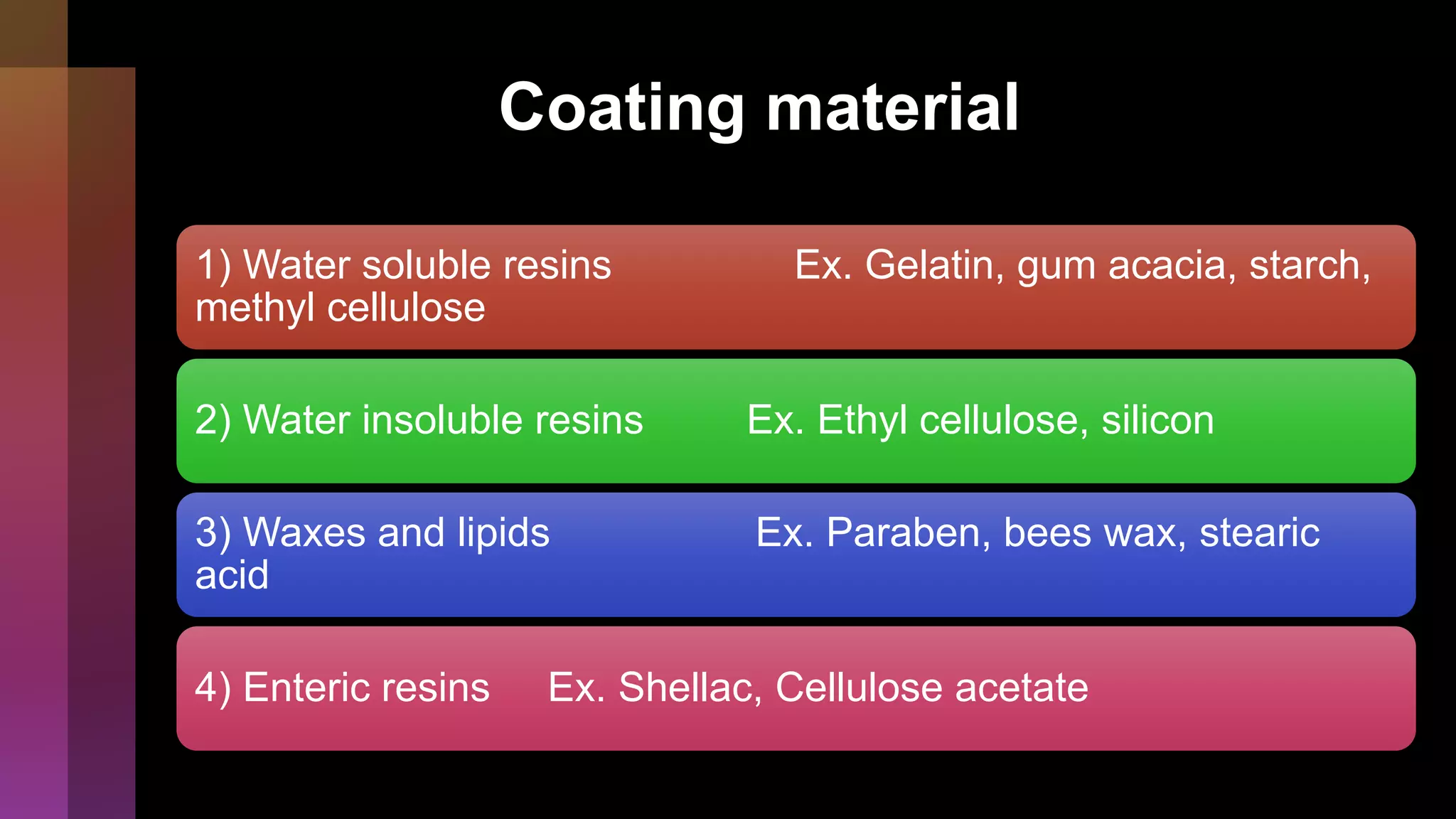
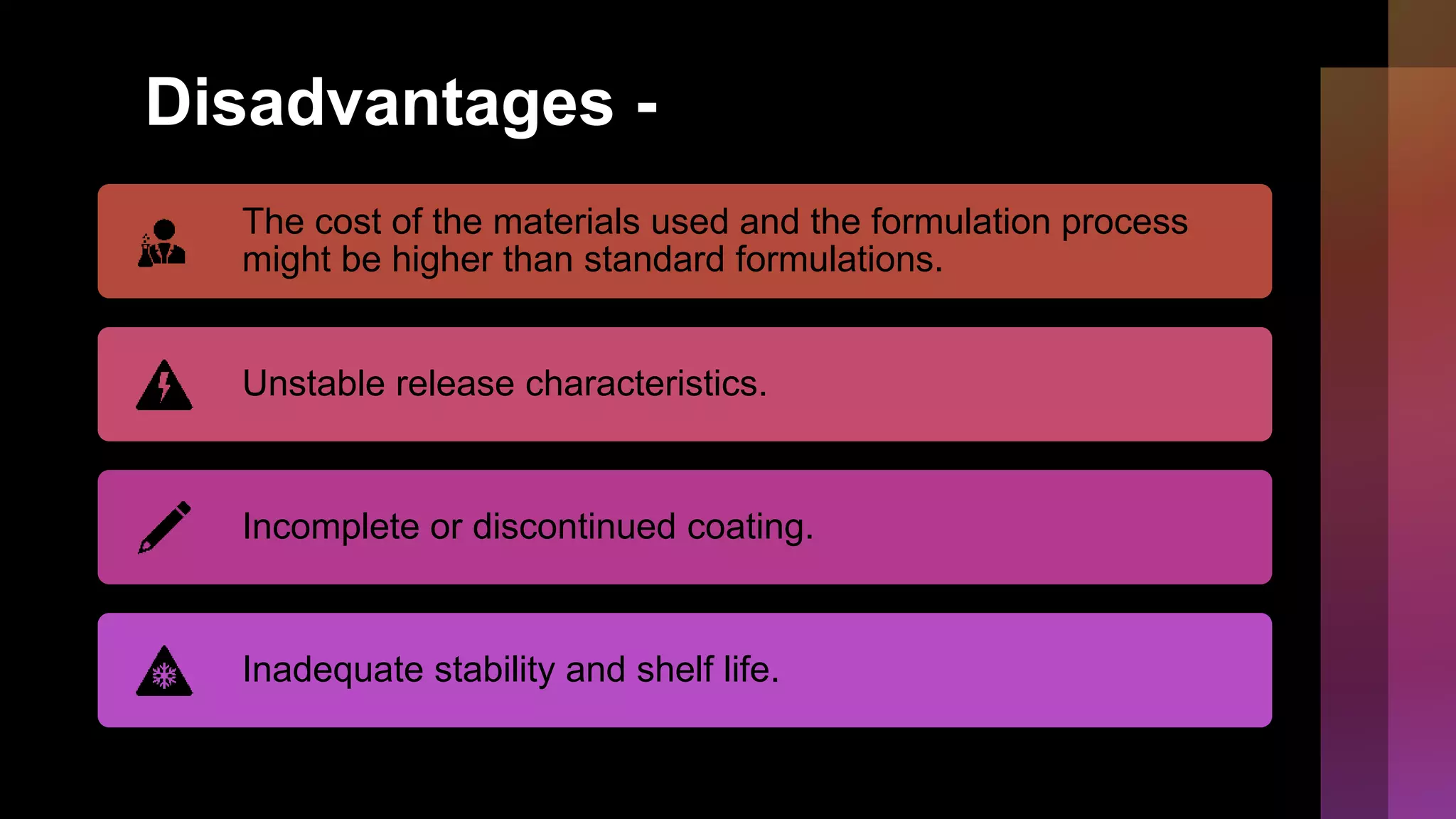
Microencapsulation involves coating active ingredients with thin polymer shells to protect them. There are several methods for microencapsulation including physicomechanical methods like pan coating and spray drying, physicochemical methods like ionotropic gelation and coacervation, and chemical methods like solvent evaporation and polymerization. Microencapsulation has advantages like masking tastes, converting liquids to powders, and enabling controlled release, but also has disadvantages like higher costs and potential stability issues. Common encapsulation methods include spray drying, pan coating, solvent evaporation, and interfacial polymerization.

![Types -
Microencapsulation [
1 to 800
micrometers]
Microencapsulation [
800 to 1000
micrometers]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/microencapsulation-221021070255-82e12210/75/Microencapsulation-3-2048.jpg)



