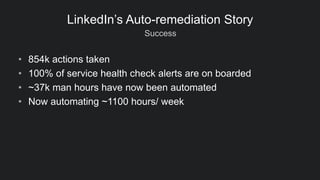
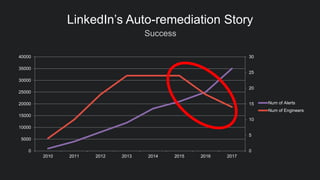
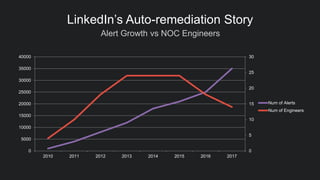
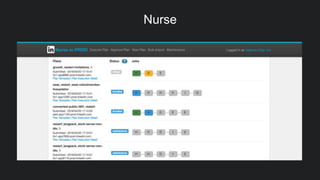
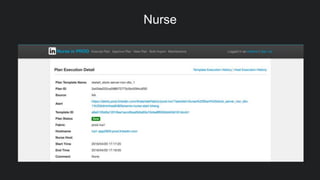
The document discusses LinkedIn's implementation of auto-remediation using SaltStack to manage production systems, addressing challenges like high alert volumes and complicated runbooks that affected response times. It details the development of an event-based system called Nurse, which integrates with existing monitoring infrastructures to automate actions and diagnostics, thereby enhancing service reliability and reducing manual workloads. The success is highlighted by the automation of approximately 37,000 man-hours and proactive management of service alerts, reinforcing the importance of thoughtful architecture in event-driven automation.













![Python Code example
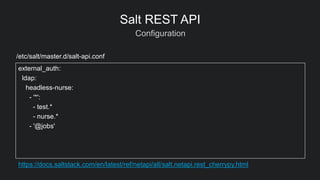
Salt REST API
from pepper.libpepper import Pepper
api = Pepper('https://salt.example.com:8888')
api.login('saltdev', 'saltdev', ’ldap')
# Run simple function
api.low([{'client': 'local', 'tgt': '*', 'fun': 'test.ping'}])
# Execute a runner function
api.runner('jobs.lookup_jid', jid=12345)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/michaelkehoesaltconf16final-160420214344/85/Using-SaltStack-to-Auto-Triage-and-Remediate-Production-Systems-19-320.jpg)