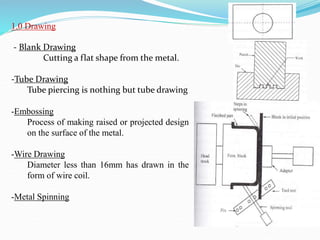
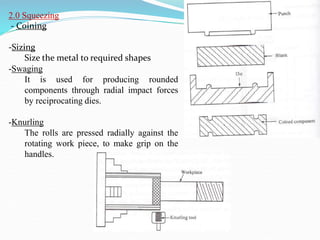
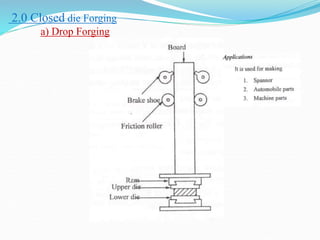
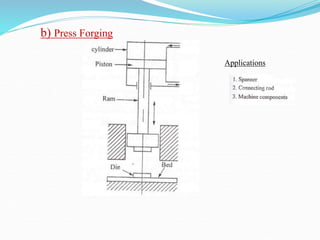
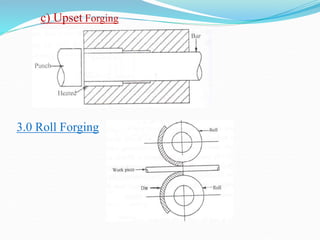
This document discusses various metal forming processes including forging, rolling, drawing, and extrusion. It provides details on:
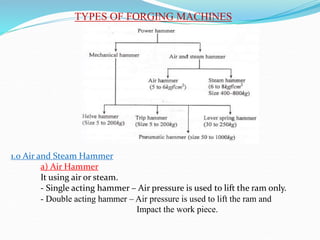
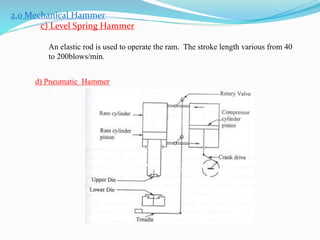
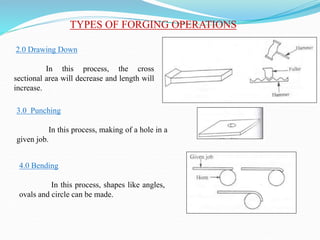
1) Hot and cold working of metals, types of forging processes, characteristics of forging, types of forging machines, and common forging operations.
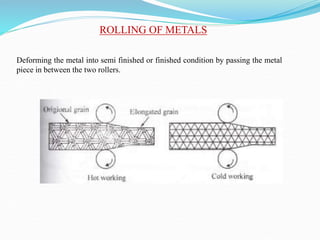
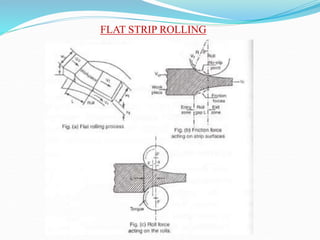
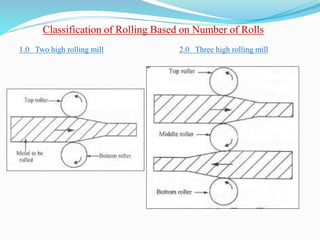
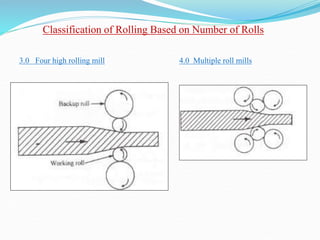
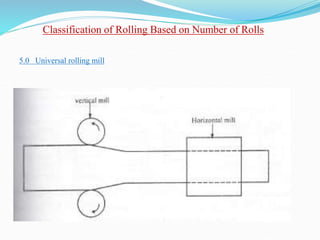
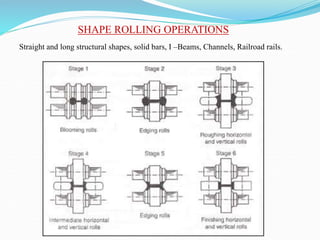
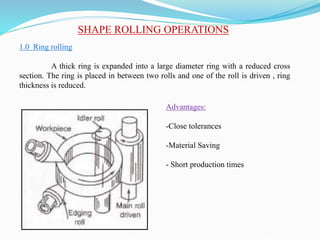
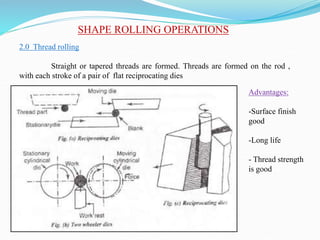
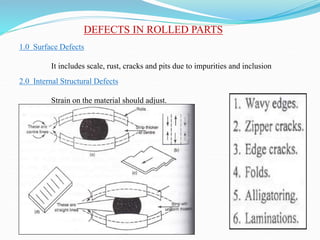
2) Types of rolling mills and rolling processes like flat strip rolling and shape rolling. It also discusses defects in rolled parts.