![A] Physicochemical methods
1. Air suspension
2. Centrifugal extrusion
3. Pan coating
4. Spray drying – co-current
- counter current
- mix flow
5. Vibrational nosal method](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/microencapsulation-221021070255-82e12210/75/Microencapsulation-10-2048.jpg)
![B] Physicochemical
methods
1. Ionotropic gelatin
2. Coacervation
C] Chemical methods
1. Solvent evaporation
2. Polymerization - interfacial
- in situ
- matrix method](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/microencapsulation-221021070255-82e12210/75/Microencapsulation-11-2048.jpg)
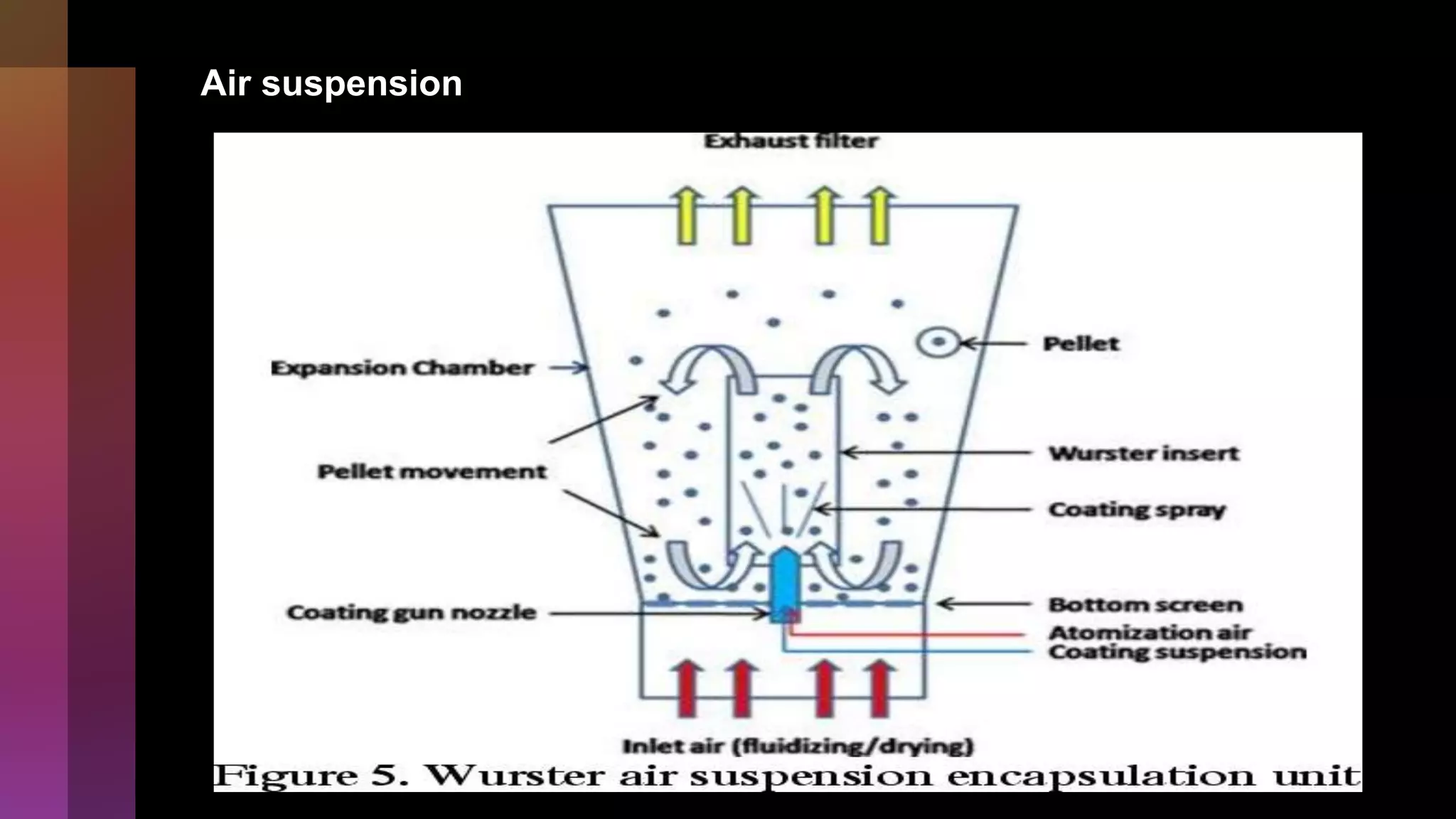
![[A] Physicomechanical methods
1]Air suspension coating
• Developed by Prof. Dale E. Wurster.
Factors to be considered…..
1. Properties of drug material and coating material
2. Concentration of coating material
3. Coating material application rate
4. Amount of coating of coating material
5. Inset and outlet pressure operative maintenance](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/microencapsulation-221021070255-82e12210/75/Microencapsulation-12-2048.jpg)

![2] Centrifugal extrusion
• Centrifugal extrusion is a liquid coextrusion process utilizing nozzles consisting. of a
concentric orifice located on the outer circumference of a rotating cylinder. i.e., the head.
• Centrifugal extrusionLiquids are encapsulated using a rotating extrusion head
containing concentric nozzles.
• This process is excellent for forming particles 400-2,000 µm in diameter
• Since the drops are formed by the breakup of a liquid jet, the process is only
suitable for liquid or slurry.
• A high production rate can be achieved, i.e., up to 22.5 kg of microcapsules can
be produced per nozzle per hour per head.
