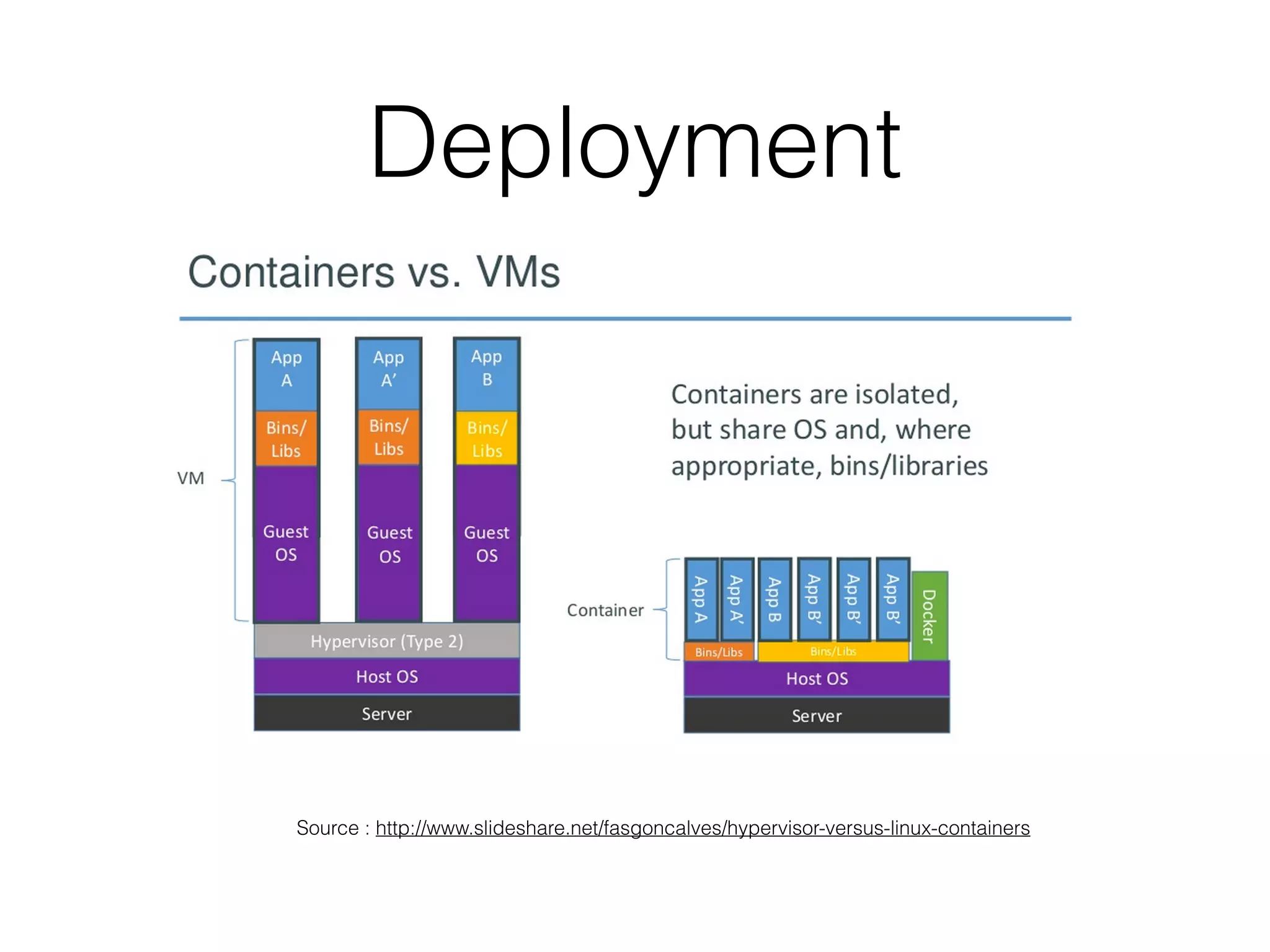
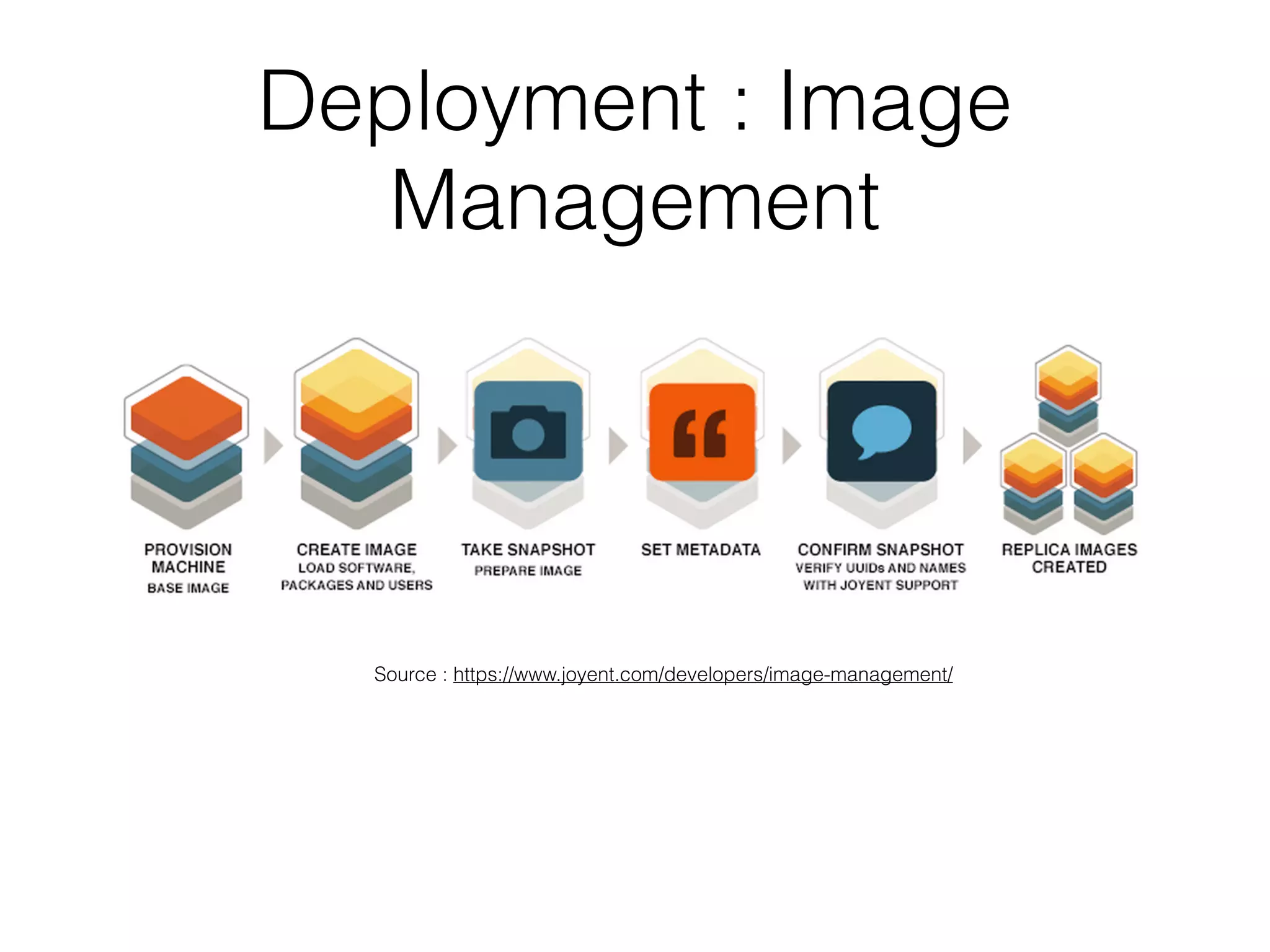
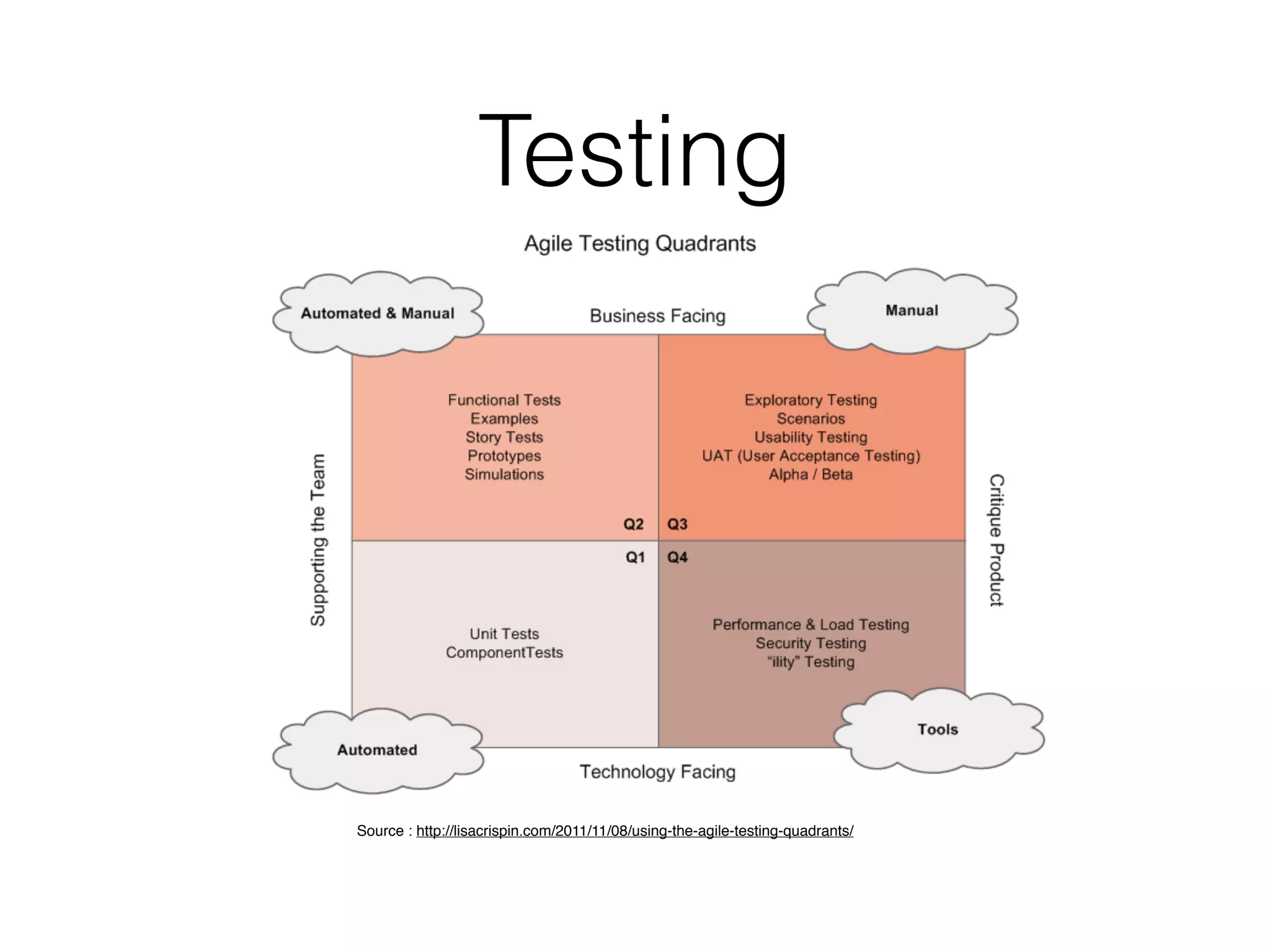
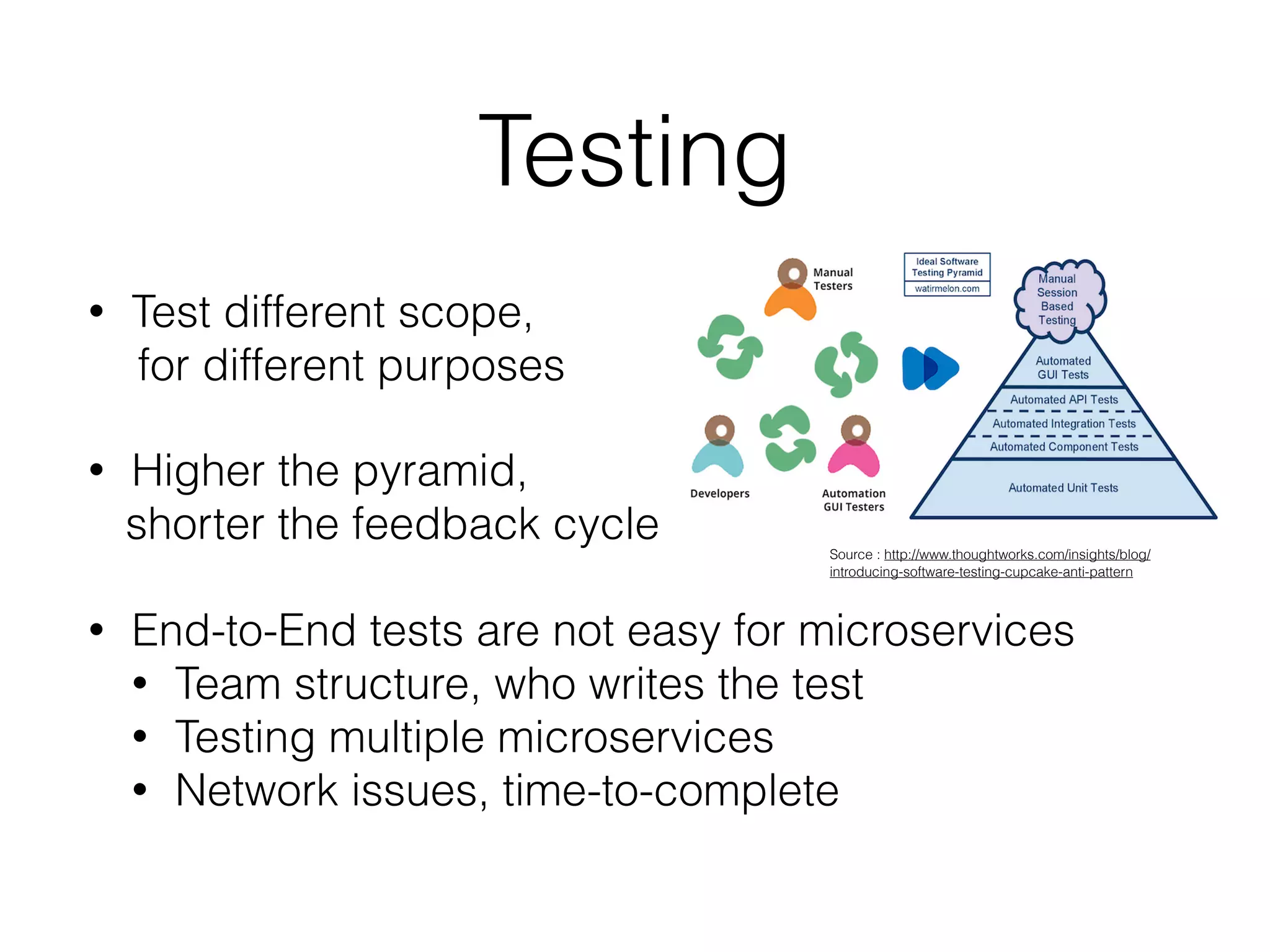
The document discusses microservice architecture and compares it to monolithic architecture. It describes microservices as small, discrete, isolated services that can be deployed separately. A monolith is a single application combining all business logic and data access. The document outlines characteristics of microservices such as single responsibility, statelessness, independent data management and communication through APIs or message queues. It also covers deployment, testing, monitoring, metrics and the need for automation and a culture open to change when using microservice architecture.