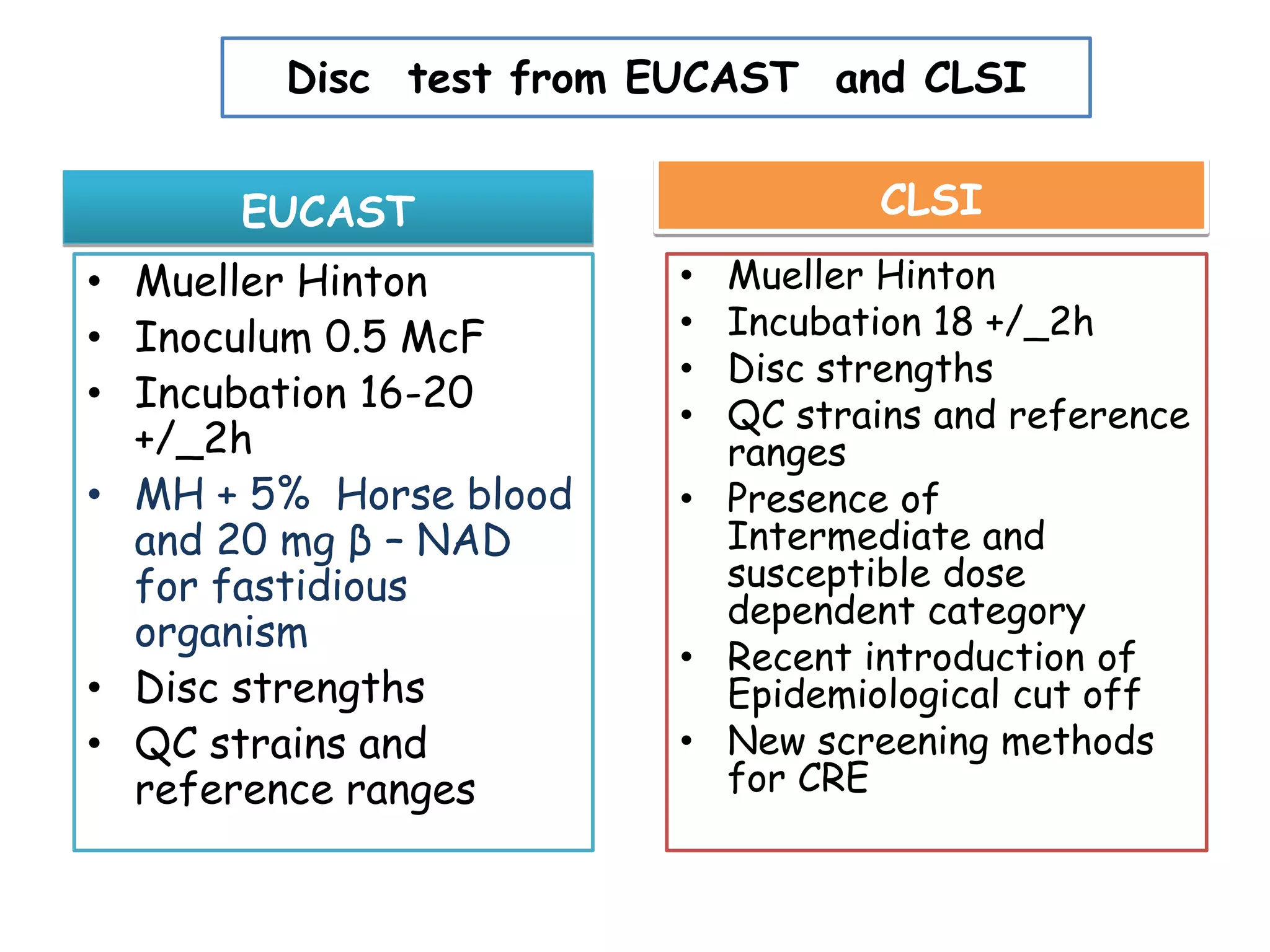
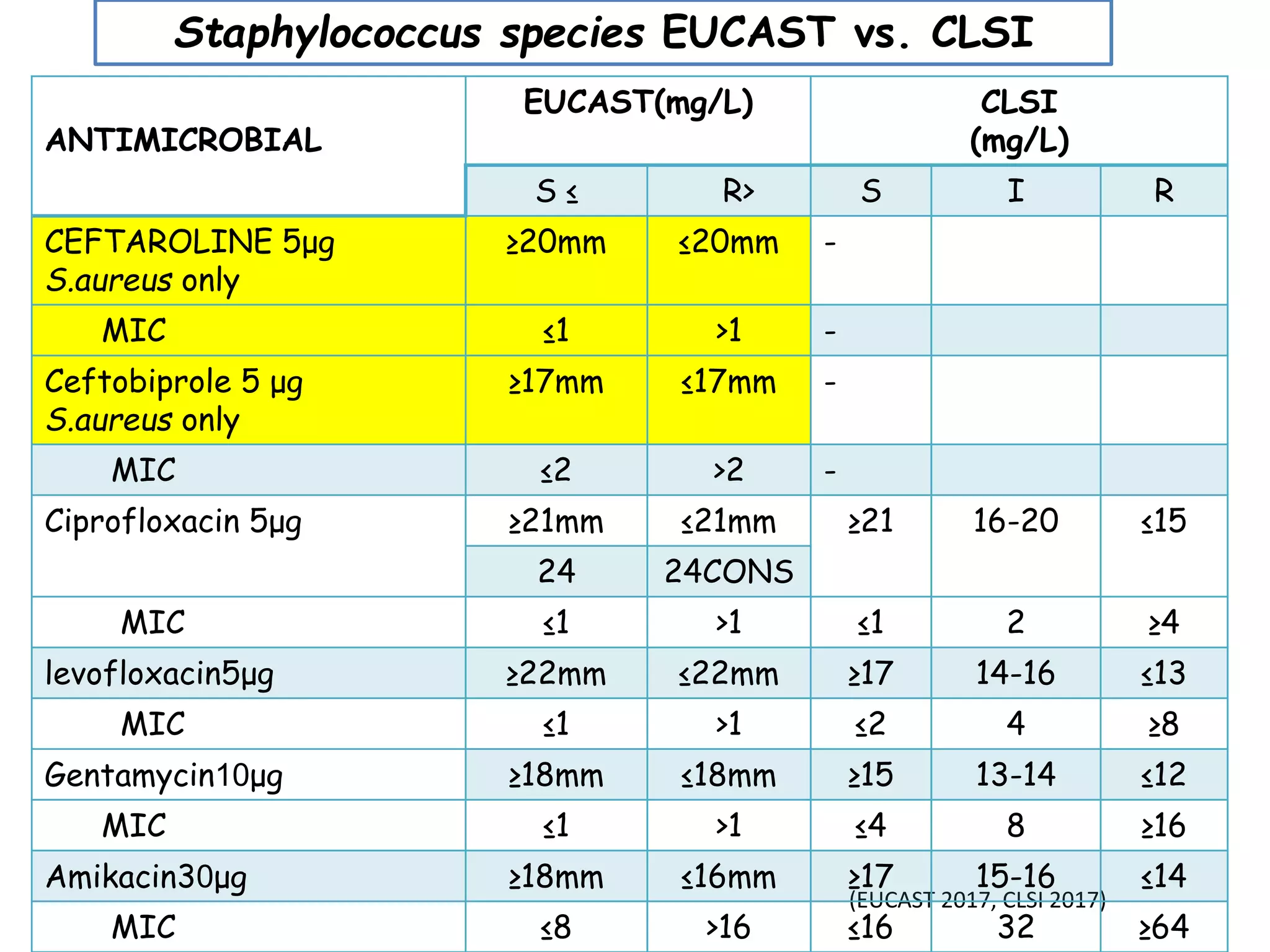
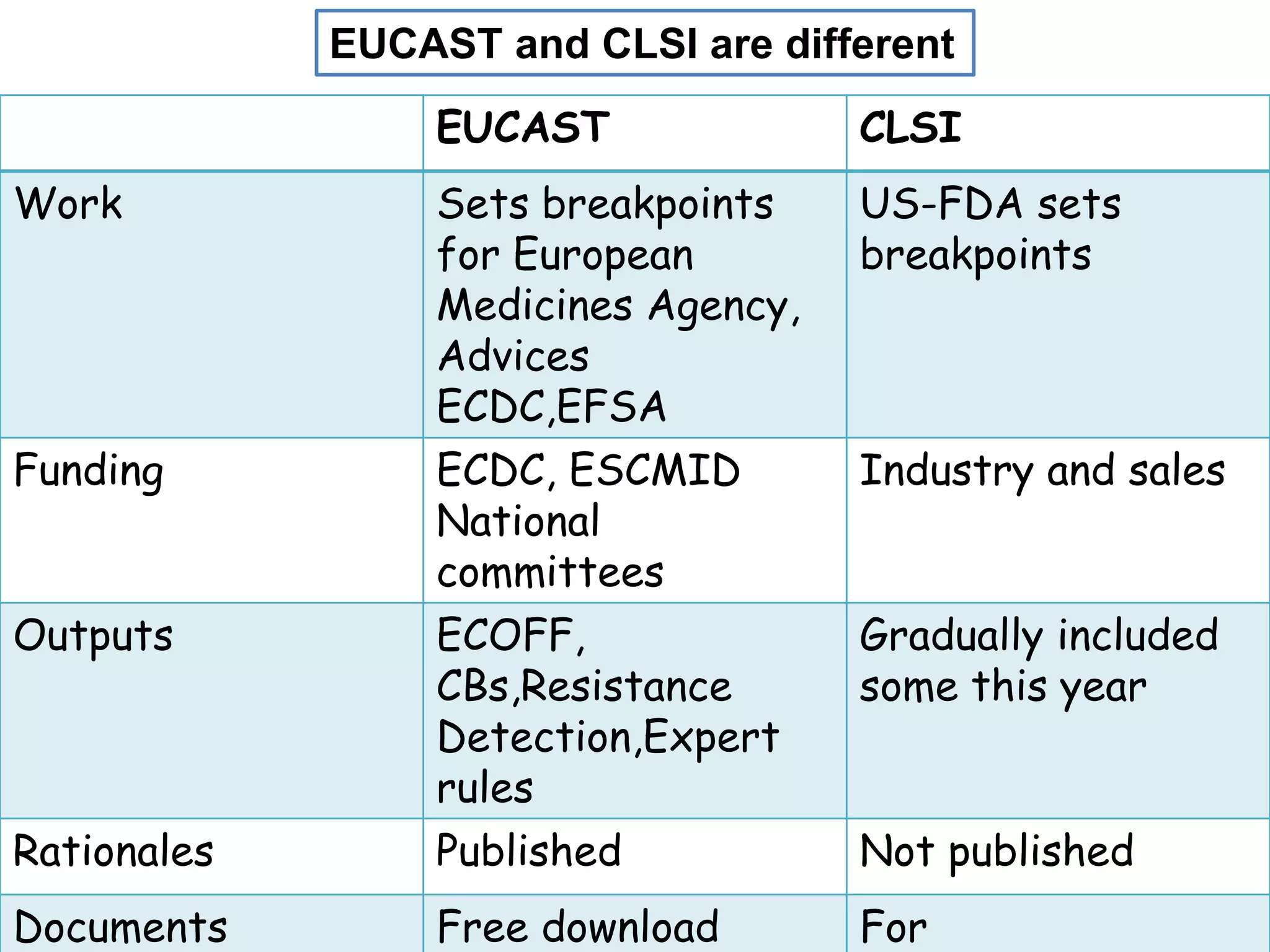