• Heads containing 16 nozzles are available.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/microencapsulation-221021070255-82e12210/75/Microencapsulation-15-2048.jpg)
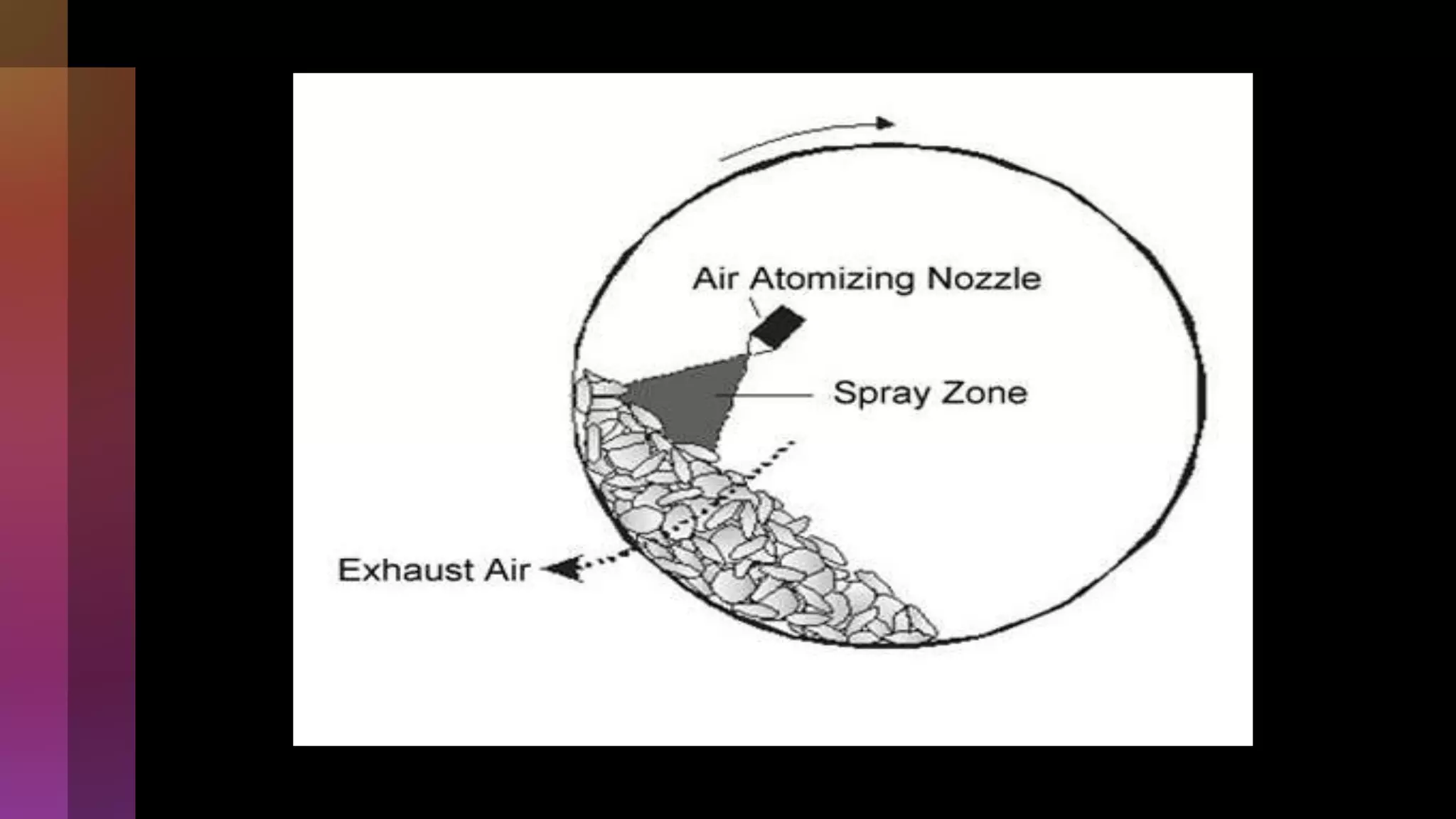
![3] Pan coating
• Pan Coating process is used for solid particles greater
than 600 microns in size.
• The coating is applied as a solution, or as an atomized
spray, to the desired solid core material in the coating pan.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/microencapsulation-221021070255-82e12210/75/Microencapsulation-16-2048.jpg)
