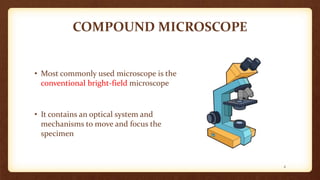
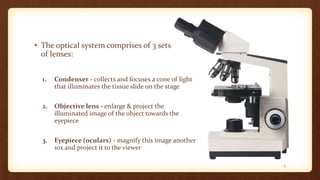
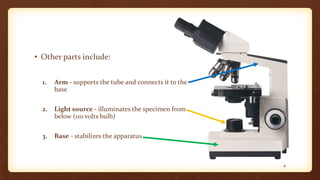
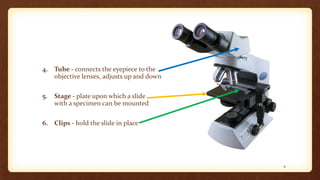
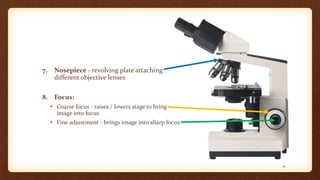
This document describes the parts and proper use of a compound microscope. It begins by listing the learning objectives of being able to describe the microscope, identify its parts, and explain the functions. It then explains that the optical system contains three sets of lenses: the condenser which illuminates the slide, various objective lenses which enlarge the image, and the eyepiece which provides further magnification. Other parts like the arm, base, stage, and nosepiece are also outlined. Guidelines for safe handling and focusing the microscope are provided.