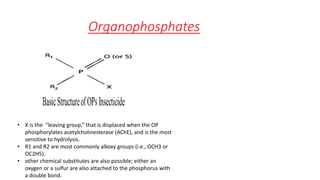
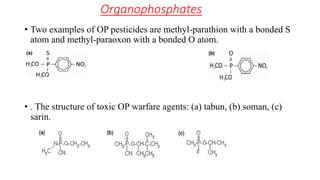
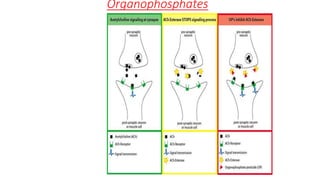
Organophosphates are a large family of chemicals that are used as pesticides in agriculture and as nerve agents in chemical warfare. They work by inhibiting the enzyme acetylcholinesterase, which causes acetylcholine to accumulate at nerve synapses and overstimulate the nervous system. While they degrade quickly in the environment, organophosphate pesticides can cause acute toxicity in humans through dermal exposure, inhalation, or ingestion, leading to effects like convulsions, respiratory failure and death. Their use has declined in some countries due to environmental and health concerns.