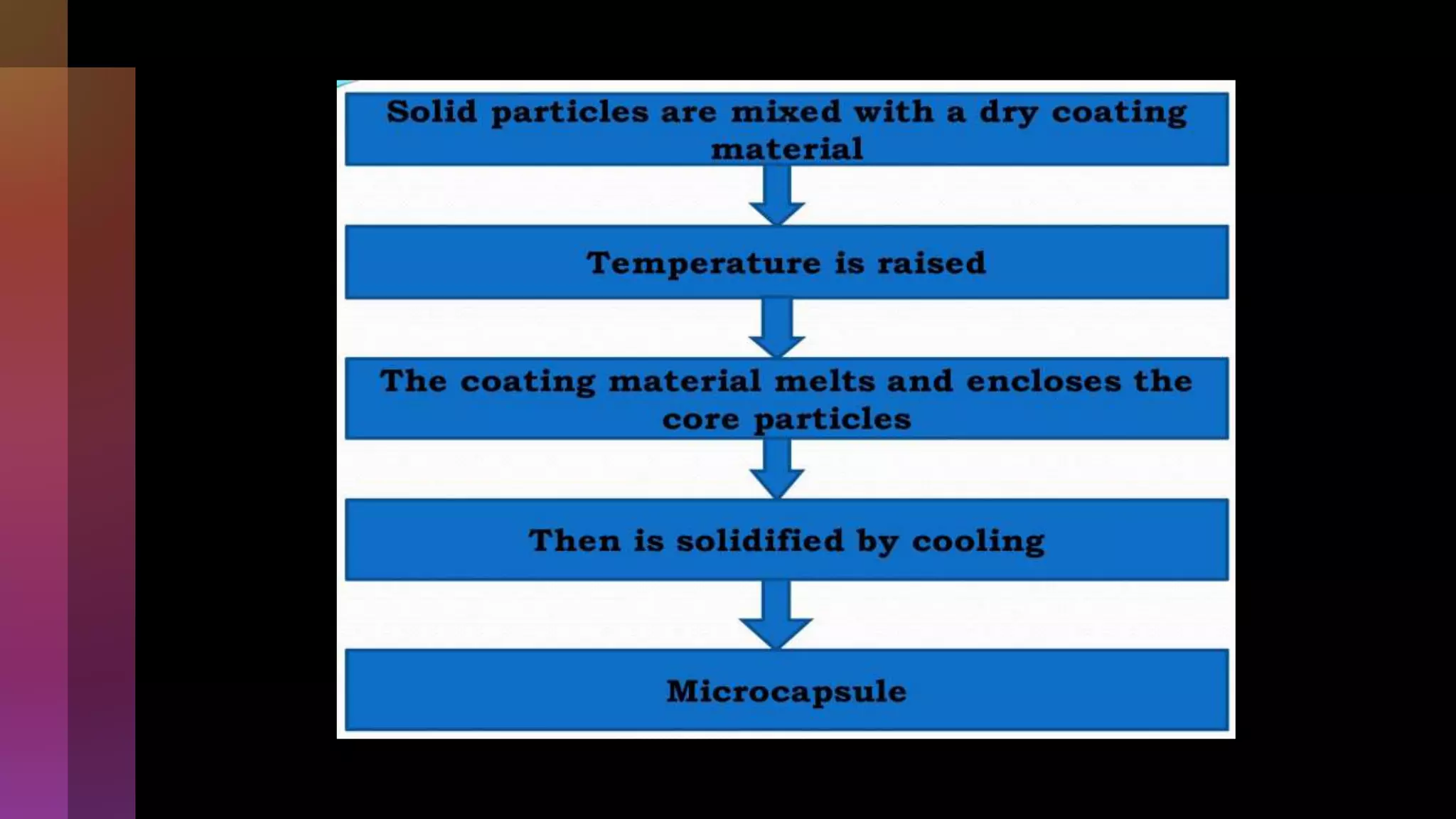
![4] Spray drying
Process….](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/microencapsulation-221021070255-82e12210/75/Microencapsulation-19-2048.jpg)




![5] Vibration nozzel method
• A fluid stream of liquid core and shell material is
pumped through concentric tubes and forms
droplets under the influence of vibration.
• Particle size 100-500 micrometer
• Capacity is 1 - 10,000 kg/ hr](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/microencapsulation-221021070255-82e12210/75/Microencapsulation-24-2048.jpg)
