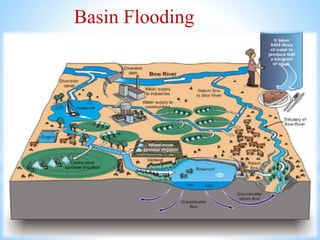
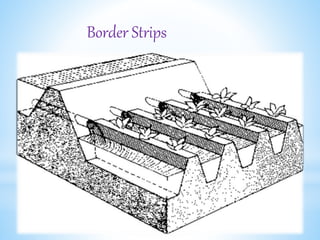
The document describes various methods of irrigation, including furrow irrigation, contour farming, flooding methods like free flooding and basin flooding, border strips, sprinkler irrigation, and drip/trickle irrigation. It provides details on how each method works and suitable crops. Advantages include more efficient water use, reduced evaporation, and ability to apply fertilizer uniformly with sprinkler and drip methods.