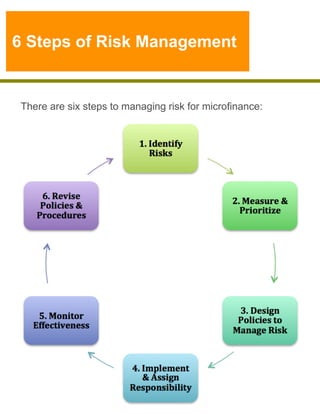
This document outlines key principles of risk and risk management in microfinance, emphasizing the importance of managing credit risk and maintaining portfolio quality. It details a six-step process for risk management, highlighting techniques and internal controls necessary for effective loan tracking and repayment. Additionally, it emphasizes the relationship between product development and risk, as well as the need for robust documentation and monitoring after loan disbursement to ensure sustainability and profitability.