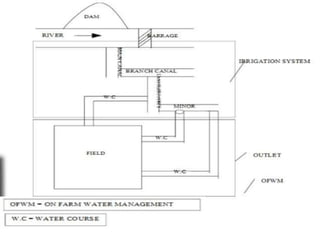
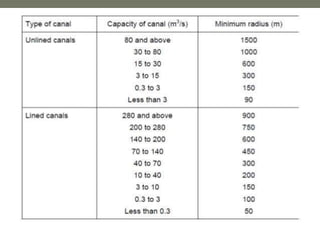
Canal design involves defining types of canals based on use and discharge. There are two main types - aqueducts for water supply and navigable waterways. Canals are also classified based on discharge into main, branch, major/minor distributaries and watercourses. Design considers canal shape, lining requirements, and layout to minimize curves and balance cuts and fills. Proper drainage systems including surface ditches and subsurface pipes are also important to control water levels and allow cultivation. Explicit equations have been developed for least-cost design of common canal shapes like triangular, rectangular, trapezoidal and circular.