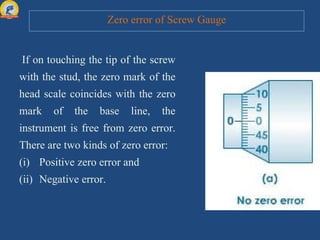
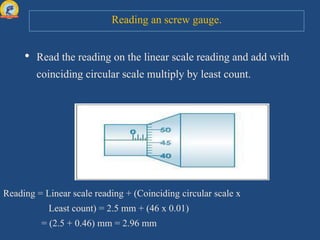
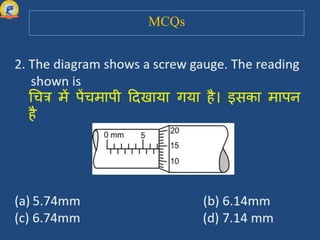
This document discusses the parts of a screw gauge and how to use one. It identifies the main parts as the pitch scale, ratchet, circular scale, and anvil. It explains that the pitch scale measures the distance the screw travels and the circular scale helps determine measurements smaller than the scale's divisions. When using a screw gauge, the reading is taken as the linear scale reading plus the coinciding circular scale reading multiplied by the least count. The document also covers zero error and how to perform measurements with a micrometer screw gauge.