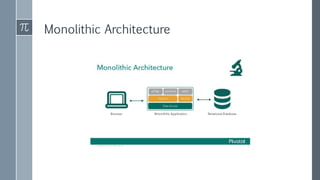
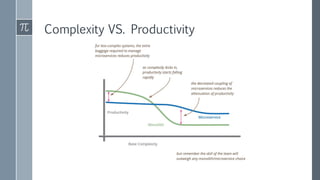
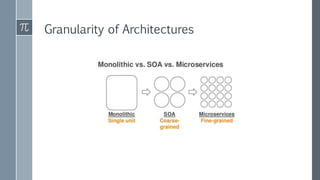
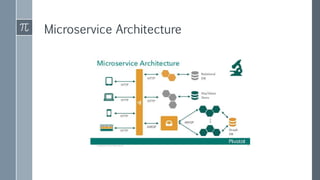
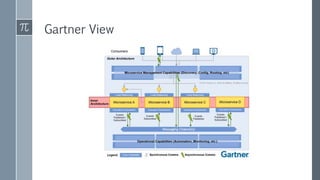
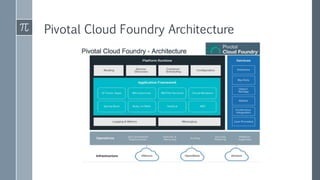
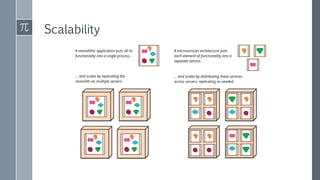
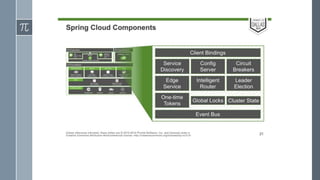
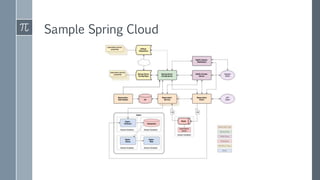
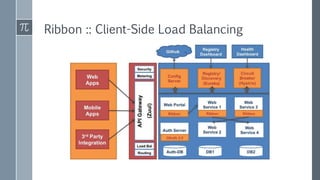
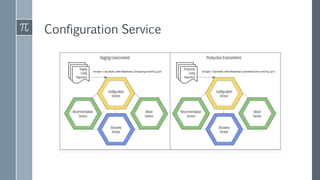
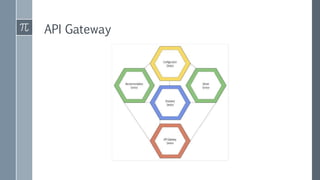
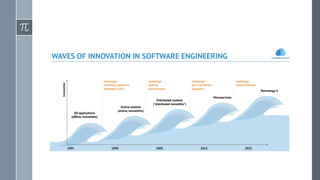
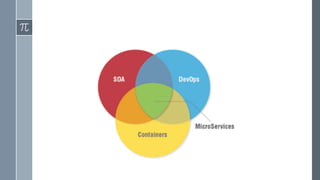
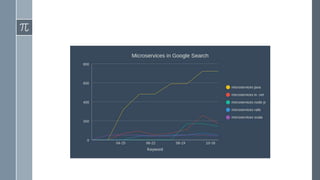
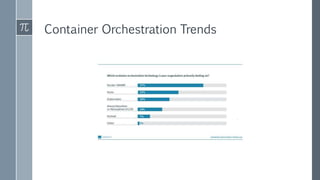
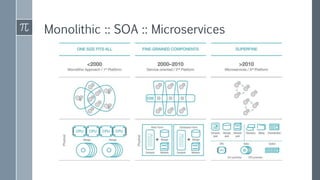
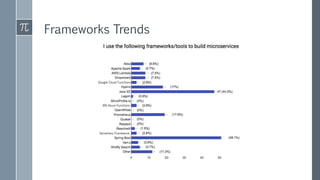
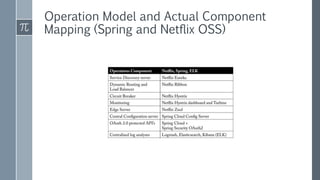
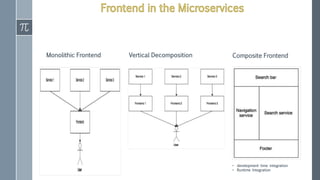
The document discusses microservice architecture as a method of developing applications as a suite of small, independently deployable services communicating through lightweight mechanisms. It highlights the advantages of microservices, such as independent scalability and polyglot persistence, where various databases can be used based on specific needs. Key components like configuration services and discovery services are essential for managing microservices effectively within a cluster.