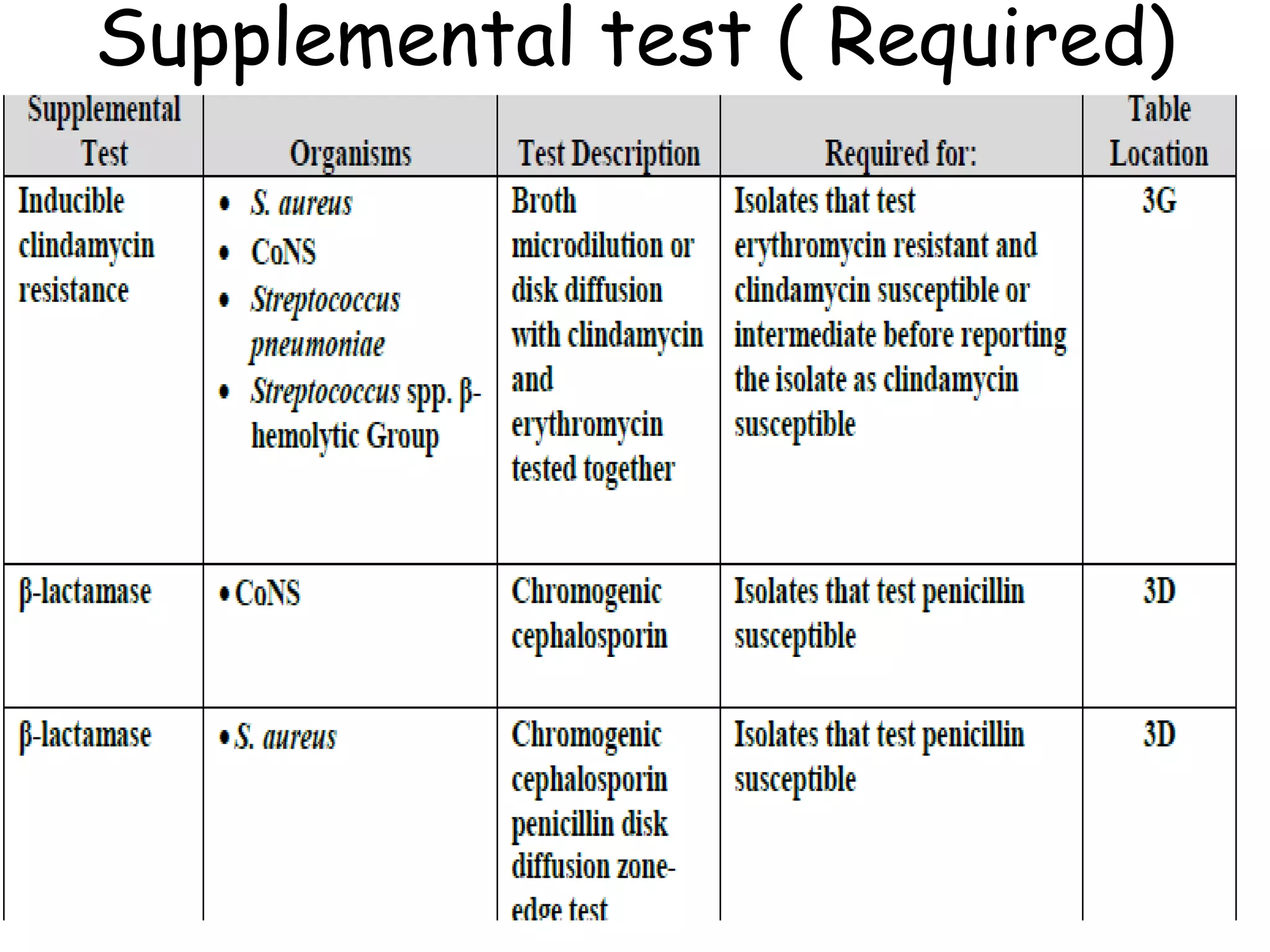
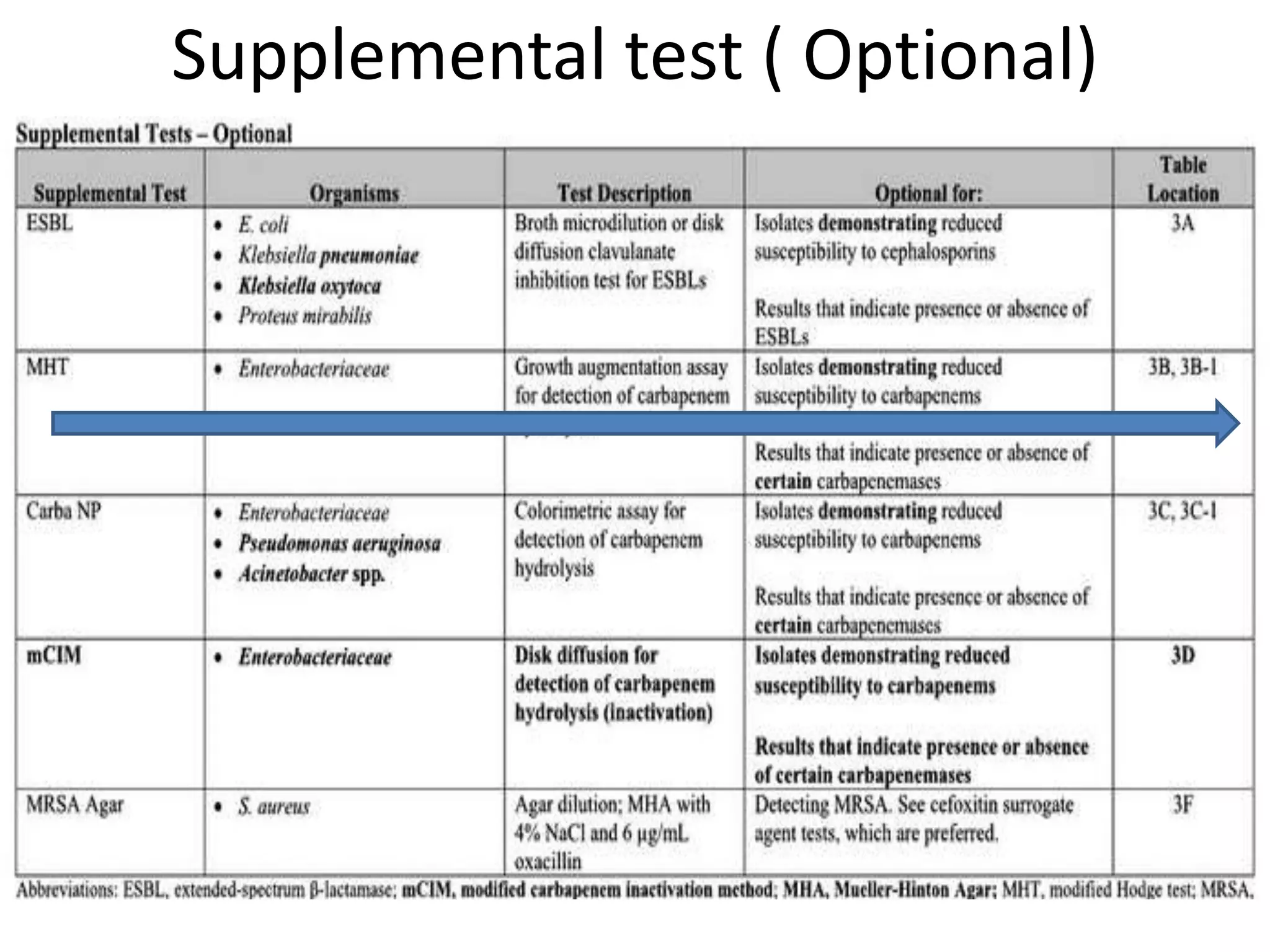
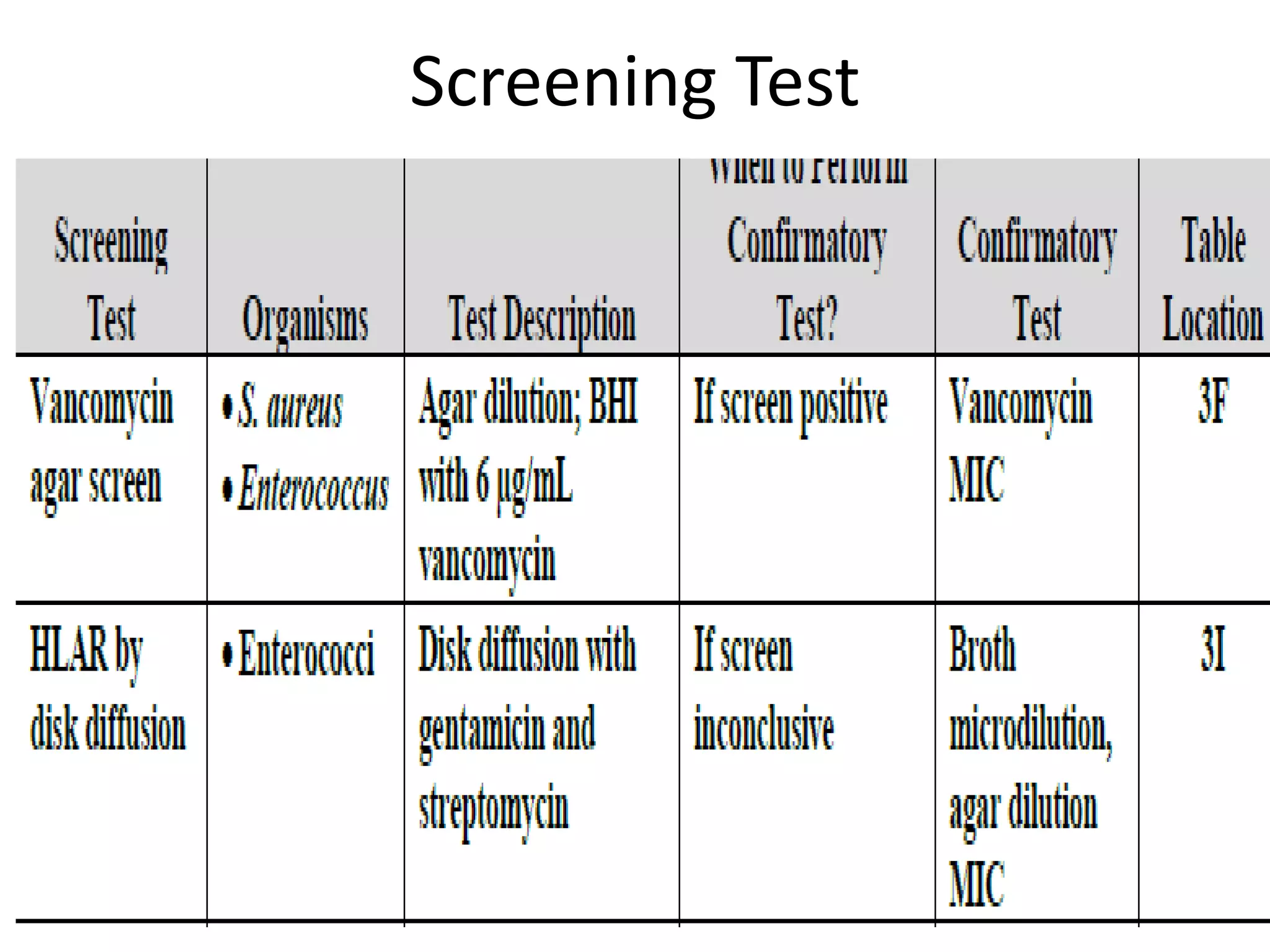
