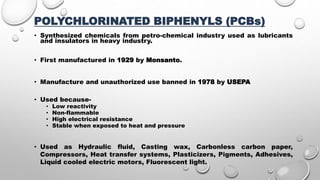
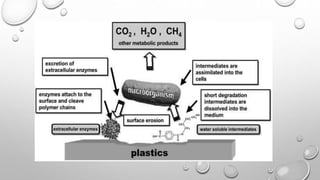
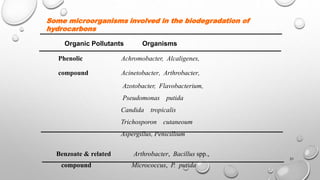
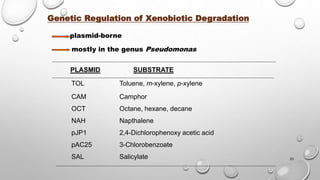
The document summarizes biodegradation of various xenobiotics including hydrocarbons, plastics, and pesticides. It discusses that xenobiotics are man-made chemicals that do not occur naturally. Biodegradation is the breakdown of these substances by microorganisms. Various pathways and microorganisms involved in the biodegradation of pesticides, plastics, hydrocarbons and other pollutants like polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons are described. Key mechanisms include hydrolysis, acidogenesis, acetogenesis, and methanogenesis. Organisms from genera Pseudomonas, Bacillus, and fungi are effective in degrading these recalcitrant compounds.





















![27
Compound Organisms Metabolite
Fluoranthene Alcaligenes denitrificans ,
Mycobacterium sp. ,
Pseudomonas putida ,
Pseudomonas paucimobilis,
Pseudomonas cepacia ,
Rhodococcus sp.
7- Acenaphthenone, 1- acenaphthenone,
7- hydroxyacenaphthylene, benzoic acid,
phenylacetic acid, adipic acid,
3- hydroxymethyl – 4,5- benzocoumarin,
9- fluorenone – 1 – carboxylic acid,
8- hydroxy – 7- methoxyfluoranthene,
9- hydroxyfluorene , 9- fluorenone,
phthalic acid, 2- carboxybenzaldehyde
Pyrene Alcaligenes denitrificans ,
Mycobacterium sp. ,
Rhodococcus sp.
Pyrene cis - and trans - 4,5 – dihydrodiol,
4 – hydroxyperinaphthenone, phthalic acid, 4-
phenanthroic acid, 1,2 - and 4,5 –
dihydroxypyrene, cinnamic acid, cis – 2 –
hydroxy – 3 – ( perinaphthenone -9-yl ) propenic
acid
Chrysene Rhodococcus sp. None determined
Benz [a]
anthracene
Alcaligenes denitrificans ,
Beijerinckia sp. ,
Pseudomonas putida
Benz [a] anthracene cis – 1,2, cis- 8,9-, and cis
– 10,11- dihydrodiols, 1- hydroxy – 2 –
anthranoic acid, 2- hydroxy – 3 – phenanthroic
acid, 3- hydroxy – 2 – phenanthroic acid .
Benz [a]
pyrene
Beijerinckia sp.,
Mycobacterium sp.
Benz [a] pyrene cis -7,8 - and cis -9,10 –
dihydrodiols .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/biodegradationofxenobiotics-150429005441-conversion-gate01-191124112448/85/Biodegradationofxenobiotics-150429005441-conversion-gate01-27-320.jpg)