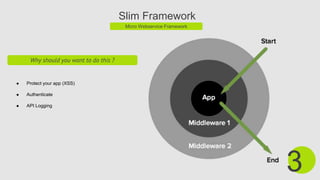
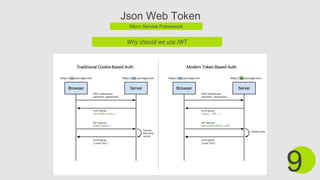
The document discusses the Slim micro web framework and JSON web tokens (JWT). Slim is a PHP micro framework that helps build simple yet powerful web apps and APIs. It uses a dispatcher to handle requests and responses. JWT are used for securely transmitting information between parties as JSON objects that can be verified. When using JWT for authentication, a token is issued upon login and included in subsequent requests to authorize the user.