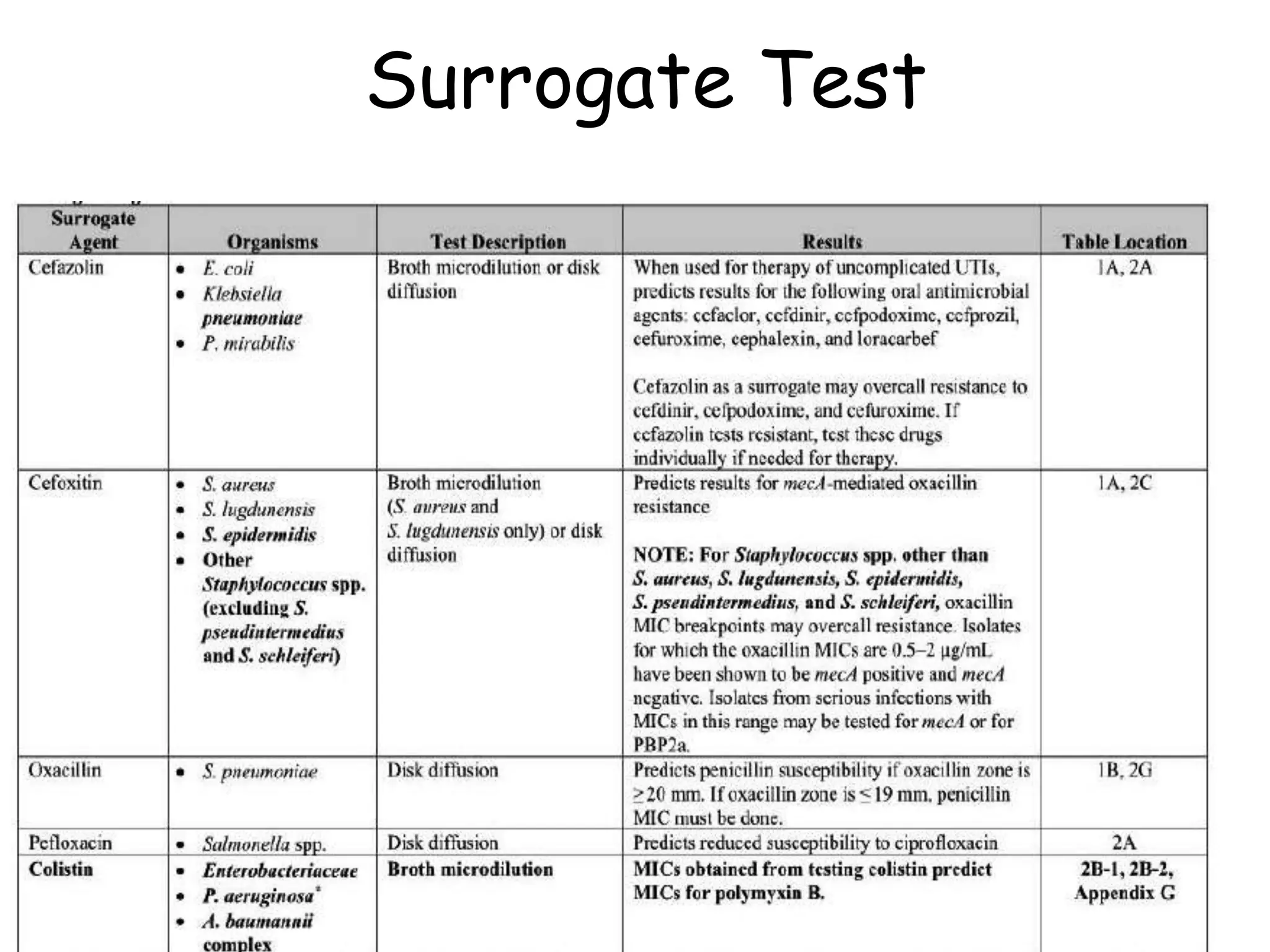
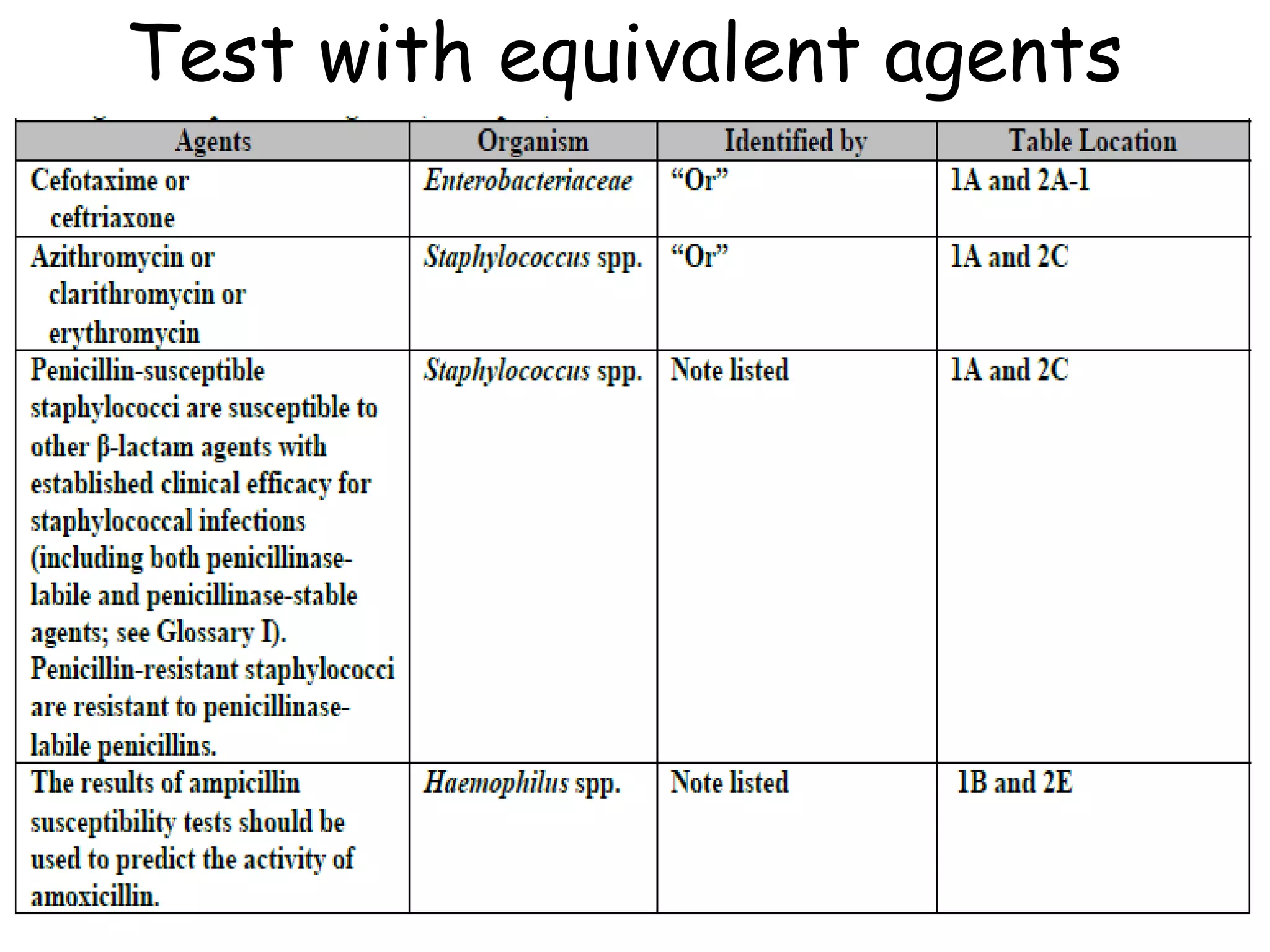
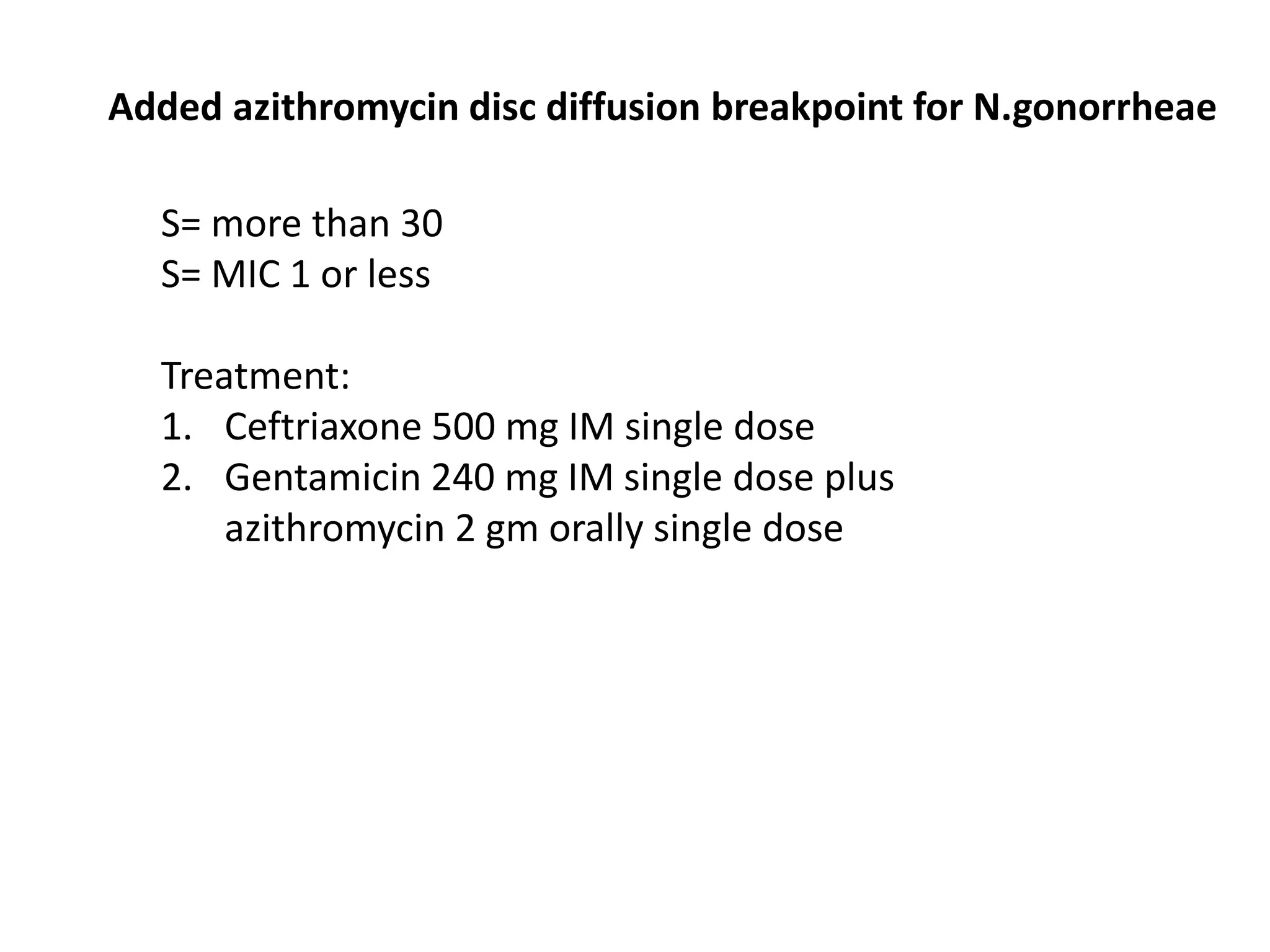
