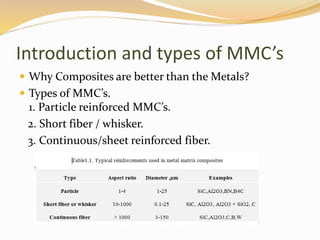
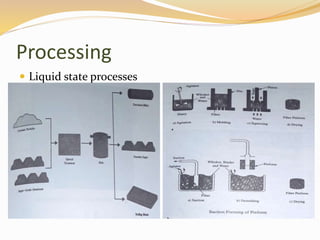
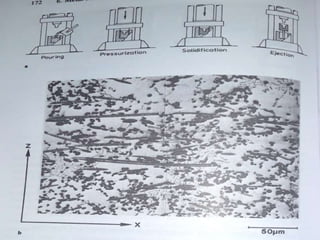
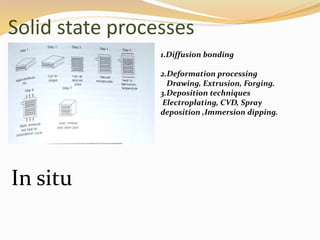
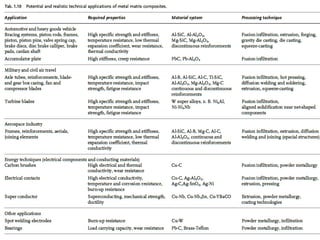
The document discusses metal matrix composites (MMCs), detailing their types, important metal matrices, processing methods, properties, and applications in various industries, particularly aerospace and automotive. It emphasizes the advantages of MMCs over traditional metals and the influence of interfacial bonding on their performance while addressing cost challenges that hinder widespread adoption. Ultimately, the document concludes that MMCs are critical for advanced applications, highlighting the need for cost-effective manufacturing methods.