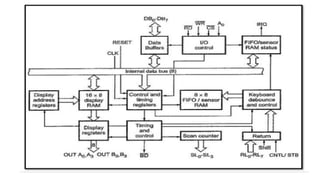
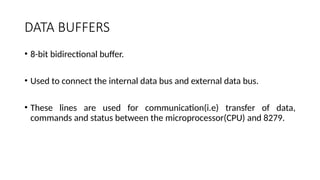
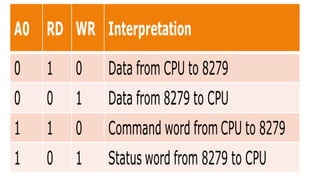
The Intel 8279 is a keyboard display controller that interfaces with a CPU and drives a display. It scans the keyboard to identify key presses, transmits data to the display, and features programmable modes of operation while alleviating the CPU from many tasks. The system includes an 8-bit bidirectional buffer, I/O control for data flow, and a debounce mechanism to ensure accurate key detection.