![[B] Physicochemical methods
1]Ionotropic gelation
• Ionotropic gelation (IG) is a technique that allows the production of nanoparticles and
microparticles by electrostatic interactions between two ionic species under certain
conditions. At least one of the species has to be a polymer.
• Example ..
Chemical reaction between sodium algenate or barium chloride with
verapamil, reduces the gastric irritation of Verapamil (antihypertensive)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/microencapsulation-221021070255-82e12210/75/Microencapsulation-25-2048.jpg)
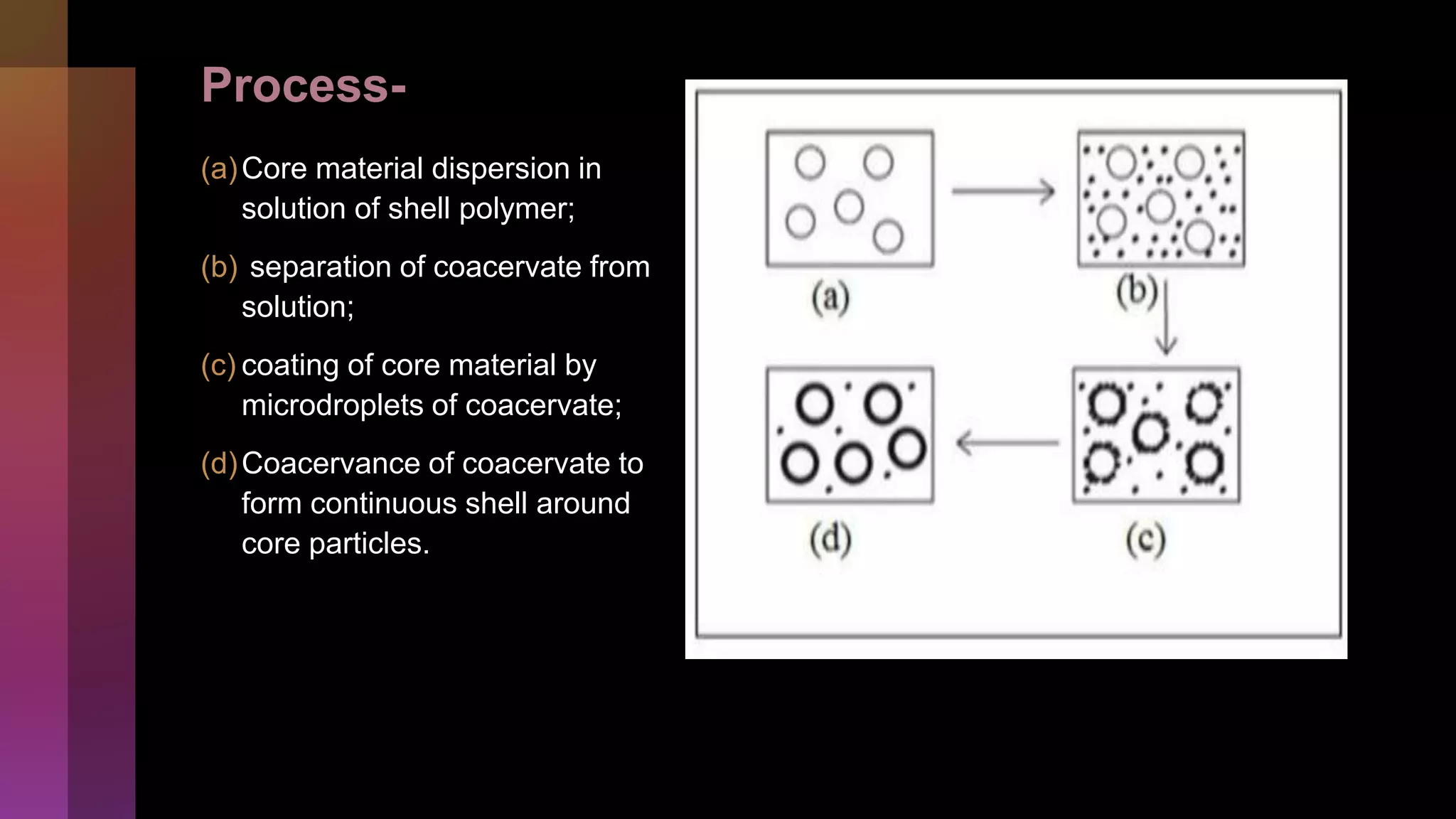
![2] Co-acervation
• Coacervation can be defined as the separation of a
macromolecular solution into two immiscible liquid
phases: a dense coacervate phase and a dilute
equilibrium one.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/microencapsulation-221021070255-82e12210/75/Microencapsulation-26-2048.jpg)
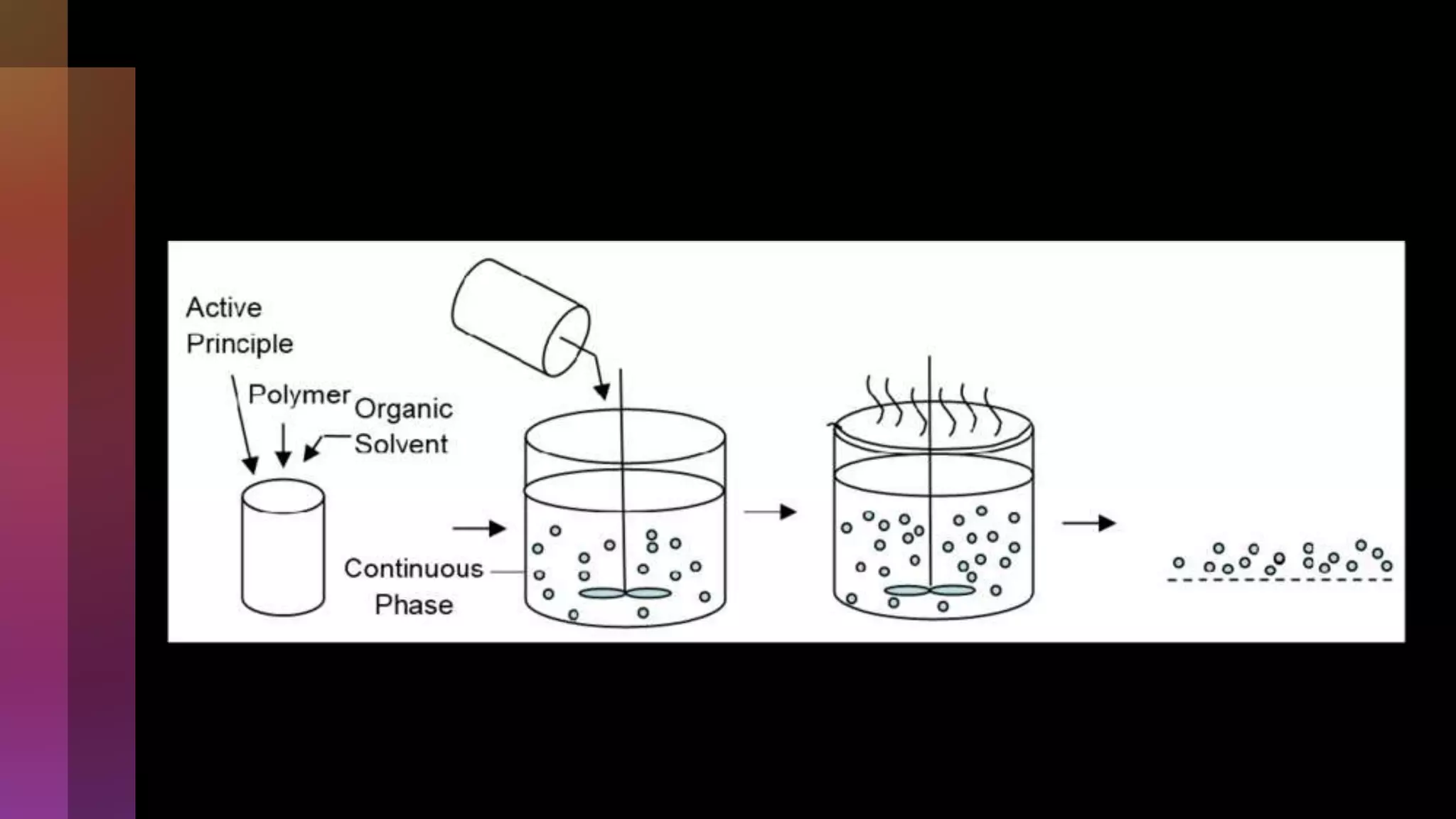
![[C] Chemical methods
1] Solvent evaporation
In the solvent evaporation method, the drug is dissolved,
dispersed, or emulsified into an organic polymer solution,