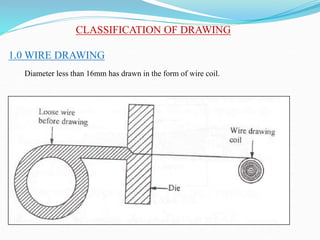
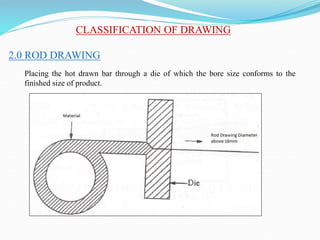
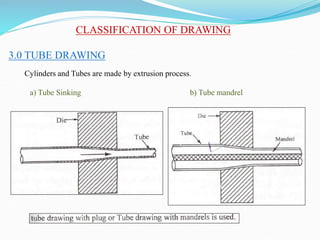
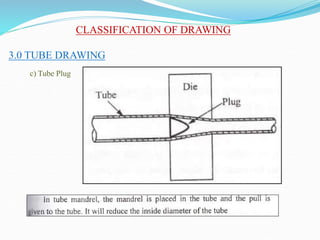
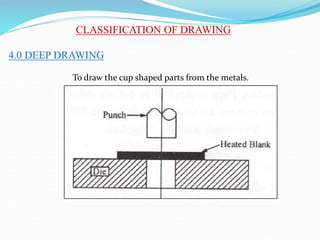
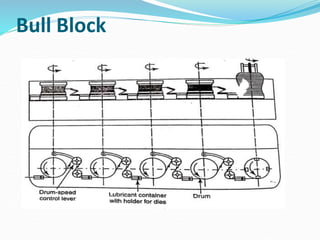
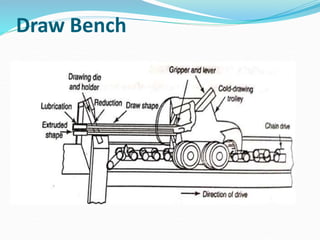
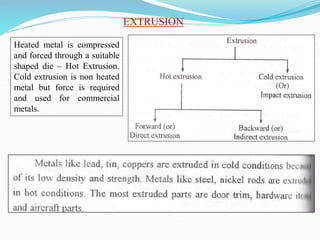
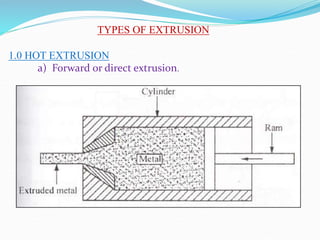
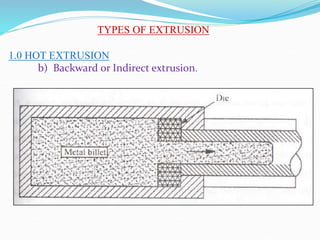
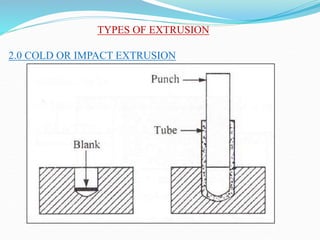
3) Principles and types of drawing and extrusion processes. Drawing processes include wire, rod, tube, and deep drawing. Extrusion can be hot or cold.