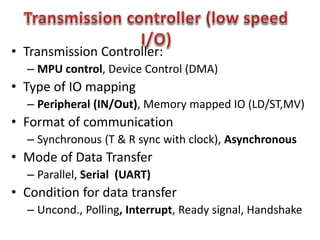
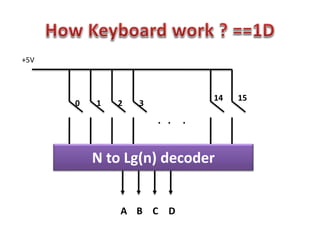
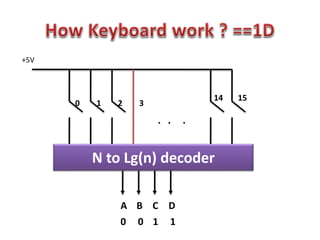
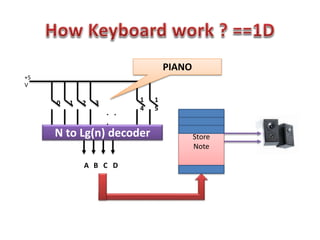
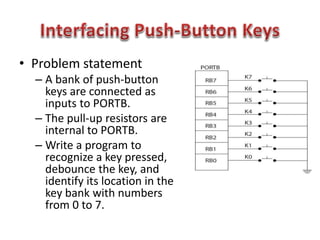
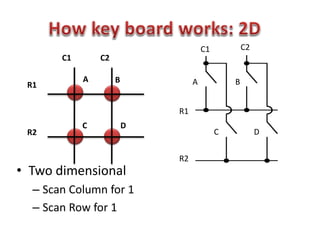
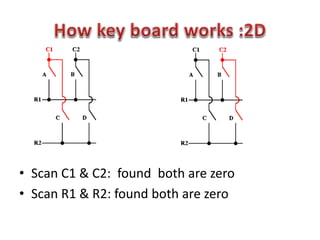
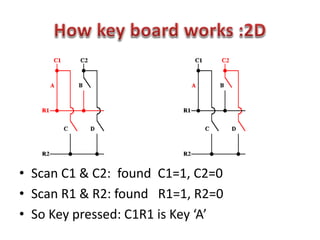
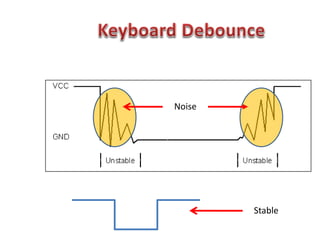
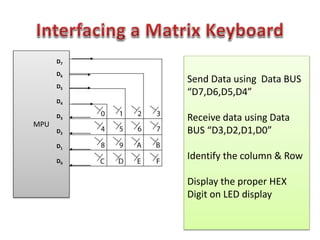
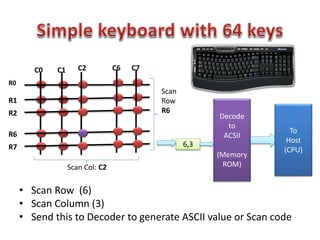
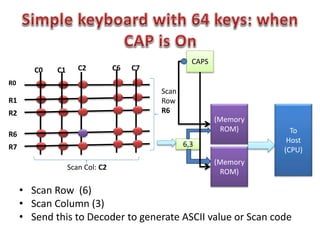
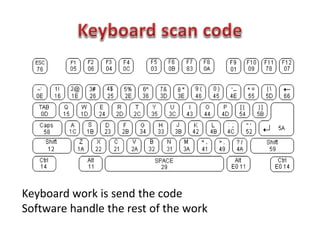
This document discusses keyboard interfacing and scanning techniques. It describes 1D and 2D keyboard layouts and interfacing methods. It discusses asynchronous and synchronous communication, interrupt-driven and polling-based I/O, and different types of I/O mapping such as memory-mapped and peripheral I/O. The document also covers keyboard encoding standards and scan codes, debouncing, and interfacing a basic keyboard matrix to a microprocessor.