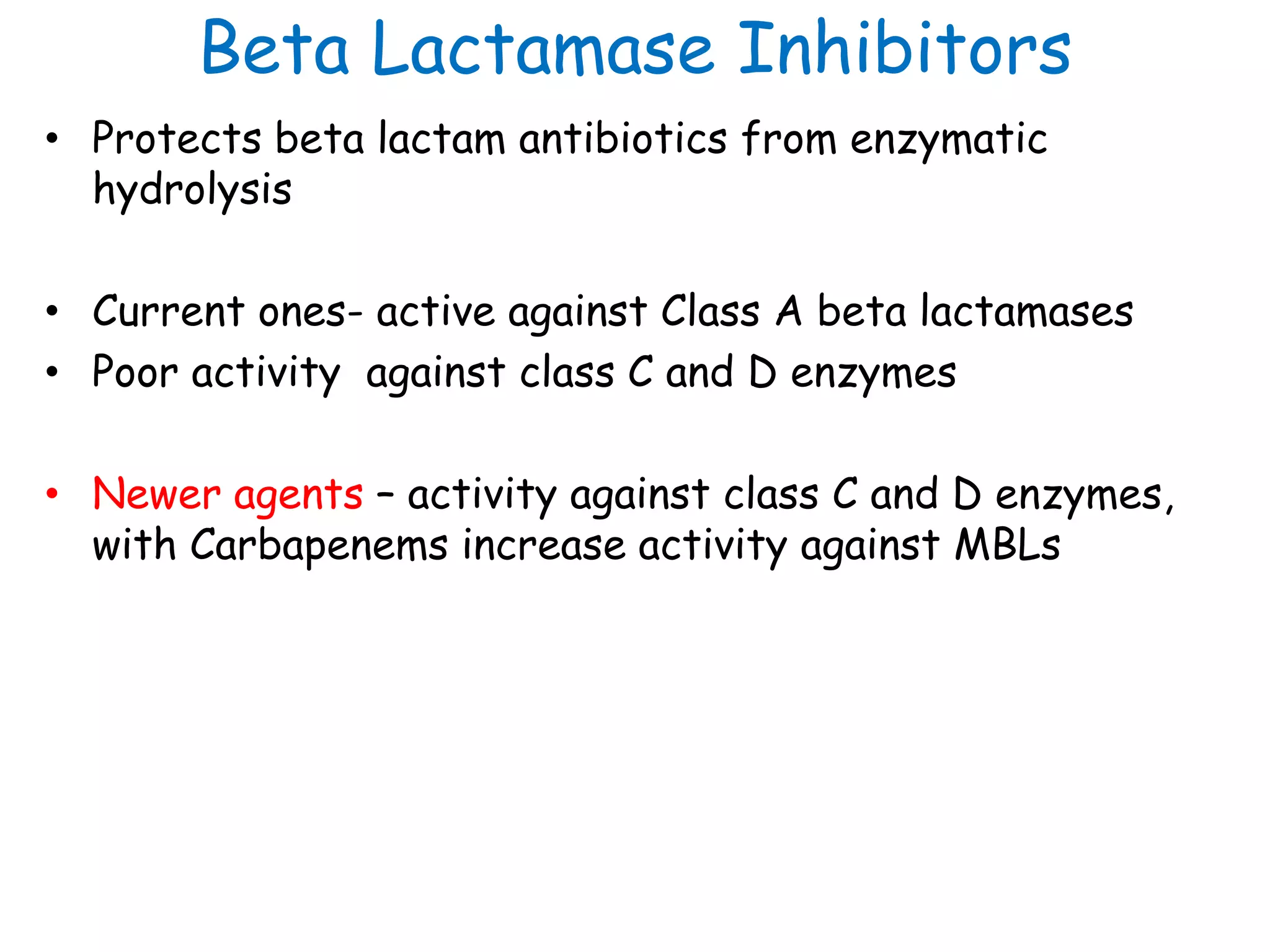
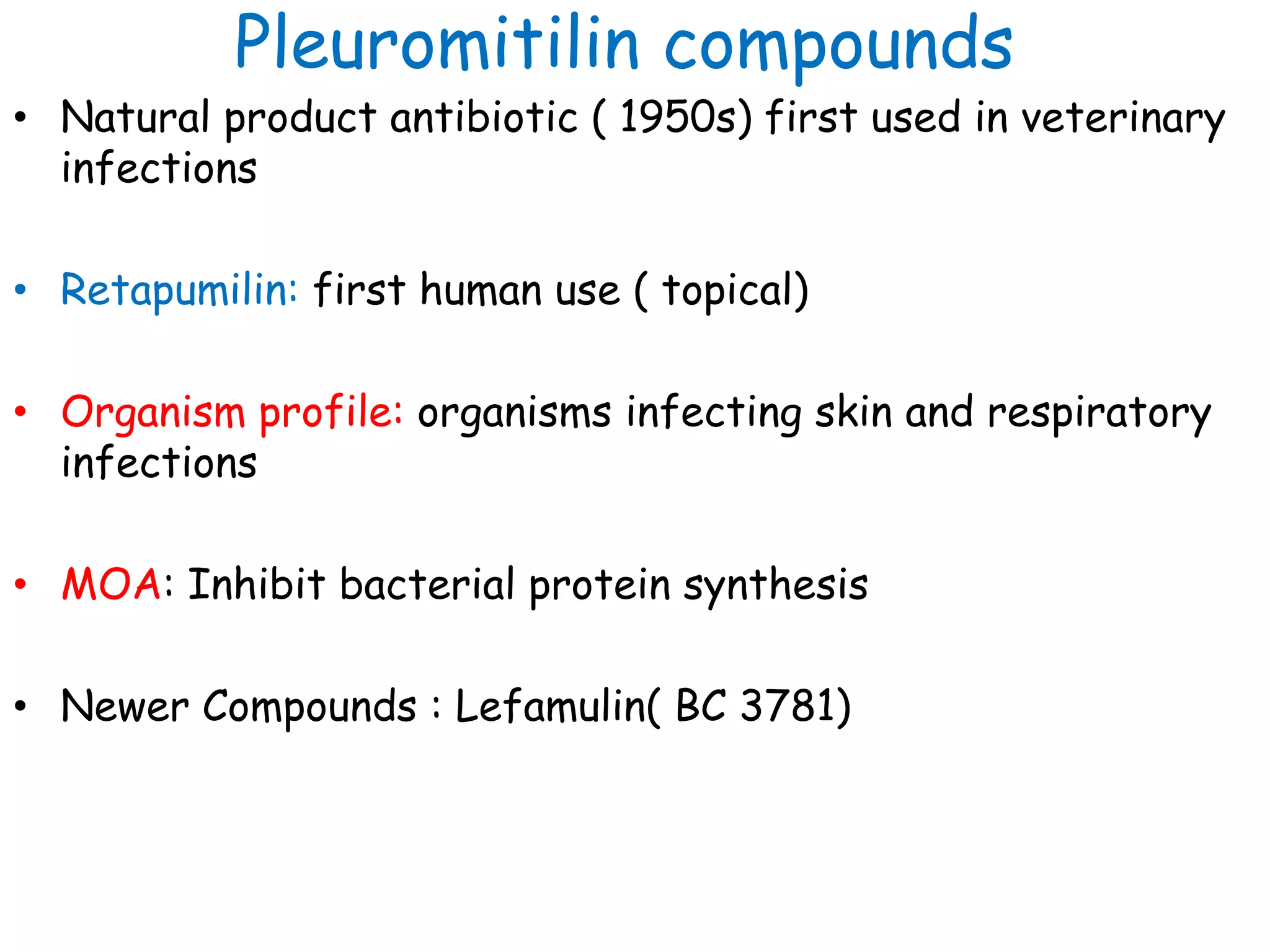
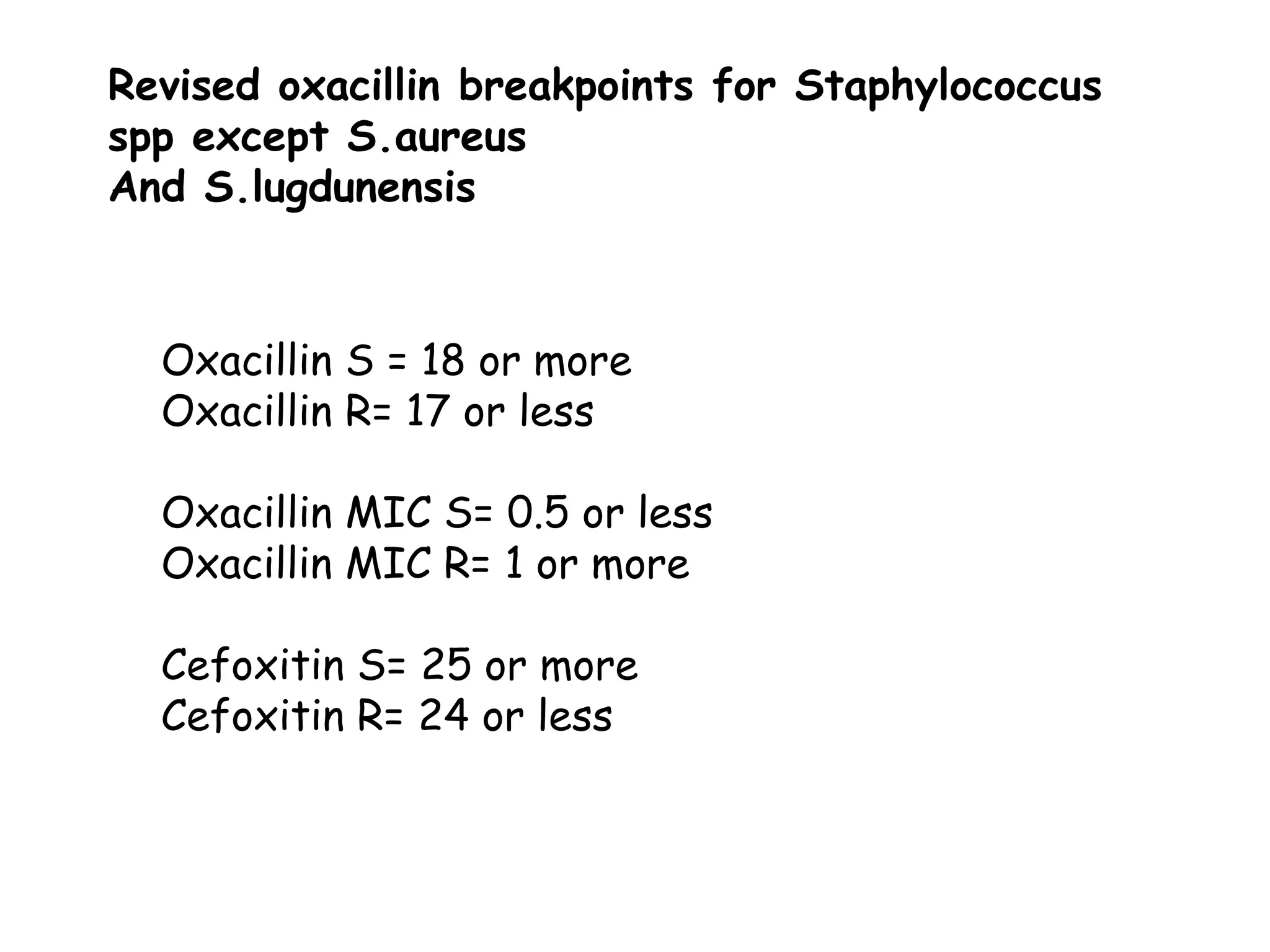
