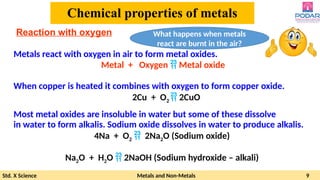
The document discusses the properties and reactions of metals and non-metals, highlighting their physical characteristics such as malleability, ductility, conductivity, and their reactions with oxygen, water, and acids. It also covers the reactivity series of metals, the process of corrosion (rusting), and methods to prevent it. Additionally, the document explains the formation and uses of various metal alloys.