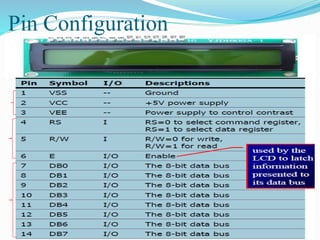
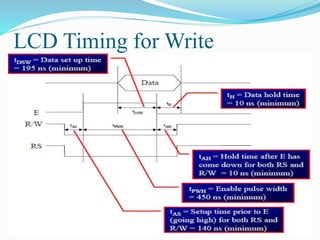
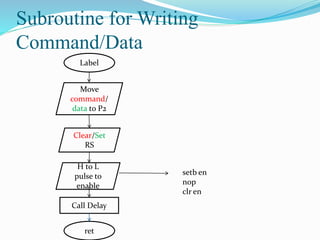
This document discusses interfacing an LCD display to an 8051 microcontroller. It covers the objectives of connecting an LCD to an 8051, deciding which ports to use, important LCD commands, timing considerations, and writing a subroutine to write data to the LCD. Example pseudo-code is provided to initialize the LCD and display text on the two lines by calling subroutines to write commands and data. Additional steps are needed during hardware testing to fully initialize the LCD. The tasks for the lab involve displaying a workstation number and student IDs on the LCD's two lines.