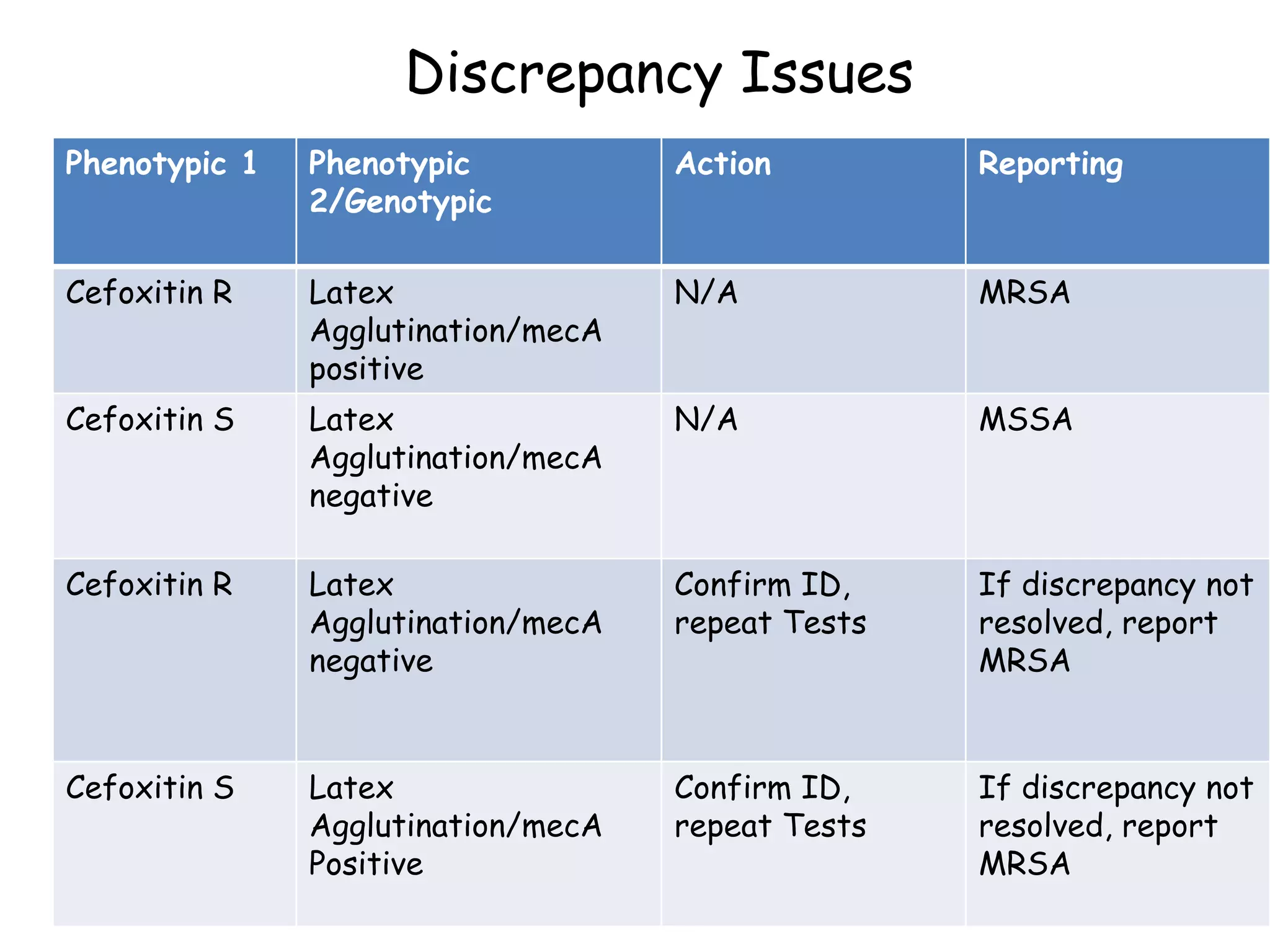
This document discusses guidelines from CLSI and EUCAST for antimicrobial susceptibility testing. It provides information on how CLSI and EUCAST establish breakpoints and testing methods. It also summarizes recent changes made by CLSI, including adding new breakpoints for certain antibiotics and organisms, clarifying interpretive categories, and providing warnings for inappropriate reporting of test results.