which is then emulsified into an external aqueous or oil
phase.
The microspheres are formed after solvent diffusion/evaporation
and polymer precipitation.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/microencapsulation-221021070255-82e12210/75/Microencapsulation-28-2048.jpg)
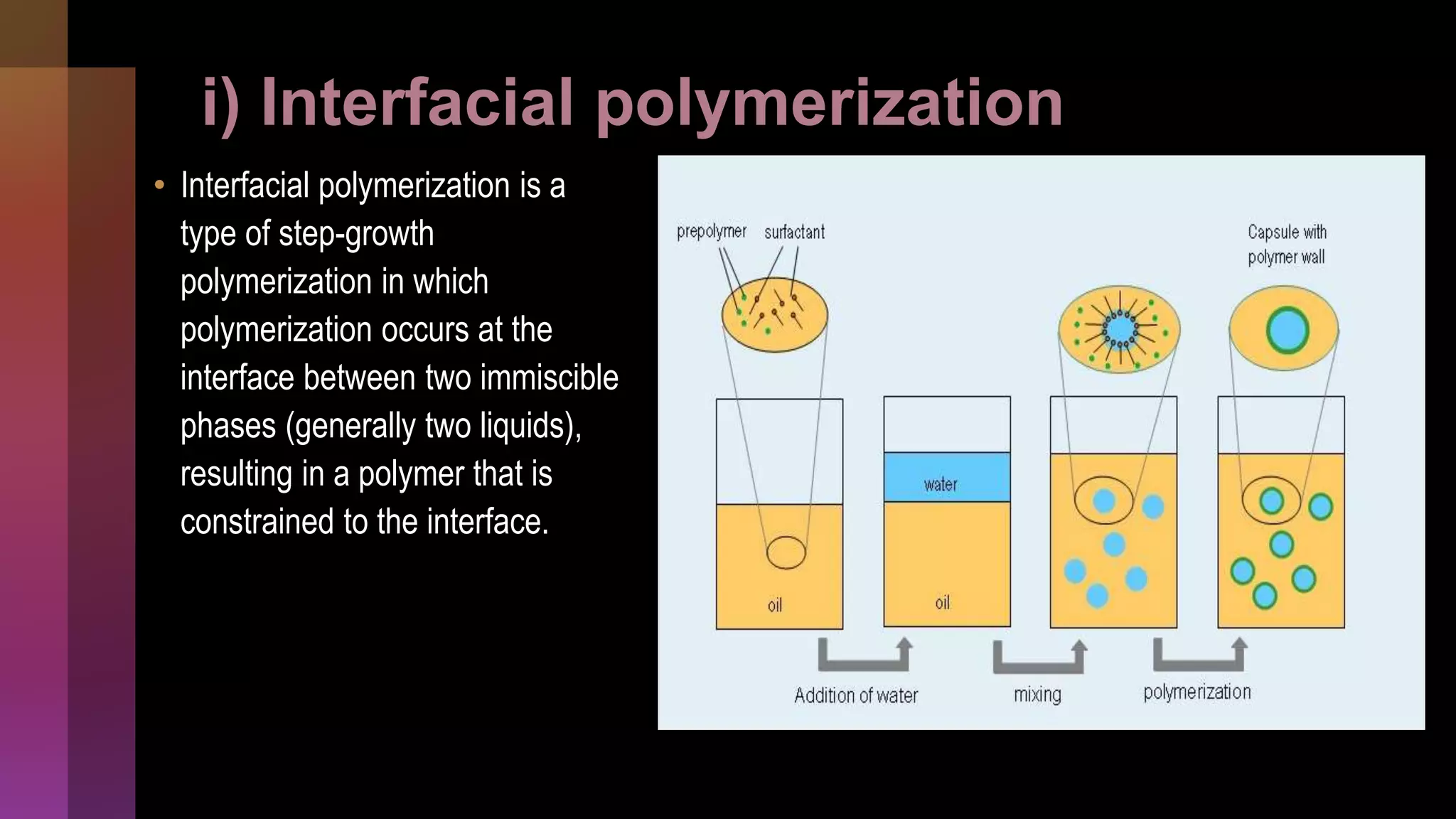
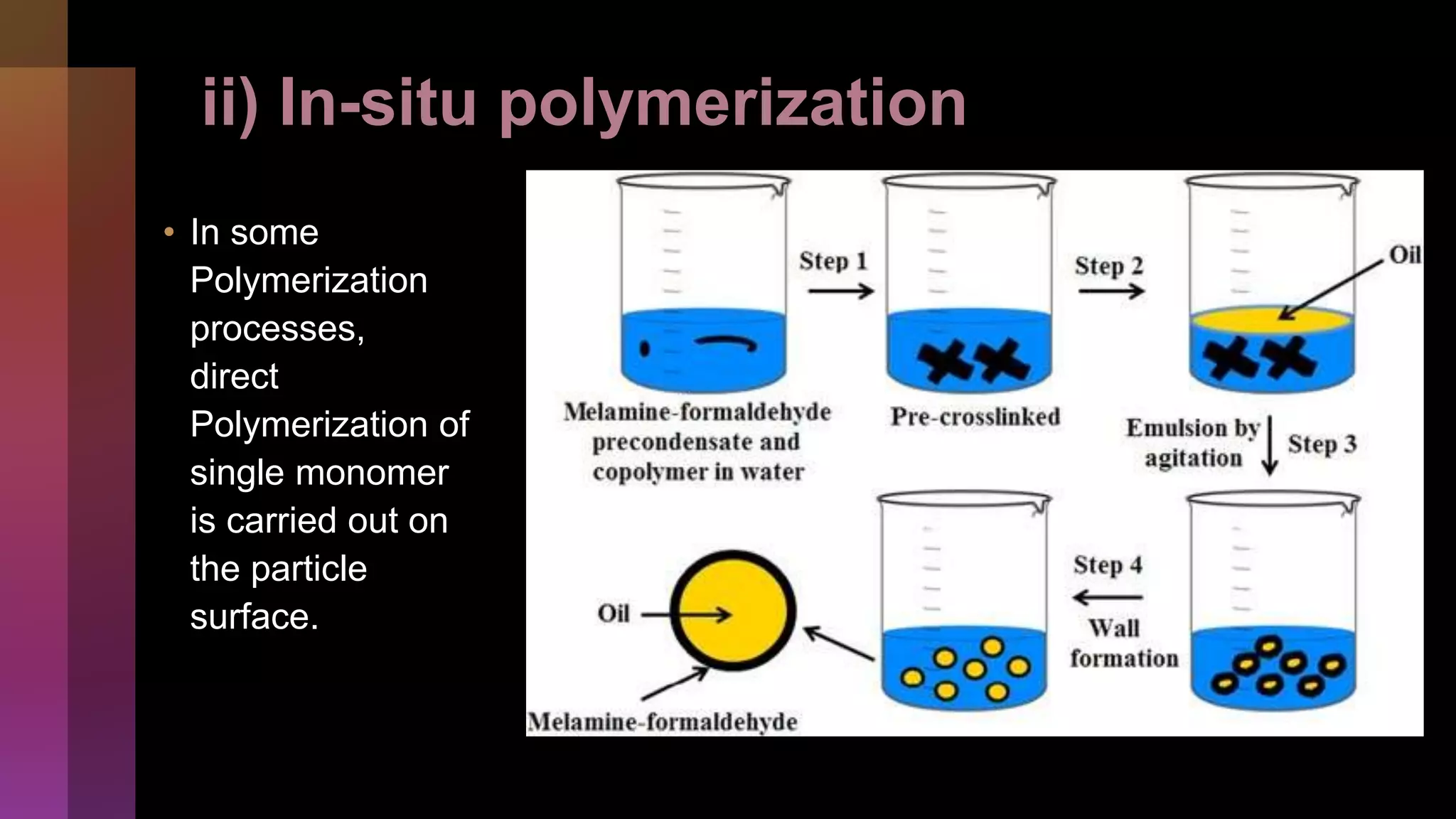
![2] Polymerization
i) Interfacial
ii) In-situ
iii) Matrix](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/microencapsulation-221021070255-82e12210/75/Microencapsulation-30-2048.jpg)